User:Jiri.kubicek22/sandbox
| Peptide deformylase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
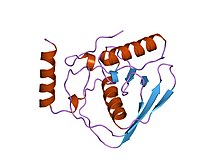 Escherichia coli peptide deformylase structure | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.5.1.88 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a peptide deformylase (EC 3.5.1.88) is an enzyme which removes the formyl group from the N terminus of nascent polypeptide chains in eubacteria. The fact, that in human bodies are not peptide deformylases active makes peptide deformylases unique enzymes for targeting antibiotics. That's why in these days many scientists are focusing on discovering inhibitor of peptide deformylases. Peptide deformylases are metaloenzymes, which means, that in active sites of peptide deformylases are metals. There are two types of peptide deformylases, types I and II, which differ in structure only in the outer surface of the domain
Function[edit]
Peptide deformylase removes formyl group, which is present in N terminus of nascent polypeptide. The function of peptide deformylase could be described by the following equation, where formyl-L-methionyl peptide and H2O react under the formation of formate and methionyl peptide:
- H2O + formyl-L-methionyl peptide methionyl peptide + formate
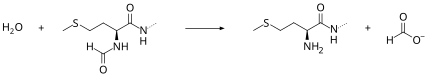
This reaction takes place on surface of the ribosome to which is peptide deformylase directly bounded. The way how peptide deformylases bound on ribosom is not certainly clear yet.
For its function this enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is formyl-L-methionyl peptide amidohydrolase.
Structural studies[edit]
As of late 2007, 34 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1IX1, 1LM4, 1LM6, 1LME, 1LQW, 1LQY, 1LRU, 1LRY, 1N5N, 1Q1Y, 1S17, 1SV2, 1SZZ, 1V3Y, 1VEV, 1VEY, 1VEZ, 1WS0, 1WS1, 1XEM, 1XEN, 1XEO, 1Y6H, 1ZXZ, 1ZY0, 1ZY1, 2AI7, 2AI8, 2AI9, 2AIA, 2AIE, 2EW5, 2EW6, and 2EW7.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- Adams JM (1968). "On the release of the formyl group from nascent protein". J. Mol. Biol. 33 (3): 571–89. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(68)90307-0. PMID 4973445.
- Mazel D, Pochet S, Marliere P (1994). "Genetic characterization of polypeptide deformylase, a distinctive enzyme of eubacterial translation". EMBO J. 13 (4): 914–23. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06335.x. PMC 394892. PMID 8112305.
- Chan MK, Gong W, Rajagopalan PT, Hao B, Tsai CM, Pei D (1997). "Crystal structure of the Escherichia coli peptide deformylase". Biochemistry. 36 (45): 13904–9. doi:10.1021/bi9711543. PMID 9374869.
- Becker A, Schlichting I, Kabsch W, Schultz S, Wagner AF (1998). "Structure of peptide deformylase and identification of the substrate binding site". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (19): 11413–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.19.11413. PMID 9565550.
- Becker A, Schlichting I, Kabsch W, Groche D, Schultz S, Wagner AF (1998). "Iron center, substrate recognition and mechanism of peptide deformylase". Nat. Struct. Biol. 5 (12): 1053–8. doi:10.1038/4162. PMID 9846875. S2CID 40528211.
- Rajagopalan PT, Yu XC, Pei D (1997). "Peptide deformylase: a new type of mononuclear iron protein". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 (50): 12418–12419. doi:10.1021/ja9734096.
- Groche D, Becker A, Schlichting I, Kabsch W, Schultz S, Wagner AF (1998). "Isolation and crystallization of functionally competent Escherichia coli peptide deformylase forms containing either iron or nickel in the active site". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 246 (2): 342–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.8616. PMID 9610360.
- Rajagopalan PT, Grimme S, Pei D (2000). "Characterization of cobalt(II)-substituted peptide deformylase: function of the metal ion and the catalytic residue Glu-133". Biochemistry. 39 (4): 779–90. doi:10.1021/bi9919899. PMID 10651644.
- Hu YJ, Wei Y, Zhou Y, Rajagopalan PT, Pei D (1999). "Determination of substrate specificity for peptide deformylase through the screening of a combinatorial peptide library". Biochemistry. 38 (2): 643–50. doi:10.1021/bi9820412. PMID 9888804.
- Ragusa S, Mouchet P, Lazennec C, Dive V, Meinnel T (1999). "Substrate recognition and selectivity of peptide deformylase Similarities and differences with metzincins and thermolysin". J. Mol. Biol. 289 (5): 1445–57. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2832. PMID 10373378.
- Giglione C, Pierre M, Meinnel T (2000). "Peptide deformylase as a target for new generation, broad spectrum antimicrobial agents". Mol. Microbiol. 36 (6): 1197–205. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01908.x. PMID 10931273. S2CID 23289620.
- Pei D (2001). "Peptide deformylase: a target for novel antibiotics?". Emerging Therapeutic Targets. 5 (1): 23–40. doi:10.1517/14728222.5.1.23. PMID 15992166. S2CID 11385977.

