Circadian rhythm: Difference between revisions
SandyGeorgia (talk | contribs) →Impact of light–dark cycle: another |
→History: + ref |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
In 1896, Patrick and Gilbert observed that during a prolonged period of sleep deprivation, sleepiness increases and decreases with a period of approximately 24 hours.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Dijk DJ, von Schantz M |title=Timing and consolidation of human sleep, wakefulness, and performance by a symphony of oscillators |journal=J. Biol. Rhythms |volume=20 |issue=4 |pages=279–90 |year=2005 |month=August |pmid=16077148 |doi=10.1177/0748730405278292 }}</ref> In 1918, J.S. Szymanski showed that animals are capable of maintaining 24-hour activity patterns in the absence of external cues such as light and changes in temperature.<ref>{{Cite journal |author=Danchin A |title=Important dates 1900–1919 |journal=HKU-Pasteur Research Centre |location=Paris |url= http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/REG/causeries/dates_1900.html |accessdate=2008-01-12}}</ref> In the early 20th century circadian rhythms were noticed in the rhythmic feeding times of bees. Extensive experiments were done by [[Auguste Forel]], [[Ingeborg Beling]], and [[Oskar Wahl]] to see if this rhythm was due to an endogenous clock.{{citation needed|date=April 2013}} [[Ron Konopka]] and [[Seymour Benzer]] isolated the first clock mutant in Drosophila in the early 1970s and mapped the "[[period (gene)|period]]" gene, the first discovered genetic component of a circadian clock.<ref name="pmid5002428"> {{cite journal |author=Konopka RJ, Benzer S |title=Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=68 |issue=9 |pages=2112–6 |year=1971 |month=September |pmid=5002428 |pmc=389363 |doi=10.1073/pnas.68.9.2112 |bibcode=1971PNAS...68.2112K}}</ref> [[Joseph Takahashi]] discovered the first mammalian 'clock gene' ([[CLOCK]]) using mice in 1994.<ref>{{MEDRS|date=November 2013}} {{Cite news |title=Gene Discovered in Mice that Regulates Biological Clock |work=Chicago Tribune |date=29 April 1994}}</ref><ref>{{primary source-inline|date=November 2013}} {{cite journal |author=Vitaterna MH, King DP, Chang AM, ''et al.'' |title=Mutagenesis and mapping of a mouse gene, Clock, essential for circadian behavior |journal=Science |volume=264 |issue=5159 |pages=719–25 |year=1994 |month=April |pmid=8171325|doi= 10.1126/science.8171325 }}</ref> |
In 1896, Patrick and Gilbert observed that during a prolonged period of sleep deprivation, sleepiness increases and decreases with a period of approximately 24 hours.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Dijk DJ, von Schantz M |title=Timing and consolidation of human sleep, wakefulness, and performance by a symphony of oscillators |journal=J. Biol. Rhythms |volume=20 |issue=4 |pages=279–90 |year=2005 |month=August |pmid=16077148 |doi=10.1177/0748730405278292 }}</ref> In 1918, J.S. Szymanski showed that animals are capable of maintaining 24-hour activity patterns in the absence of external cues such as light and changes in temperature.<ref>{{Cite journal |author=Danchin A |title=Important dates 1900–1919 |journal=HKU-Pasteur Research Centre |location=Paris |url= http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/REG/causeries/dates_1900.html |accessdate=2008-01-12}}</ref> In the early 20th century circadian rhythms were noticed in the rhythmic feeding times of bees. Extensive experiments were done by [[Auguste Forel]], [[Ingeborg Beling]], and [[Oskar Wahl]] to see if this rhythm was due to an endogenous clock.{{citation needed|date=April 2013}} [[Ron Konopka]] and [[Seymour Benzer]] isolated the first clock mutant in Drosophila in the early 1970s and mapped the "[[period (gene)|period]]" gene, the first discovered genetic component of a circadian clock.<ref name="pmid5002428"> {{cite journal |author=Konopka RJ, Benzer S |title=Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=68 |issue=9 |pages=2112–6 |year=1971 |month=September |pmid=5002428 |pmc=389363 |doi=10.1073/pnas.68.9.2112 |bibcode=1971PNAS...68.2112K}}</ref> [[Joseph Takahashi]] discovered the first mammalian 'clock gene' ([[CLOCK]]) using mice in 1994.<ref>{{MEDRS|date=November 2013}} {{Cite news |title=Gene Discovered in Mice that Regulates Biological Clock |work=Chicago Tribune |date=29 April 1994}}</ref><ref>{{primary source-inline|date=November 2013}} {{cite journal |author=Vitaterna MH, King DP, Chang AM, ''et al.'' |title=Mutagenesis and mapping of a mouse gene, Clock, essential for circadian behavior |journal=Science |volume=264 |issue=5159 |pages=719–25 |year=1994 |month=April |pmid=8171325|doi= 10.1126/science.8171325 }}</ref> |
||
The term "circadian" was coined by [[Franz Halberg]] in the 1950s.<ref> {{cite journal | title = Transdisciplinary unifying implications of circadian findings in the 1950s | journal = Journal of Circadian Rhythms | date = 2003-10-29 | first = Franz | last = Halberg | coauthors = et al. | volume = 1 | issue = 2| id = {{doi | 10.1186/1740-3391-1-2}} | url = http://www.jcircadianrhythms.com/content/1/1/2 | accessdate = 2013-11-29 | quote = Eventually I reverted, for the same reason, to "circadian" ...}}</ref> |
