Trombiculidae
| Trombiculidae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Trombiculid mite larva | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | Trombiculidae |
| Type species | |
| Trombicula autumnalis (Shaw, 1790)
| |
| Genera[2] | |
| |
| |
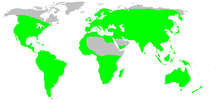
| The distribution of trombiculid species, which is nearly everywhere in the world. | |
Trombiculidae (/trɒmbɪˈkjuːlɪdiː/; also called berry bugs, harvest mites, red bugs, scrub-itch mites and aoutas) are a family of mites.[3] The best known of the Trombiculidae are the chiggers. The two widely recognized definitions of "chigger" are the scientific (or taxonomic) and the common, the latter of which can be found in English and medical[4] dictionaries. According to most dictionaries, the several species of Trombiculidae that bite their host in their larval stage and cause "intense irritation"[5] or "a wheal, usually with severe itching and dermatitis",[6][7] are called chiggers.[8] The scientific definition seemingly includes many more, but not all species of Trombiculidae.
Trombiculidae live in forests and grasslands and are also found in the vegetation of low, damp areas such as woodlands, berry bushes, orchards, along lakes and streams, and even in drier places where vegetation is low, such as lawns, golf courses, and parks.[9] They are most numerous in early summer when grass, weeds, and other vegetation are heaviest. In their larval stage, they attach to various animals, including humans, and feed on skin, often causing itching. These relatives of ticks are nearly microscopic, measuring 0.4 mm (1/60 of an inch) and have a chrome-orange hue.[10][11] There is a marked constriction in the front part of the body in the nymph and adult stages. The best known species of chigger in North America[12] is the hard-biting Trombicula alfreddugesi of the southeastern United States, humid Midwest[13] and Mexico; in the UK, the most prevalent chigger, called the "harvest mite", is Trombicula autumnalis, with distribution through Western Europe to Eastern Asia.[14]
Trombiculid mites go through a lifecycle of egg, larva, nymph, and adult.[15] The larval mites feed on the skin cells of animals. The six-legged parasitic larva feeds on a large variety of creatures, including humans, rabbits, toads, box turtles, quail, and even some insects. After crawling onto their hosts, they inject digestive enzymes into the skin that break down skin cells. They do not actually "bite", but instead form a hole in the skin called a stylostome and chew up tiny parts of the inner skin, thus causing severe irritation and swelling. The severe itching is accompanied by red, pimple-like bumps (papules) or hives and skin rash or lesions on a sun-exposed area. For humans, itching usually occurs after the larvae detach from the skin.[16]
After feeding on their hosts, the larvae drop to the ground and become nymphs, then mature into adults which have eight legs and are harmless to humans. In the postlarval stage, they are not parasitic and feed on plant material. The females lay three to eight eggs in a clutch, usually on a leaf or under the roots of a plant, and die by autumn.[16]
History
Trombiculidae, from Greek τρομειν ("to tremble") and Latin culex, genitive culicis ("gnat" or "midge"), was first described as an independent family by Henry Ellsworth Ewing in 1944.[17] Then, when the family was first described, it included two subfamilies, Hemitrombiculinae and Trombiculinae. Womersley added another, Leeuwenhoekiinae, which at the time contained only Leeuwenhoekia. Later, he erected the family Leeuwenhoekiidae for the genus and subfamily, having six genera; they have a pair of submedian setae present on the dorsal plate.[18]
References to chiggers, however, go as far back as sixth-century China, and by 1733, the first recognition of trombiculid mites in North America was made. In 1758, Carl Linnaeus described a single species, Acarus batatas (now Trombicula batatas). However, most information about chiggers came from problems that arose during and after World War II.[19]
Distribution
Trombiculid mites are found throughout the world. In Europe and North America, they tend to be more prevalent in the hot and humid regions. In the more temperate regions, they are found only during the summer (in French, harvest mites are called aoûtat because they are common in August[20]). In the United States, they are found mostly in the southeast, the south, and the Midwest. They are not present, or barely found, in far northern areas, high mountains, and deserts.[21] In the British Isles, the species Trombicula autumnalis is called harvest mites, in North America the species Trombicula alfreddugesi, and the species Trombicula (eutrombicula) hirsti which are found in Australia and are commonly called the scrub-itch mite.[22]
Life cycle

The length of the mite's cycle depends on species and environment but normally lasts two to 12 months. The number of cycles in a year depends on the region. For example, in a temperate region, there might only be three per year, but in tropical regions the cycle might be continuous all year long.[15] Adult harvest mites overwinter in protected places such as slightly below the soil. Females become active in the spring, and once the ground temperature is regularly above 60 °F (16 °C), she lays eggs in vegetation, up to 15 eggs per day. The eggs are round and are dormant for about six days, after which the nonfeeding prelarvae emerge, with only three pairs of legs. After about six days, the prelarva grows into its larval stage.[15]
Larva
The larvae, commonly called chiggers, are about 0.17–0.21 mm (0.007–0.008 in) in diameter, normally light red in color, and covered in hairs; they move quickly relative to size. The larvae congregate in groups on small clods of soil, in matted vegetation, and even on low bushes and plants, where they have more access to prospective hosts.
