Time in Brazil

| ACT | Acre Time | UTC−5 | (BRT–2) | |
| AMT | Amazon Time | UTC−4 | (BRT−1) | |
| BRT | Brasília Time | UTC−3 | (BRT) | |
| FNT | Fernando de Noronha Time | UTC−2 | (BRT+1) |
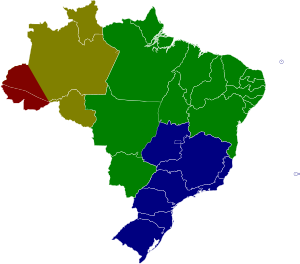
Time in Brazil is calculated using standard time, and the country (including its offshore islands) is divided into four standard time zones: UTC−02:00, UTC−03:00, UTC−04:00 and UTC−05:00.
Only part of the country observes daylight saving time, or "summer time" (Template:Lang-pt), as it is officially called. These areas are the Southern, Southeast and Central-Western Brazilian states.
Time zones
Brasília time +1 (UTC−02:00)
This is the standard time zone only on a few small offshore Atlantic islands. The only such island with a permanent population is Fernando de Noronha, with 2,837 inhabitants (2013 estimate), 0.0014% of Brazil's population.[1] The other islands (Trindade, Martim Vaz, Rocas Atoll and Saint Peter and Saint Paul Archipelago) either are totally uninhabited or have small seasonally rotating Brazilian Navy garrisons or teams of scientists.
This zone is at UTC−02:00 and it does not use daylight saving time.
Brasília time, BRT (UTC−03:00)
The main time zone of Brazil corresponds to the time at the national capital city, Brasília. All the other time zones are given as offsets to it.
In addition to the Federal District (which includes Brasília), it comprises the states in the Southeast Region, the South Region and the Northeast Region, plus the states of Goiás, Tocantins, Pará and Amapá. The small islands mentioned above are excepted. Almost 94% of the Brazilian population live in this time zone, which covers about 60% of the country's land area.[1]
Outside of summer time, it corresponds to UTC−03:00. During summer time, it changes to UTC−02:00, but this change is not followed by Northern and Northeastern states.
Brasília time −1 (UTC−04:00)
Outside of summer time, this time zone corresponds to UTC−04:00; during summer time, it changes to UTC−03:00, but this change is not followed by Northern states. This time zone is used in the states of Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Rondônia, Roraima, and most of Amazonas. Although this time zone covers about 34% of the land area of Brazil (an area larger than Argentina), little more than 5% of the country's population live there (about 11 million people, less than the city of São Paulo).[1]
Until 2008, the areas of the state of Pará west of the Xingu River and north of the Amazon River were also part of this time zone; then they joined the rest of the state in observing Brasília time (UTC−03:00). Although other changes to Brazilian time zones enacted at that time have since been reverted (see below), Western and Northern Pará still remain in UTC−03:00.
Brasília time −2 (UTC−05:00)
This time zone was in 2013, after having been abolished for over five years. It is used in the far-western tip of the country, which includes the entire state of Acre and the southwestern portion of the state of Amazonas (west of a line connecting the cities of Tabatinga and Porto Acre, but in practice a somewhat larger area, because all municipalities that are at least partially west of that line follow this time zone in their entirety). These areas cover only about 6% of the Brazilian territory (although that is still about the size of France) and have only about 0.5% of the country's population (little more than 1 million people).[1]
On 24 June 2008, these areas advanced their clocks by an hour, so that they became part of the UTC−04:00 time zone.[2] However, in a non-binding referendum held on 31 October 2010, a slight majority of Acre voters voted in favour of returning the state to the UTC-05.[3] On 30 October 2013, Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff enacted Law 12876, establishing that the time zone switch would occur on Sunday, 10 November 2013.[4] Since then, the state of Acre and 13 municipalities in the southwestern part of the state of Amazonas[5] are again 5 hours behind UTC.