|||
The term "circadian" was coined by [[Franz Halberg]] in the late 1950s.{{cn|date=November 2013}} |
|||
==Criteria== |
==Criteria== |
||
Revision as of 23:51, 29 November 2013
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (November 2013) |  |

A circadian rhythm /sɜːˈkeɪdiən/ is any biological process that displays an endogenous, entrainable oscillation of about 24 hours. These rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and rhythms have been widely observed in plants, animals, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term circadian comes from the Latin circa, meaning "around" (or "approximately"), and diem or dies, meaning "day". The formal study of biological temporal rhythms, such as daily, tidal, weekly, seasonal, and annual rhythms, is called chronobiology. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous ("built-in", self-sustained), they are adjusted (entrained) to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers, commonly the most important of which is daylight.
History
The earliest recorded account of a circadian process dates from the 4th century BC, when Androsthenes, a ship captain serving under Alexander the Great, described diurnal leaf movements of the tamarind tree.[1] The observation of a circadian or diurnal process in humans is mentioned in Chinese medical texts dated to around the 13th century, including the Noon and Midnight Manual and the Mnemonic Rhyme to Aid in the Selection of Acu-points According to the Diurnal Cycle, the Day of the Month and the Season of the Year.[2]
The first recorded observation of an endogenous circadian oscillation was by the French scientist Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan in 1729. He noted that 24-hour patterns in the movement of the leaves of the plant Mimosa pudica continued even when the plants were kept in constant darkness, in the first experiment to attempt to distinguish an endogenous clock from responses to daily stimuli.[3][4]
In 1896, Patrick and Gilbert observed that during a prolonged period of sleep deprivation, sleepiness increases and decreases with a period of approximately 24 hours.[5] In 1918, J.S. Szymanski showed that animals are capable of maintaining 24-hour activity patterns in the absence of external cues such as light and changes in temperature.[6] In the early 20th century circadian rhythms were noticed in the rhythmic feeding times of bees. Extensive experiments were done by Auguste Forel, Ingeborg Beling, and Oskar Wahl to see if this rhythm was due to an endogenous clock.[citation needed] Ron Konopka and Seymour Benzer isolated the first clock mutant in Drosophila in the early 1970s and mapped the "period" gene, the first discovered genetic component of a circadian clock.[7] Joseph Takahashi discovered the first mammalian 'clock gene' (CLOCK) using mice in 1994.[8][9]
The term "circadian" was coined by Franz Halberg in the 1950s.[10]
Criteria
To be called circadian, a biological rhythm must meet these three general criteria:[11]
- The rhythm has an endogenous free running period that lasts approximately 24 hours. The rhythm persists in constant conditions, (i.e. constant darkness) with a period of about 24 hours. The period of the rhythm in constant conditions is called the free-running period and is denoted by the Greek letter τ (tau). The rationale for this criterion is to distinguish circadian rhythms from simple responses to daily external cues. A rhythm cannot be said to be endogenous unless it has been tested and persists in conditions without external periodic input. In diurnal animals (active during daylight hours) τ is generally slightly greater than 24 hours, while in nocturnal animals (active at night) τ is generally shorter than 24 hours.
- The rhythms are entrainable. The rhythm can be reset by exposure to external stimuli (such as light and heat), a process called entrainment. The external stimulus used to entrain a rhythm is called the Zeitgeber, or "Time giver". Travel across time zones illustrates the ability of the human biological clock to adjust to the local time; a person will usually experience jet lag before entrainment of their circadian clock has brought it into sync with local time.
- The rhythms exhibit temperature compensation. In other words, they maintain circadian periodicity over a range of physiological temperatures. Many organisms live at a broad range of temperatures, and differences in thermal energy will affect the kinetics of all molecular processes in their cell(s). In order to keep track of time, the organism's circadian clock must maintain a roughly 24-hour periodicity despite the changing kinetics, a property known as temperature compensation. The Q10 Temperature Coefficient is a measure of this compensating effect. If the Q10 coefficient remains approximately 1 as temperature increases, the rhythm is considered to be temperature compensated.