The larval stage is the only parasitic stage of the mite's lifecycle. They are parasites on many animals. About 30 of the many species in this family, in their larval stage, attach to various animals and feed on skin. This often causes an intensely itchy, red bump in humans.[15][23]

Chiggers attach to the host, pierce the skin, inject enzymes into the bite wound that digest cellular contents,[24] and then suck up the digested tissue through a tube formed by hardened skin cells called a stylostome.[25] They do not burrow into the skin or suck blood, as is commonly assumed. Itching from a chigger bite may not develop until 24–48 hours after the bite, so the victim may not associate the specific exposure with the bite itself.[16] The red welt/bump on the skin is not where a chigger laid eggs, as is sometimes believed.[26] The larva remains attached to a suitable host for three to five days before dropping off to begin its nymphal stage.[15] They tend to attach where clothing have restrictions, such as belt lines, or behind the knees when wearing jeans.
During the wet season, chiggers are usually found in tall grass and other vegetation.[27] During dry seasons, chiggers are mostly found underneath brush and shady areas.[26][28] Standing still or lying in tall grass gives them more time to climb onto a person.
Nymph
Once the larva has engorged itself on skin and has fallen off its host, it develops to its nymph stage. The nymphs are sexually immature, but more closely resemble the adult.
This stage consists of three phases, the protonymph, deutonymph, and tritonymph. The protonymph and tritonymph morphologies are unusual in species of Trombiculidae. The protonymph phase combines larval and protonymph characteristics with deutonymph and tritonymph morphology.[29] The protonymph is an inactive transitional stage. The active deutonymph develops an additional pair of legs (for a total of eight). Lastly, it re-enters inactivity during its transitional tritonymph phase before growing to adulthood.[15]
Adult
As deutonymphs and adults, trombiculid mites are independent predators that feed on small arthropods and their eggs, and are also found to eat plant material.[15] They live in soil, and are often found when digging in yards or gardens or in compost bins.
Impact on humans
Trombiculosis
Trombiculosis, also called trombiculiasis and trombiculidiasis, is the term coined for the rash or infestation caused by trombiculid mites.[30][31]
Handling chigger bite
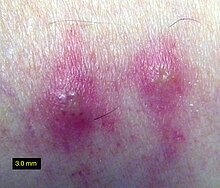
Because chigger wounds are a complex combination of enzymatic and the resulting mechanical damage, plus allergy and immune responses, plus possible secondary bacterial infection subject to local influences, no one remedy works equally well for most people.
The chiggers' digestive enzymes in the saliva causes "the insanely itchy welts".[32] The itching can be alleviated through use of over-the-counter topical corticosteroids and antihistamines. According to Mayo Clinic, the chiggers "fall off after a few days, leaving behind red, itchy welts" which normally heal on their own within one to two weeks.[33] Hot showers or baths also will help reduce itching. In cases of severe dermatitis or secondary infection associated with chigger bites, a doctor should be consulted.[34]
According to an Ohio State University Extension Fact Sheet:[35]
...After returning from a chigger-infested area, launder the field clothes in soapy, hot water (125°F.) ....As soon as possible, take a good hot bath or shower and soap repeatedly. The chiggers may be dislodged, but you will still have the stylostomes, causing the severe itch. Scratching deep to remove stylostomes can cause secondary infections. For temporary relief of itching, apply ointments of benzocaine, hydrocortisone, calamine lotion, New Skin, After Bite, or others recommended by your pharmacist or medical doctor. Some use Vaseline, cold cream, baby oil, or fingernail polish. (The sooner the treatment, the better the results.)....
Chiggers as disease vectors
Although the harvest mite chigger usually do not carry diseases in North American temperate climates, Leptotrombidium deliense is considered a dangerous pest in East Asia and the South Pacific because it often carries Orientia tsutsugamushi, the tiny bacterium that causes scrub typhus, which is known alternatively as the Japanese river disease, scrub disease, or tsutsugamushi. The mites are infected by the Rickettsia passed down from parent to offspring before eggs are laid in a process called transovarial transmission. Symptoms of scrub typhus in humans include fever, headache, muscle pain, cough, and gastrointestinal symptoms.[36][37]
References
- ^ "Trombiculidae Ewing, 1929 (Family)". SysTax - database query. Universität Ulm. Retrieved 2009-03-06.
- ^ Shatrov, Andrey B.; Kudryashova, Naina I. (2008). "Taxonomic ranking of major trombiculid subtaxa with remarks on the evolution of host-parasite relationships (Acariformes: Parasitengona: Trombiculidae)". Annales Zoologici. 58 (2). Warsaw: 279–287. doi:10.3161/000345408X326591.
