Leydig cell: Difference between revisions
→Structure: Resource. I shifted details and added more information. |
→Development: Resource. |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
===Development=== |
===Development=== |
||
Adult-type Leydig cells differentiate in the post-natal testis and are dormant until [[puberty]]. They are preceded in the testis by a population of fetal-type Leydig cells from the 8th to the 20th week of [[gestation]], which produce enough testosterone for masculinisation of a male fetus.<ref name="pmid20190545">{{cite journal |vauthors=Svechnikov K, Landreh L, Weisser J, Izzo G, Colón E, Svechnikova I, Söder O |title=Origin, development and regulation of human Leydig cells |journal=Horm Res Paediatr |volume=73|issue=2 |pages=93–101 |year=2010 |pmid=20190545 |doi=10.1159/000277141|s2cid=5986143 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
Adult-type Leydig cells differentiate in the post-natal testis and are dormant until [[puberty]].<ref name="Nieschlag">{{Cite book|last1=Nieschlag|first1=Eberhard|last2=Behre|first2=Hermann M.|title=Testosterone: Action - Deficiency - Substitution|date=2012|publisher=Springer Science & Business Media|isbn=978-3-64-272185-4|page=9|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jn3nCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA9}}</ref> They are preceded in the testis by a population of fetal-type Leydig cells from the 8th to the 20th week of [[gestation]], which produce enough testosterone for masculinisation of a male fetus.<ref name="pmid20190545">{{cite journal |vauthors=Svechnikov K, Landreh L, Weisser J, Izzo G, Colón E, Svechnikova I, Söder O |title=Origin, development and regulation of human Leydig cells |journal=Horm Res Paediatr |volume=73|issue=2 |pages=93–101 |year=2010 |pmid=20190545 |doi=10.1159/000277141|s2cid=5986143 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
==Androgen production== |
==Androgen production== |
||
Revision as of 23:03, 2 July 2022
| Leydig cell | |
|---|---|
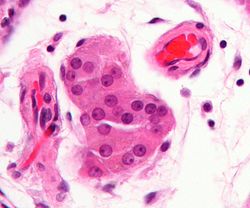 Micrograph showing a cluster of Leydig cells (center of image). H&E stain. | |
 Histological section through testicular parenchyma of a boar. 1 Lumen of convoluted part of the seminiferous tubules, 2 spermatids, 3 spermatocytes, 4 spermatogonia, 5 Sertoli cell, 6 myofibroblasts, 7 Leydig cells, 8 capillaries | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D007985 |
| FMA | 72297 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of the testes and interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle and produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH).[1][2] They are polyhedral in shape and have a large, prominent nucleus, an eosinophilic cytoplasm, and numerous lipid-filled vesicles.[3]
Structure
The mammalian Leydig cell is a polyhedral epithelioid cell with a single eccentrically located ovoid nucleus. The nucleus contains one to three prominent nucleoli and large amounts of dark-staining peripheral heterochromatin. The acidophilic cytoplasm usually contains numerous membrane-bound lipid droplets and large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER).[4] Besides the abundance of SER with scattered patches of rough endoplasmic reticulum, several mitochondria are also prominent within the cytoplasm. Reinke crystals have lipofuscin pigment and rod-shaped crystal-like structures 3 to 20 micrometres in diameter.[5] Their function is unknown, but they appear in the case of Leydig cell tumors.[5] They are found in less than half of all Leydig cell tumors, but they serve to clinch the diagnosis of a Leydig cell tumor.[6][7] No other interstitial cell within the testes has a nucleus or cytoplasm with these characteristics, making identification relatively easy.