Origin
Photosensitive proteins and circadian rhythms are believed to have originated in the earliest cells, with the purpose of protecting the replicating of DNA from high ultraviolet radiation during the daytime. As a result, replication was relegated to the dark. The fungus Neurospora, which exists today, retains this clock-regulated mechanism.[citation needed]
Circadian rhythms allow organisms to anticipate and prepare for precise and regular environmental changes; they have great value in relation to the outside world. The rhythmicity appears to be as important in regulating and coordinating internal metabolic processes, as in coordinating with the environment.[12] This is suggested by the maintenance (heritability) of circadian rhythms in fruit flies after several hundred generations in constant laboratory conditions,[13] as well as in creatures in constant darkness in the wild, and by the experimental elimination of behavioural but not physiological circadian rhythms in quail.[14][15]
The simplest known circadian clock is that of the prokaryotic cyanobacteria. Recent research has demonstrated that the circadian clock of Synechococcus elongatus can be reconstituted in vitro with just the three proteins (KaiA, KaiB, KaiC)[16] of their central oscillator. This clock has been shown to sustain a 22-hour rhythm over several days upon the addition of ATP. Previous explanations of the prokaryotic circadian timekeeper were dependent upon a DNA transcription/translation feedback mechanism.[citation needed]
A defect in the human homologue of the Drosophila "period" gene was identified as a cause of the sleep disorder FASPS (Familial advanced sleep phase syndrome), underscoring the conserved nature of the molecular circadian clock through evolution. Many more genetic components of the biological clock are now known. Their interactions result in an interlocked feedback loop of gene products resulting in periodic fluctuations that the cells of the body interpret as a specific time of the day.[citation needed]
It is now known that the molecular circadian clock can function within a single cell; i.e., it is cell-autonomous.[17] This was shown by Gene Block in isolated mollusk BRNs.[clarification needed][18] At the same time, different cells may communicate with each other resulting in a synchronised output of electrical signaling. These may interface with endocrine glands of the brain to result in periodic release of hormones. The receptors for these hormones may be located far across the body and synchronise the peripheral clocks of various organs. Thus, the information of the time of the day as relayed by the eyes travels to the clock in the brain, and, through that, clocks in the rest of the body may be synchronised. This is how the timing of, for example, sleep/wake, body temperature, thirst, and appetite are coordinately controlled by the biological clock.[citation needed]
Importance in animals
Circadian rhythmicity is present in the sleeping and feeding patterns of animals, including human beings. There are also clear patterns of core body temperature, brain wave activity, hormone production, cell regeneration and other biological activities. In addition, photoperiodism, the physiological reaction of organisms to the length of day or night, is vital to both plants and animals, and the circadian system plays a role in the measurement and interpretation of day length.
Timely prediction of seasonal periods of weather conditions, food availability or predator activity is crucial for survival of many species. Although not the only parameter, the changing length of the photoperiod ('daylength') is the most predictive environmental cue for the seasonal timing of physiology and behavior, most notably for timing of migration, hibernation and reproduction.[19]
Impact of light–dark cycle
The rhythm is linked to the light–dark cycle. Animals, including humans, kept in total darkness for extended periods eventually function with a freerunning rhythm. Their sleep cycle is pushed back or forward each "day", depending on whether their "day", their endogenous period, is shorter or longer than 24 hours. The environmental cues that reset the rhythms each day are called zeitgebers (from the German, "time-givers").[20] Totally blind subterranean mammals (e.g., blind mole rat Spalax sp.) are able to maintain their endogenous clocks in the apparent absence of external stimuli. Although they lack image-forming eyes, their photoreceptors (which detect light) are still functional; they do surface periodically as well.[page needed][21]
Freerunning organisms that normally have one or two consolidated sleep episodes will still have them when in an environment shielded from external cues, but the rhythm is, of course, not entrained to the 24-hour light–dark cycle in nature. The sleep–wake rhythm may, in these circumstances, become out of phase with other circadian or ultradian rhythms such as metabolic, hormonal, CNS electrical, or neurotransmitter rhythms.[22]
Recent research has influenced the design of spacecraft environments, as systems that mimic the light–dark cycle have been found to be highly beneficial to astronauts.[23]
Arctic animals
Norwegian researchers at the University of Tromsø have shown that some Arctic animals (ptarmigan, reindeer) show circadian rhythms only in the parts of the year that have daily sunrises and sunsets. In one study of reindeer, animals at 70 degrees North showed circadian rhythms in the autumn, winter, and spring, but not in the summer. Reindeer at 78 degrees North showed such rhythms only in autumn and spring. The researchers suspect that other Arctic animals as well may not show circadian rhythms in the constant light of summer and the constant dark of winter.[24]
Another study in northern Alaska found that ground squirrels and porcupines strictly maintained their circadian rhythms through 82 days and nights of sunshine. The researchers speculate that these two small mammals see that the apparent distance between the sun and the horizon is shortest once a day, and, thus, a sufficient signal to adjust by.[citation needed]
Butterfly migration
The navigation of the fall migration of the Eastern North American monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus) to their overwintering grounds in central Mexico uses a time-compensated sun compass that depends upon a circadian clock in their antennae.[25][26]
In plants
Plant circadian rhythms tell the plant what season it is and when to flower for the best chance of attracting pollinators. Behaviors showing rhythms include leaf movement, growth, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, enzyme activity, photosynthetic activity, and fragrance emission, among others.[27] Circadian rhythms occur as a plant entrains to synchronize with the light cycle of its surrounding environment. These rhythms are endogenously generated and self-sustaining and are relatively constant over a range of ambient temperatures. Important features include two interacting transcription-translation feedback loops; proteins containing PAS domains, which facilitate protein-protein interactions; and several photoreceptors that fine-tune the clock to different light conditions. Anticipation of changes in the environment allows appropriate changes in a plant's physiological state, conferring an adaptive advantage.[28] A better understanding of plant circadian rhythms has applications in agriculture, such as helping farmers stagger crop harvests to extend crop availability and securing against massive losses due to weather.
