Idrocilamide
Appearance
(Redirected from Talval)
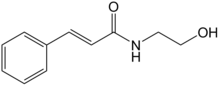 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Talval, Srilane, Relaxnova, Brolitène |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.414 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 191.230 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Idrocilamide (trade names Talval, Srilane, Relaxnova, Brolitène[1]) is a medication with skeletal muscle relaxant[2] and anti-inflammatory actions[3] used as a topical cream to treat lumbago and other kinds of muscular pain;[4] it is available on prescription or over-the-counter[citation needed] in France and various other countries.[1]
Interactions
[edit]Idrocilamide has been reported to be a potent inhibitor of the metabolism of caffeine.[5][6]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Drugs.com: International Drug Names
- ^ Bouron A, Rivet M, Nasri-Sebdani M, Guillemain J, Durbin P, Guerrier D, Raymond G (1990). "The direct depressant effect of LCB29 (idrocilamide) on mechanical tension of rat soleus muscle fibers". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 68 (12): 1503–1509. doi:10.1139/y90-228. PMID 2085796.
- ^ Bannwarth B, Le Huec JC, Vinçon G, Labat L, Demotes-Mainard F, Rivaille F, Le Rebeller A (1993). "[Tissue and systemic diffusion of idrocilamide after cutaneous administration]". Revue du Rhumatisme (in French). 60 (12): 932–6. PMID 8012322.
- ^ Stehman M, Lehert P (1990). "Clinical double-blind study with idrocilamide ointment in the treatment of acute lumbago". Acta Belgica. Medica Physica. 13 (1): 29–32. PMID 2140002.
- ^ Carrillo JA, Benitez J (2000). "Clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions between dietary caffeine and medications". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 39 (2): 127–53. doi:10.2165/00003088-200039020-00004. PMID 10976659.
- ^ Brazier JL, Descotes J, Lery N, Ollagnier M, Evreux JC (1980). "Inhibition by idrocilamide of the disposition of caffeine". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 17 (1): 37–43. doi:10.1007/bf00561675. PMID 7371698.
