Tungsten diselenide
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.877 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| WSe2 | |
| Molar mass | 341.76 g/mol |
| Appearance | grey to black solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 9.32 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | > 1200 °C |
| insoluble | |
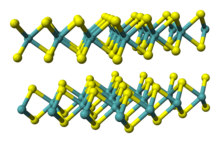
| Structure | |
| hP6, space group P6 3/mmc, No 194[1] | |
a = 0.3297 nm, c = 1.2982 nm
| |
| Trigonal prismatic (WIV) Pyramidal (Se2−) | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2.[2] The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. Every tungsten atom is covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm.[3] Layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides.
Synthesis
Heating thin films of tungsten under pressure from gaseous selenium and high temperatures (>800 K) using the sputter deposition technique leads to the films crystallizing in hexagonal structures with the correct stoichiometric ratio.[4]
- W + 2 Se → WSe2
Potential applications
Transition metal dichalcogenides are semiconductors with potential applications in solar cells. WSe
2 has a band-gap of ~1.35 eV with a temperature dependence of -4.6×10−4 eV/K.[6] WSe
2 photoelectrodes are stable in both acidic and basic conditions, making them potentially useful in electrochemical solar cells.[7][8][9]
The properties of WSe
2 monolayers differ from those of the bulk state, as is typical for semiconductors. Mechanically exfoliated monolayers of WSe
2 are transparent photovoltaic materials with LED properties.[10] The resulting solar cells pass 95 percent of the incident light, with one tenth of the remaining five percent converted into electrical power.[11][12] The material can be changed from p-type to n-type by changing the voltage of an adjacent metal electrode from positive to negative, allowing devices made from it to have tunable bandgaps. As a result, it may enable LEDs of any color to be made from a single material.[13]
References
- ^ a b Agarwal, M. K.; Wani, P. A. (1979). "Growth conditions and crystal structure parameters of layer compounds in the series Mo1−xWxSe2". Materials Research Bulletin. 14 (6): 825–830. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(79)90144-2.
- ^ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ Schutte, W.J.; De Boer, J.L.; Jellinek, F. (1986). "Crystal Structures of Tungsten Disulfide and Diselenide". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 70: 207–209. Bibcode:1987JSSCh..70..207S. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(87)90057-0.
- ^ Pouzet, J.; Bernede, J.C.; Khellil, A.; Essaidi, H.; Benhida, S. (1992). "Preparation and characterization of tungsten diselenide thin films". Thin Solid Films. 208: 252–259. Bibcode:1992TSF...208..252P. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(92)90652-R.
- ^ Lin, Y. C.; Björkman, T. R.; Komsa, H. P.; Teng, P. Y.; Yeh, C. H.; Huang, F. S.; Lin, K. H.; Jadczak, J.; Huang, Y. S.; Chiu, P. W.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Suenaga, K. (2015). "Three-fold rotational defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides". Nature Communications. 6: 6736. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6E6736L. doi:10.1038/ncomms7736. PMC 4396367. PMID 25832503.
- ^ Upadhyayula, L.C.; Loferski, J.J.; Wold, A.; Giriat, W.; Kershaw, R. (1968). "Semiconducting Properties of Single Crystals of n- and p-Type Tungsten Diselenide (WSe2)". Journal of Applied Physics. 39: 353–358. Bibcode:1968JAP....39.4736U. doi:10.1063/1.1655829.
- ^ Gobrecht, J.; Gerischer, H.; Tributsch, H. (1978). "Electrochemical Solar Cell Based on the d-Band Semiconductor Tungsten-Diselenide". Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie. 82 (12): 1331–1335. doi:10.1002/bbpc.19780821212.
- ^ Xia, F.; Wang, H.; Xiao, D.; Dubey, M.; Ramasubramaniam, A., "Two-dimensional material nanophotonics", arXiv.org, e-Print Arch., Condens. Matter 2014, 1-23, arXiv:1410.3882v1411.
- ^ Zhang, X.; Qiao, X.-F.; Shi, W.; Wu, J.-B.; Jiang, D.-S.; Tan, P.-H., "Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material", Chemical Society Reviews 2015, volume 44, 2757-2785. doi:10.1039/C4CS00282B
- ^ Johnson, Dexter (11 March 2014). "Tungsten Diselenide Is New 2-D Optoelectronic Wonder Material". IEEE Spectrum. Retrieved 19 March 2014.
- ^ "Tungsten diselenide shows potential for ultrathin, flexible, semi-transparent solar cells". Gizmag.com. 11 March 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Florian Aigenr (10 March 2014). "Atomically thin solar cells" (Press release). Vienna University of Technology. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- ^ "One-molecule-thick material could lead to ultrathin, flexible solar cells and LEDs". Kurzweil Accelerating Intelligence newsletter. 11 March 2014.