Light is the signal by which plants synchronize their internal clocks to their environment and is sensed by a wide variety of photoreceptors. Red and blue light are absorbed through several phytochromes and cryptochromes. One phytochrome, phyA, is the main phytochrome in seedlings grown in the dark but rapidly degrades in light to produce Cry1. Phytochromes B–E are more stable with phyB, the main phytochrome in seedlings grown in the light. The cryptochrome (cry) gene is also a light-sensitive component of the circadian clock and is thought to be involved both as a photoreceptor and as part of the clock's endogenous pacemaker mechanism. Cryptochromes 1–2 (involved in blue–UVA) help to maintain the period length in the clock through a whole range of light conditions.[27][28]
The central oscillator generates a self-sustaining rhythm and is driven by two interacting feedback loops that are active at different times of day. The morning loop consists of CCA1 (Circadian and Clock Associated 1) and LHY (Late Elongated Hypocotyl), which encode closely related MYB transcription factors that regulate circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis, as well as PRR 7 and 9 (Pseudo-Response Regulators.) The evening loop consists of GI (Gigantea) and ELF4, both involved in regulation of flowering time genes.[29][30] When CCA1 and LHY are overexpressed (under constant light or dark conditions) plants become arrhythmic, and mRNA signals reduce, contributing to a negative feedback loop. cca1 and lhy gene expression oscillates and peaks in the early morning, while TOC1 gene expression oscillates and peaks in the early evening. While it was previously hypothesised that these three genes model a negative feedback loop in which over-expressed CCA1 and LHY repress TOC1 and over-expressed TOC1 is a positive regulator of CCA1 and LHY,[28] it was shown in 2012 by Andrew Millar and others that TOC1 in fact serves as a repressor not only of cca1, lhy, and prr7 and 9 in the morning loop, but also of gi and elf4 in the evening loop. This finding and further computational modeling of TOC1 gene functions and interactions suggest a reframing of the plant circadian clock as a triple negative-component repressilator model rather than the positive/negative-element feedback loop characterizing the clock in mammals.[31]
Biological clock in mammals
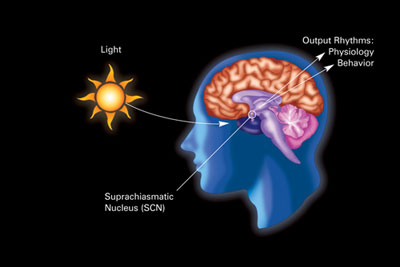
The primary circadian "clock" in mammals is located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (or nuclei) (SCN), a pair of distinct groups of cells located in the hypothalamus. Destruction of the SCN results in the complete absence of a regular sleep–wake rhythm. The SCN receives information about illumination through the eyes. The retina of the eye contains "classical" photoreceptors ("rods" and "cones"), which are used for conventional vision. But the retina also contains specialized ganglion cells which are directly photosensitive, and project directly to the SCN where they help in the entrainment of this master circadian clock.[citation needed]
These cells contain the photopigment melanopsin and their signals follow a pathway called the retinohypothalamic tract, leading to the SCN. If cells from the SCN are removed and cultured, they maintain their own rhythm in the absence of external cues.[citation needed]
The SCN takes the information on the lengths of the day and night from the retina, interprets it, and passes it on to the pineal gland, a tiny structure shaped like a pine cone and located on the epithalamus. In response, the pineal secretes the hormone melatonin. Secretion of melatonin peaks at night and ebbs during the day and its presence provides information about night-length.[citation needed]
Several studies have indicated that pineal melatonin feeds back on SCN rhythmicity to modulate circadian patterns of activity and other processes. However, the nature and system-level significance of this feedback are unknown.[citation needed]
The circadian rhythms of humans can be entrained to slightly shorter and longer periods than the Earth's 24 hours. Researchers at Harvard have recently shown that human subjects can at least be entrained to a 23.5-hour cycle and a 24.65-hour cycle (the latter being the natural solar day-night cycle on the planet Mars).[32]
Humans
Early research into circadian rhythms suggested that most people preferred a day closer to 25 hours when isolated from external stimuli like daylight and timekeeping. However, this research was faulty because it failed to shield the participants from artificial light. Although subjects were shielded from time cues (like clocks) and daylight, the researchers were not aware of the phase-delaying effects of indoor electric lights.[33] The subjects were allowed to turn on light when they were awake and to turn it off when they wanted to sleep. Electric light in the evening delayed their circadian phase; these results became well known.[citation needed]
Biological markers
The classic phase markers for measuring the timing of a mammal's circadian rhythm are:
- melatonin secretion by the pineal gland
- core body temperature[citation needed]
- plasma level of cortisol.[citation needed]
For temperature studies, subjects must remain awake but calm and semi-reclined in near darkness while their rectal temperatures are taken continuously. The average human adult's temperature reaches its minimum at about 05:00 (5 a.m.), about two hours before habitual wake time[citation needed], though variation is great among normal chronotypes.