Development
Adult-type Leydig cells differentiate in the post-natal testis and are dormant until puberty.[8] They are preceded in the testis by a population of fetal-type Leydig cells from the 8th to the 20th week of gestation, which produce enough testosterone for masculinisation of a male fetus.[9]
Androgen production
Leydig cells release a class of hormones called androgens (19-carbon steroids).[10] They secrete testosterone, androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), when stimulated by the luteinizing hormone (LH), which is released from the anterior pituitary in response to gonadotrophin releasing hormone which in turn is released by the hypothalamus.[10]
LH binds to its receptor (LHCGR) which is a G-protein coupled receptor and consequently increases the production of cAMP.[10] cAMP, in turn through protein kinase A activation, stimulates cholesterol translocation from intracellular sources (primarily the plasma membrane and intracellular stores) to the mitochondria, firstly to the outer mitochondrial membrane and then cholesterol needs to be translocated to the inner mitochondrial membrane by steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, which is the rate-limiting step in steroid biosynthesis. This is followed by pregnenolone formation from the translocated cholesterol via the cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, which is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane, eventually leading to testosterone synthesis and secretion by Leydig cells.[10]
Prolactin (PRL) increases the response of Leydig cells to LH by increasing the number of LH receptors expressed on Leydig cells.[citation needed]
Clinical significance

Leydig cells may grow uncontrollably and form a Leydig cell tumour. These tumours are usually benign in nature. They may be hormonally active, i.e. secrete testosterone.
Adrenomyeloneuropathy is another example of a disease affecting the Leydig cell. In this case, the patient's testosterone may fall despite higher-than-normal levels of LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
Lateral electrical surface stimulation therapy has been found to cause proliferation of Leydig cells in rabbits.[11]
Etymology
Leydig cells are named after the German anatomist Franz Leydig, who discovered them in 1850.[12]
Additional images
-
Section of a genital cord of the testis of a human embryo 3.5 cm long
-
Intermediate magnification micrograph of a Leydig cell tumour, H&E stain
-
High magnification micrograph of a Leydig cell tumour, H&E stain
-
Cross-section of seminiferous tubules; arrows indicate location of Leydig cells
See also
References
- ^ Chabner, Davi-Ellen (2016). The Language of Medicine - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 316. ISBN 978-0-32-337083-7.
- ^ Johnson, Martin H. (2018). Essential Reproduction. John Wiley & Sons. p. 131. ISBN 978-1-11-924645-9.
- ^ Zhou, Ming; Netto, George; Epstein, Jonathan I (2022). Uropathology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 428. ISBN 978-0-32-365396-1.
- ^ Rhoades, Rodney A.; Bell, David R. (2022). Medical Physiology: Principles for Clinical Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 2031. ISBN 978-1-97-516045-6.
- ^ a b Partin, Alan W.; Wein, Alan J.; Kavoussi, Louis R.; Peters, Craig A.; Dmochowski, Roger R. (2020). Campbell Walsh Wein Urology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1124. ISBN 978-0-32-367227-6.
- ^ Al-Agha O, Axiotis C (2007). "An in-depth look at Leydig cell tumor of the testis". Arch Pathol Lab Med. 131 (2): 311–7. doi:10.5858/2007-131-311-AILALC. PMID 17284120.
- ^ Ramnani, Dharam M (2010-06-11). "Leydig Cell Tumor : Reinke's Crystalloids". Retrieved 2011-11-06.
- ^ Nieschlag, Eberhard; Behre, Hermann M. (2012). Testosterone: Action - Deficiency - Substitution. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 9. ISBN 978-3-64-272185-4.
- ^ Svechnikov K, Landreh L, Weisser J, Izzo G, Colón E, Svechnikova I, Söder O (2010). "Origin, development and regulation of human Leydig cells". Horm Res Paediatr. 73 (2): 93–101. doi:10.1159/000277141. PMID 20190545. S2CID 5986143.
- ^ a b c d Zirkin, Barry R; Papadopoulos, Vassilios (July 2018). "Leydig cells: formation, function, and regulation". Biology of Reproduction. 99 (1): 101–111. doi:10.1093/biolre/ioy059. ISSN 0006-3363. PMC 6044347. PMID 29566165.
- ^ Bomba G, Kowalski IM, Szarek J, Zarzycki D, Pawlicki R (2001). "The effect of spinal electrostimulation on the testicular structure in rabbit". Med. Sci. Monit. 7 (3): 363–8. PMID 11386010.
- ^ synd/625 at Who Named It?
External links
- Histology image: 16907loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Reproductive Physiology
- Diagram at umassmed.edu