No part of this time zone observes daylight saving time.[6]
Daylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST; Template:Lang-pt) starts on the third Sunday of October and ends on the third Sunday of February. Occasionally, in years when the Carnival celebrations fall on the third Sunday of February, DST's ending is postponed to the following Sunday.[6]
It is observed by Southern, Southeast and Central-Western Brazil (i.e. the states of Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, Paraná, São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, plus the Federal District).[6] This means that approximately 64% of the Brazilian population live in areas that observe daylight saving time.
During the 2011-12 summer, the Northeastern state of Bahia also observed daylight saving time as an experiment.[7] In the 2012-13 summer, the Northern state of Tocantins observed it, also as a test, for the first time since the state was created in 1988.[8] Starting from the 2013-14 summer, neither state will observe DST any more.
The clock is moved forward by one hour between the start and end dates, moving Brasília Official Time from UTC-03 to UTC-02; the other states that do not follow summer time observe a change of the offset to Brasília time.
-
Timezones used from 13 October 2011 to 15 October 2012.
-
Timezones used from 25 June 2008 to 13 October 2011.
IANA time zone database
The IANA time zone database contains 16 zones for Brazil. Columns marked with * are from the file zone.tab of the database.
| c.c.* | coordinates* | TZ* | comments* | UTC offset | DST | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | −0351−03225 | America/Noronha | Atlantic islands | −02:00 | - | |
| BR | −0127−04829 | America/Belem | Pará (east), Amapá | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −0343−03830 | America/Fortaleza | Brazil (northeast: MA, PI, CE, RN, PB) | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −0803−03454 | America/Recife | Pernambuco | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −0712−04812 | America/Araguaina | Tocantins | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −0940−03543 | America/Maceio | Alagoas, Sergipe | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −1259−03831 | America/Bahia | Bahia | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −2332−04637 | America/Sao_Paulo | Brazil (southeast: GO, DF, MG, ES, RJ, SP, PR, SC, RS) | −03:00 | −02:00 | |
| BR | −2027−05437 | America/Campo_Grande | Mato Grosso do Sul | −04:00 | −03:00 | |
| BR | −1535−05605 | America/Cuiaba | Mato Grosso | −04:00 | −03:00 | |
| BR | −0226−05452 | America/Santarem | Pará (west) | −03:00 | - | |
| BR | −0846−06354 | America/Porto_Velho | Rondônia | −04:00 | - | |
| BR | +0249−06040 | America/Boa_Vista | Roraima | −04:00 | - | |
| BR | −0308−06001 | America/Manaus | Amazonas (east) | −04:00 | - | |
| BR | −0640−06952 | America/Eirunepe | Amazonas (west) | −05:00 | - | |
| BR | −0958−06748 | America/Rio_Branco | Acre | −05:00 | - |
See also
References
- ^ a b c d IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics) (2013-07-01). "Estimativas da População Residente nos Municípios Brasileiros com Data de Referência em 1º de Julho de 2013" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2013-10-20.
- ^ "Brazil Abolishes Its Fourth Time Zone in 2008". Retrieved 2008-06-25.
- ^ "Time Zone Change is Possible in Acre, Brazil".
- ^ Subdirectorate for Legal Affairs. "Lei nº 12.876, de 30 de outubro de 2013" (in Portuguese). The Presidency of the Federative Republic of Brazil. Retrieved 2014-05-01.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ The municipalities are: Atalaia do Norte, Benjamin Constant, Boca do Acre, Eirunepé, Envira, Guajará, Ipixuna, Itamarati, Jutaí, Lábrea, Pauini, São Paulo de Olivença, and Tabatinga.
- ^ a b c "Decreto 6.558 de 2008, sobre o Horário de Verão no Brasil" (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2008-11-08.
- ^ "Decreto 7.584 de 2011, sobre o Horário de Verão no Brasil" (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2011-10-16.
- ^ "Decreto 7.826 de 2012, sobre o Horário de Verão no Brasil" (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2012-10-19.