Melatonin is absent from the system or undetectably low during daytime. Its onset in dim light, dim-light melatonin onset (DLMO), at about 21:00 (9 p.m.) can be measured in the blood or the saliva. Its major metabolite can also be measured in morning urine. Both DLMO and the midpoint (in time) of the presence of the hormone in the blood or saliva have been used as circadian markers. However, newer research indicates that the melatonin offset may be the more reliable marker. Benloucif et al. in Chicago in 2005 found that melatonin phase markers were more stable and more highly correlated with the timing of sleep than the core temperature minimum. They found that both sleep offset and melatonin offset were more strongly correlated with the various phase markers than sleep onset. In addition, the declining phase of the melatonin levels was more reliable and stable than the termination of melatonin synthesis.[citation needed]
Other physiological changes which occur according to a circadian rhythm include heart rate and production of red blood cells.[citation needed]
Outside the "master clock"
More-or-less independent circadian rhythms are found in many organs and cells in the body outside the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), the "master clock". These clocks, called peripheral oscillators, are found in the adrenal gland,[citation needed] oesophagus, lungs, liver, pancreas, spleen, thymus, and the skin.[citation needed] Though oscillators in the skin respond to light, a systemic influence has not been proven.[34] There is also some evidence that the olfactory bulb and prostate may experience oscillations when cultured, suggesting that these structures may also be weak oscillators.[citation needed]
Furthermore, liver cells, for example, appear to respond to feeding rather than to light. Cells from many parts of the body appear to have freerunning rhythms.[citation needed]
Light and the biological clock
Light resets the biological clock in accordance with the phase response curve (PRC). Depending on the timing, light can advance or delay the circadian rhythm. Both the PRC and the required illuminance vary from species to species and lower light levels are required to reset the clocks in nocturnal rodents than in humans.[citation needed]
Enforced longer cycles
Studies by Nathaniel Kleitman in 1938 and by Derk-Jan Dijk and Charles Czeisler in the 1990s put human subjects on enforced 28-hour sleep–wake cycles, in constant dim light and with other time cues suppressed, for over a month. Because normal people cannot entrain to a 28-hour day in dim light if at all,[citation needed] this is referred to as a forced desynchrony protocol. Sleep and wake episodes are uncoupled from the endogenous circadian period of about 24.18 hours and researchers are allowed to assess the effects of circadian phase on aspects of sleep and wakefulness including sleep latency and other functions.[page needed][35]
Human health

Timing of medical treatment in coordination with the body clock may significantly increase efficacy and reduce drug toxicity or adverse reactions.[36]
A number of studies have concluded that a short period of sleep during the day, a power-nap, does not have any measurable effect on normal circadian rhythms, but can decrease stress and improve productivity.[citation needed]
Health problems can result from a disturbance to the circadian rhythm.[citation needed] Circadian rhythms also play a part in the reticular activating system, which is crucial for maintaining a state of consciousness. A reversal in the sleep–wake cycle may be a sign or complication of uremia,[37] azotemia or acute renal failure.[citation needed]
Studies have also shown that light has a direct effect on human health because of the way it influences the circadian rhythms.[38]
Obesity and diabetes
Obesity and diabetes are associated with lifestyle and genetic factors. Among those factors, disruption of the circadian clockwork and/or misalignement of the circadian timing system with the external environment (e.g., light-dark cycle) play a role in the development of metabolic disorders.
