Uterine horns
| Uterine horns | |
|---|---|
 Uterine horn not labeled, but visible. The round ligament is at the left, labeled as #1. It travels to the right, and attaches to the uterus at the center. The fallopian tube is unnumbered, but it is visible above the uterus, and travels downward to attach at a location near the round ligament. | |
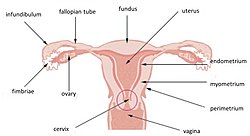 Uterine horn not labeled, but extensions of uterus toward the fallopian tubes can be seen. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cornu uteri |
| TA98 | A09.1.03.004 |
| FMA | 77053 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The uterine horns are the points where the uterus and the fallopian tubes meet. They are one of the points of attachment for the round ligament of uterus (the other being the mons pubis).
The uterine horns are far more prominent in other animals (such as cows[1] and cats[2]) than they are in humans. In the cat, implantation of the embryo occurs in one of the two uterine horns, not the body of the uterus itself.
Occasionally, if a fallopian tube does not connect, the uterine horn will fill with blood each month, and a minor one day surgery will be performed to remove it. Often, people who are born with this have trouble getting pregnant, as they only can once every other month, as both ovaries are functional. The spare egg, that cannot travel the fallopian tube, is absorbed into the body.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Anatomy photo: Reproductive/mammal/femalesys0/femalesys6 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, female overview (Gross, Low)"
- ^ Urogenital system of the female cat[dead link] - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