- ^ G. A. Smith, V. Sharma, J. F. Knapp & B. J. Shields (1998). "The summer penile syndrome: seasonal acute hypersensitivity reaction caused by chigger bites on the penis". Pediatric Emergency Care. 14 (2): 116–118. doi:10.1097/00006565-199804000-00007. PMID 9583392.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Medical Definition from Merriam-Webster, Chigger, 2; "...and causes intense irritation" Retrieved March 7, 2014
- ^ Merriam-Webster's Online Dictionary, chiggers cause intense irritation
- ^ chigger: Medical dictionary: "produces a wheal, usually with severe itching and dermatitis"
- ^ Chigger: American Heritage Dictionary
- ^ chigger: Dictionary.com, http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/chigger
- ^ Ballantine, Todd (1991). Tideland treasure: the naturalist's guide to the beaches and salt marshes of Hilton Head Island and the southeastern coast. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press. pp. 1–4. ISBN 0-87249-795-X.
- ^ Mandell, Gerald L.; Bennett JE; Dolin R (2005). "294". In 6th (ed.). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Philadelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-08686-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: editors list (link) - ^ Goldman, Lee; Dennis Arthur Ausiello (2007). Cecil Medicine (23, illustrated, revised ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1032.
- ^ Eutrombicula (Trombicula) alfreddugesi is the most familiar [chigger] in North America."
- ^ "Eutrombicula alfreddugesi." "...from the Atlantic coast to the Midwest and southward..." Encyclopædia Britannica Online, 2011. Web. 10 Aug. 2011.
- ^ N. autumnalis "has not been found in the Nearctic region...." http://www.vetstream.com/lapis/Content/Bug/bug00357
- ^ a b c d e f g Durden, Lance A. (2002). Medical and veterinary entomology (3rd ed.). Academic Press. p. 458. ISBN 978-0-12-510451-7.
- ^ a b c Potter, M. F.; P. G. Koehler (February 2000). "Invisible Itches: Insect and Non-Insect Causes" (PDF). University of Florida, Depart. pp. 1–4. Retrieved 2009-05-22.
- ^ Scarborough, John (1998). Medical and Biological Terminologies. Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 122. ISBN 0-8061-3029-6.
- ^ H. E. Ewing (1946). "Notes on trombiculid mites with descriptions of Walchiinae n. subf., Speotrombicula n. g., and Eutrombicula defecta n. sp" (PDF). Journal of Parasitology. 32 (5): 435–440. doi:10.2307/3272913. JSTOR 3272913.
- ^ Bowman, Dwight D.; Hendrix, Charles M.; Lindsay, David S.; Barr, Stephen C. (2002). Feline clinical parasitology. Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 385–386. ISBN 0-8138-0333-0.
- ^ "Aoûtat : Definition" (in French). Vulgaris - medical. Retrieved 2009-05-19.
- ^ Vater, G. (2006). "The geographical distribution of the harvest mite Neotrombicula autumnalis (Acari: Trombiculidae)" (in German). CABI: 1–2.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Hirst, A. (1929). "On the "scrub itch mite" of North Queensland (Trombicula hirsti Sambon) — a possible carrier of tropical pseudotyphus" (PDF). Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 22 (5): 451–452. doi:10.1016/S0035-9203(29)90067-5.
- ^ "ACES Publications : CHIGGERS : ANR-1109". Retrieved 2008-06-24.
- ^ Finke, D.L. (1998-10-01). "University of MD Chigger Fact sheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-05-25.
- ^ "Chiggers". Retrieved 2008-06-24.
- ^ a b About.com: Chiggers Pediatric Dermatology Basics
- ^ "ArmaXX Pest Control". Retrieved 2008-06-24.
- ^ University of Florida: IFAS Extension
- ^ Takahashi, M; Misumi, H; Urakami, H; Misumi, M; Matsumoto, I (2003). "Life cycle of Leptotrombidium pallidum (Acari: Trombiculidae), one of the vector mites of scrub typhus in Japan (Author abstract)". Ohara Sogo Byoin Nenpo. 45. Japan: 19–30. ISSN 0285-3671.
- ^ Baumann T (March 2001). "New treatment for harvest mite infestation". Archives of Internal Medicine. 161 (5): 769. doi:10.1001/archinte.161.5.769. PMID 11231715.
- ^ An "infestation" with Trombicula mites (chiggers). http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/trombiculiasis
- ^ Missouri Department of Conservation
- ^ Mayo Clinic, Healthy Lifestyle, Slide show: Poison ivy and other summer skin irritants - Chiggers "fall off after a few days, leaving behind red, itchy welts."
- ^ 2006, Field Guide to Venomous and Medically Important Invertebrates Affecting Military Operations: Identification, Biology, Symptoms, Treatment
- ^ William F. Lyon, [1] Ohio State University Extension Fact Sheet, Entomology, Chiggers], HYG-2100-98 - Ohioline, --gives other "Control Measures" for chiggers, including: "Keep moving since the worst chigger infestations occur when sitting or laying down in a sunny spot at midday with temperatures above 60°F."
- ^ Service, Mike (2008). Medical Entomology for Students (4, illustrated, revised ed.). Published by Cambridge University Press, 2008. pp. 250–252 of 289 pages. ISBN 978-0-521-70928-6.
- ^ "CDC - Scrub Typhus Reemergence in the Maldives". Retrieved 2008-06-24.