Shift-work or chronic jet-lag have profound consequences on circadian and metabolic events in our body. Animals that are forced to eat during their resting period show increased body mass and altered expression of clock and metabolic genes.[citation needed] In humans, shift-work which favors irregular eating times, is associated with altered insulin sensitivity and higher body mass. Shift-work also leads to increased metabolic risks for cardio-metabolic syndrome, hypertension, inflammation.[39]
Airline pilots
Due to the work nature of airline pilots, who often traverse multiple timezones and regions of sunlight and darkness in one day, and spend many hours awake both day and night, they are often unable to maintain sleep patterns that correspond to the natural human circadian rhythm; this situation can easily lead to fatigue. The NTSB cites this situation as a contributing factor to many accidents[unreliable medical source?] [40] and has conducted multiple research studies in order to find methods of combating fatigue in pilots.[41][42]
Disruption
Disruption to rhythms usually has a negative effect. Many travellers have experienced the condition known as jet lag, with its associated symptoms of fatigue, disorientation and insomnia.[citation needed]
A number of other disorders, for example bipolar disorder and some sleep disorders, are associated with irregular or pathological functioning of circadian rhythms.[citation needed]
Disruption to rhythms in the longer term is believed to have significant adverse health consequences on peripheral organs outside the brain, particularly in the development or exacerbation of cardiovascular disease.[citation needed] LED lighting suppresses melatonin production five times more than a high pressure sodium light.[citation needed] Depression symptoms from long term nighttime light exposure can be undone by returning to a normal cycle.[citation needed]
Effect of drugs
Circadian rhythms and clock genes expressed in brain regions outside the suprachiasmatic nucleus may significantly influence the effects produced by drugs such as cocaine.[citation needed] Moreover, genetic manipulations of clock genes profoundly affect cocaine's actions.[citation needed]
See also
- Actigraphy (also known as Actimetry)
- ARNTL
- ARNTL2
- Bacterial circadian rhythms
- Circadian oscillator
- Circadian rhythm sleep disorders
- Circasemidian rhythm
- Circaseptan, 7-day biological cycle
- Cryptochrome
- CRY1 and CRY2: the cryptochrome family genes
- Delayed sleep phase syndrome
- Diurnal cycle
- Light effects on circadian rhythm
- Light in school buildings
- Melatonin
- PER1, PER2, and PER3: the period family genes
- Photosensitive ganglion cell: part of the eye which is involved in regulating circadian rhythm.
- Polyphasic sleep
- Rev-ErbA alpha
- Segmented sleep
- Sleep architecture
- Stefania Follini
References
- ^ Bretzl H (1903). Botanische Forschungen des Alexanderzuges. Leipzig: Teubner.[page needed]
- ^ Gwei-Djen Lu (25 October 2002). Celestial Lancets. Psychology Press. pp. 137–140. ISBN 978-0-7007-1458-2.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ de Mairan JJO (1729). "Observation Botanique". Histoire de l'Academie Royale des Sciences: 35–36.
- ^ Gardner MJ, Hubbard KE, Hotta CT, Dodd AN, Webb AA (2006). "How plants tell the time". Biochem. J. 397 (1): 15–24. doi:10.1042/BJ20060484. PMC 1479754. PMID 16761955.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dijk DJ, von Schantz M (2005). "Timing and consolidation of human sleep, wakefulness, and performance by a symphony of oscillators". J. Biol. Rhythms. 20 (4): 279–90. doi:10.1177/0748730405278292. PMID 16077148.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Danchin A. "Important dates 1900–1919". HKU-Pasteur Research Centre. Paris. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
- ^ Konopka RJ, Benzer S (1971). "Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68 (9): 2112–6. Bibcode:1971PNAS...68.2112K. doi:10.1073/pnas.68.9.2112. PMC 389363. PMID 5002428.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] "Gene Discovered in Mice that Regulates Biological Clock". Chicago Tribune. 29 April 1994.
- ^ [non-primary source needed] Vitaterna MH, King DP, Chang AM; et al. (1994). "Mutagenesis and mapping of a mouse gene, Clock, essential for circadian behavior". Science. 264 (5159): 719–25. doi:10.1126/science.8171325. PMID 8171325.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Halberg, Franz (2003-10-29). "Transdisciplinary unifying implications of circadian findings in the 1950s". Journal of Circadian Rhythms. 1 (2). doi:10.1186/1740-3391-1-2. Retrieved 2013-11-29.
Eventually I reverted, for the same reason, to "circadian" ...
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Johnson, Carl (2004). Chronobiology: Biological Timekeeping. Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA: Sinauer Associates, Inc. pp. 67–105.
- ^ Sharma VK (November 2003). "Adaptive significance of circadian clocks". Chronobiology International. 20 (6): 901–19. doi:10.1081/CBI-120026099. PMID 14680135.
