Trams in Mainz
| Mainz tramway network | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 GT6M tram at Mainz Hauptbahnhof, 2009. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Mainz, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Mainz tramway network (Template:Lang-de) is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Mainz, the capital city of the federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Opened in 1883, the network has been operated since 2001 by Mainzer Verkehrsgesellschaft (MVG).
Lines
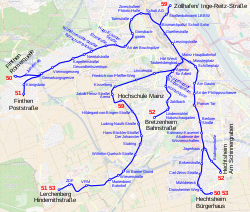
As of 2011[update], the Mainz tramway network had the following three tram lines:
| Line | Route |
|---|---|
| 50 | Hechtsheim/Bürgerhaus ↔ Hechtsheim/Mühldreieck ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Mombach/Turmstraße (Haltepunkt Waggonfabrik) ↔ Gonsenheim/Kapellenstraße ↔ Finthen/Gemarkungsgrenze ↔ Finthen/Römerquelle |
| 51 | Hechtsheim/Bürgerhaus ↔ Hechtsheim/Mühldreieck ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Mombach/Turmstraße (Bahnhof Waggonfabrik) ↔ Gonsenheim/Kapellenstraße ↔ Finthen/Gemarkungsgrenze ↔ Finthen/Poststraße (after the opening of line 53 line 51 will lead from Finthen to Lerchenberg) |
| 51a | Zollhafen ↔ Bismarckplatz ↔ Mainz Hauptbahnhof ↔ Hauptbahnhof West ↔ Universität (planned) |
| 52 | Hechtsheim/Am Schinnergraben ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Mainz/Zahlbach ↔ Bretzenheim/Bahnstraße |
| 53 | Hechtsheim/Bürgerhaus ↔ Hechtsheim/Mühldreieck ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Universität ↔ Lerchenberg (under construction) |
Currently there is a new line under construction. From autumn 2016 the new "Mainzelbahn" will transport passengers from Hauptbahnhof West (main station, west entrance) via University and Marienborn to Lerchenberg and offer a fast connection between the Main Station and the University as well as the headquarter of ZDF ("Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen", a public television channel in Germany) in the district of Lerchenberg. Further a new linie is planned. The "Zollhafen Tram" will link the new Zollhafen residential area with the Tram Network. For operating the new lines MVG ordered 10 more Variotrams at Stadler rail.[1]
Fleet
| Manufacturer | Type | Quantity | Numbers | built in | low-floor vehicle | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duewag / Siemens | M8S | 4 | 277–280 | 1975 | no | bought in 1987/89 from Bielefeld Stadtbahn; retirement planned due to the delivery of the new Variotrams |
| Duewag / Siemens | M8C | 6 | 271–276 | 1984 | no | modernisation at ceglec in Prague |
| Adtranz | GT6M-ZR | 16 | 201–216 | 1996 | yes | |
| Stadler Rail | Variobahn | 9 | 217–223 | 2011/12 | yes | ten further ordered for operating the new Mainzelbahn and Zollhafentram |
See also
References
- Herbst, Günther (2008). 125 Jahre Mainzer Straßenbahn 1883 – 2008: Die letzten 14 Jahre 1994 – 2008 (in German).
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Huber, Wilhelm (2002). Das Mainz-Lexicon (in German). Mainz: Verlag Hermann Schmidt. ISBN 3-87439-600-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Kochems, Michael; Höltge, Dieter (2011). Straßen- und Stadtbahnen in Deutschland [Tramways and Stadtbahnen in Germany] (in German). Vol. Band 12: Rheinland-Pfalz/Saarland [Volume 2: Rhineland-Palatinate/Saarland]. Freiburg i. B., Germany: EK-Verlag. ISBN 9783882553932.
- Neise, Harald (1983). Mainz und seine Straßenbahn 1883 – 1983 (in German). Kohlhammer.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Neise, Harald (1994). 111 Jahre Mainzer öffentlicher Personennahverkehr 1883 – 1994 (in German).
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Neise, Harald; Weismüller, Dirk, eds. (3 July 2004). Wenn der Funke überspringt (in German). Mainz: Mainzer Verkehrsgesellschaft mbH.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Schwandl, Robert (2012). Schwandl's Tram Atlas Deutschland (in German and English) (3rd ed.). Berlin: Robert Schwandl Verlag. pp. 100–101. ISBN 9783936573336.
External links
![]() Media related to Trams in Mainz at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Trams in Mainz at Wikimedia Commons
- Mainz database / photo gallery and Mainz tram list at Urban Electric Transit – in various languages, including English.
- Mainz database / photo gallery at Phototrans – in various languages, including English.