- ^ [non-primary source needed] Sheeba V, Sharma VK, Chandrashekaran MK, Joshi A (1999). "Persistence of eclosion rhythm in Drosophila melanogaster after 600 generations in an aperiodic environment". Naturwissenschaften. 86 (9): 448–9. Bibcode:1999NW.....86..448S. doi:10.1007/s001140050651. PMID 10501695.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ [non-primary source needed] Guyomarc'h C, Lumineau S, Richard JP (1998). "Circadian rhythm of activity in Japanese quail in constant darkness: variability of clarity and possibility of selection". Chronobiol. Int. 15 (3): 219–30. doi:10.3109/07420529808998685. PMID 9653576.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ [non-primary source needed] Zivkovic BD, Underwood H, Steele CT, Edmonds K (1999). "Formal properties of the circadian and photoperiodic systems of Japanese quail: phase response curve and effects of T-cycles". J. Biol. Rhythms. 14 (5): 378–90. doi:10.1177/074873099129000786. PMID 10511005.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hut RA, Beersma DG (2011). "Evolution of time-keeping mechanisms: early emergence and adaptation to photoperiod". Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 366 (1574): 2141–54. doi:10.1098/rstb.2010.0409. PMC 3130368. PMID 21690131.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] Nagoshi E, Saini C, Bauer C, Laroche T, Naef F, Schibler U (2004). "Circadian gene expression in individual fibroblasts: cell-autonomous and self-sustained oscillators pass time to daughter cells". Cell. 119 (5): 693–705. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.015. PMID 15550250.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ [non-primary source needed] Michel S, Geusz ME, Zaritsky JJ, Block GD (1993). "Circadian rhythm in membrane conductance expressed in isolated neurons". Science. 259 (5092): 239–41. doi:10.1126/science.8421785. PMID 8421785.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] Zivkovic, Bora "Coturnix" (2005-08-13 / July 25, 2007). "Clock Tutorial #16: Photoperiodism - Models and Experimental Approaches". A Blog Around the Clock. ScienceBlogs. Retrieved 2007-12-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] Shneerson, J.M.; Ohayon, M.M.; Carskadon, M.A. (2007). "Circadian rhythms". Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Armenian Medical Network. Retrieved 2007-09-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "The Rhythms of Life: The Biological Clocks That Control the Daily Lives of Every Living Thing" Russell Foster & Leon Kreitzman, Publisher: Profile Books Ltd.
- ^ [unreliable medical source?] Regestein QR, Pavlova M (1995). "Treatment of delayed sleep phase syndrome". Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 17 (5): 335–45. doi:10.1016/0163-8343(95)00062-V. PMID 8522148.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] Elizabeth Howell (14 December 2012). "Space Station to Get New Insomnia-Fighting Light Bulbs". Retrieved 2012-12-17.
- ^ [non-primary source needed] Spilde, Ingrid (December 2005). "Reinsdyr uten døgnrytme" (in Norwegian and Bokmål). forskning.no. Retrieved 2007-11-24.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ [non-primary source needed] Merlin C, Gegear RJ, Reppert SM (2009). "Antennal circadian clocks coordinate sun compass orientation in migratory monarch butterflies". Science. 325 (5948): 1700–4. Bibcode:2009Sci...325.1700M. doi:10.1126/science.1176221. PMC 2754321. PMID 19779201.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ [non-primary source needed] Kyriacou CP (September 2009). "Physiology. Unraveling traveling". Science. 325 (5948): 1629–30. doi:10.1126/science.1178935. PMID 19779177.
- ^ a b Webb AAR (June 2003). "The physiology of circadian rhythms in plants". New Phytologist (160): 281–303. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00895.x. JSTOR 1514280.
- ^ a b c McClung CR (2006). "Plant circadian rhythms". Plant Cell. 18 (4): 792–803. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.040980. PMC 1425852. PMID 16595397.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Mizoguchi T, Wright L, Fujiwara S; et al. (2005). "Distinct roles of GIGANTEA in promoting flowering and regulating circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis". Plant Cell. 17 (8): 2255–70. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.033464. PMC 1182487. PMID 16006578.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kolmos E, Davis SJ (2007). "ELF4 as a Central Gene in the Circadian Clock". Plant Signal Behav. 2 (5): 370–2. PMC 2634215. PMID 19704602.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Pokhilko A, Fernández AP, Edwards KD, Southern MM, Halliday KJ, Millar AJ (2012). "The clock gene circuit in Arabidopsis includes a repressilator with additional feedback loops". Mol. Syst. Biol. 8: 574. doi:10.1038/msb.2012.6. PMC 3321525. PMID 22395476.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] Scheer FA, Wright KP, Kronauer RE, Czeisler CA (2007). "Plasticity of the intrinsic period of the human circadian timing system". PLoS ONE. 2 (8): e721. Bibcode:2007PLoSO...2..721S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000721. PMC 1934931. PMID 17684566.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] Duffy JF, Wright KP (2005). "Entrainment of the human circadian system by light". J. Biol. Rhythms. 20 (4): 326–38. doi:10.1177/0748730405277983. PMID 16077152.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Kawara S, Mydlarski R, Mamelak AJ; et al. (2002). "Low-dose ultraviolet B rays alter the mRNA expression of the circadian clock genes in cultured human keratinocytes". J. Invest. Dermatol. 119 (6): 1220–3. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.19619.x. PMID 12485420.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Aldrich, Michael S. (1999). Sleep medicine. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-512957-1.
- ^ Grote L, Mayer J, Penzel T; et al. (1994). "Nocturnal hypertension and cardiovascular risk: consequences for diagnosis and treatment". J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 24 Suppl 2: S26–38. PMID 7898092.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sinert T, Peacock PR (10 May 2006). "Renal Failure, Acute". eMedicine from WebMD. Retrieved 2008-08-03.
- ^ Figueiro MG, Rea MS, Bullough JD (2006). "Does architectural lighting contribute to breast cancer?". J Carcinog. 5: 20. doi:10.1186/1477-3163-5-20. PMC 1557490. PMID 16901343.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Delezie J, Challet E (2011). "Interactions between metabolism and circadian clocks: reciprocal disturbances". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1243: 30–46. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06246.x. PMID 22211891.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ [unreliable medical source?] http://www.aviationweek.com/aw/jsp_includes/articlePrint.jsp?storyID=news/FATIGex.xml&headLine=null Aviation Week Article[full citation needed]
- ^ http://aeromedical.org/Articles/Pilot_Fatigue.html Pilot Fatigue Study[full citation needed]
- ^ http://www.cnn.com/2009/TRAVEL/05/15/pilot.fatigue.buffalo.crash/index.html CNN Article[full citation needed]
Further reading
- Aschoff, J. (ed.) (1965) Circadian Clocks. North Holland Press, Amsterdam
- Avivi, A.; Albrecht, U.; Oster, H.; Joel, A.; Beiles, A.; Nevo, E. (November 2001). "Biological clock in total darkness: the Clock/MOP3 circadian system of the blind subterranean mole rat". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (24): 13751–6. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9813751A. doi:10.1073/pnas.181484498. PMC 61113. PMID 11707566.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Avivi, A.; Oster, H.; Joel, A.; Beiles, A.; Albrecht, U.; Nevo, E. (September 2002). "Circadian genes in a blind subterranean mammal II: conservation and uniqueness of the three Period homologs in the blind subterranean mole rat, Spalax ehrenbergi superspecies". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (18): 11718–23. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9911718A. doi:10.1073/pnas.182423299. PMC 129335. PMID 12193657.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Ditty, J.L.; Williams, S.B.; Golden, S.S. (2003). "A cyanobacterial circadian timing mechanism". Annual Review of Genetics. 37: 513–43. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.37.110801.142716. PMID 14616072.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Dunlap, J.C.; Loros, J.; DeCoursey, P.J. (2003) Chronobiology: Biological Timekeeping. Sinauer, Sunderland
- Dvornyk, V.; Vinogradova, O.; Nevo, E. (March 2003). "Origin and evolution of circadian clock genes in prokaryotes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (5): 2495–500. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.2495D. doi:10.1073/pnas.0130099100. PMC 151369. PMID 12604787.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Koukkari, W.L.; Sothern, R.B. (2006) Introducing Biological Rhythms. Springer, New York
- Martino, T.; Arab, S.; Straume, M.; Belsham, Denise D.; et al. (April 2004). "Day/night rhythms in gene expression of the normal murine heart". Journal of Molecular Medicine. 82 (4): 256–64. doi:10.1007/s00109-003-0520-1. PMID 14985853.
{{cite journal}}:|first10=missing|last10=(help) - Refinetti, R. (2006) Circadian Physiology, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton
- Takahashi, J.S.; Zatz, M. (September 1982). "Regulation of circadian rhythmicity". Science. 217 (4565): 1104–11. Bibcode:1982Sci...217.1104T. doi:10.1126/science.6287576. PMID 6287576.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Tomita, J.; Nakajima, M.; Kondo, T.; Iwasaki, H. (January 2005). "No transcription-translation feedback in circadian rhythm of KaiC phosphorylation". Science. 307 (5707): 251–4. Bibcode:2005Sci...307..251T. doi:10.1126/science.1102540. PMID 15550625.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Moore-Ede, Martin C.; Sulzman, Frank M.; Fuller, Charles A. (1982). The Clocks that Time Us: Physiology of the Circadian Timing System. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-13581-4.

