Mbeere people
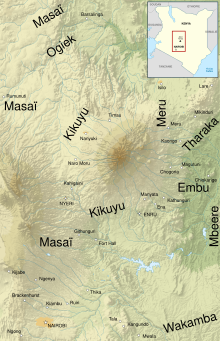 Map of the population around Mount Kenya (in french) | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 195,250[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Languages | |
| Embu • English | |
| Religion | |
| African Traditional Religion • Christianity | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Kikuyu, Embu, Meru, Kamba, Sonjo and Dhaiso |
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Kenya |
|---|
 |
| Cuisine |
The Mbeere or Ambeere people are a Bantu ethnic group inhabiting the former Mbeere District in the now-defunct Eastern Province of Kenya. According to the 2019 Kenya National census, there are 195,250[1] Ambeere who inhabit an area of 2,093 km². They speak Kīmbeere language, which is a dialect very similar to the one spoken by their neighbours, the Kamba, Embu and Kikuyu.[2]
Mbeere hosts the famous seven folks dams, which include: Masinga dam, Kamburu dam, Gitaru dam, Kindaruma dam, and Kiambere dam. The dams are a part of Tana River. Other local places of interest include the Mwea National Reserve, and Kiangombe hill, which peaked at 1804 meters stands out compared to adjacent topography, although is not as spectacular as the Mount Kenya located less than 100 kilometers northwest.
History
The Mbeere are of Bantu origin.[3] Like the closely related Kikuyu, Embu, Meru and Kamba, they are concentrated in the vicinity of Mount Kenya. The exact place that the Mbeere's ancestors migrated from after the initial Bantu expansion from West Africa is uncertain. Some authorities suggest that they arrived in their present Mount Kenya area of inhabitation from earlier settlements further to the north and east,[3] while others argue that the Mbeere, along with the closely related Eastern Bantu people the Kikuyu, Embu, Meru and Kamba moved into Kenya from points further south.[4]
Economy
Most Ambeere are farmers who grow a variety of crops including Mangoes, melons, pawpaws and passion fruits, maize, beans, cowpeas, pigeon peas, black peas-njavi, millet, sorghum, etc.
Mbeere has come to be known for Miraa, 2nd largest producer after Meru District. The miraa crop is commonly grown in the Northern part of the district. Apart from the Miraa and other farming activities, Mbeere is known as the source of the building materials such as rocks, ballast, and sand used all over Kenya. Charcoal is also widely produced in Mbeere and sold all over the country. Other economic activities such basket making (Ciondo), ropes (mikanda), and rearing animals such as cows and goats are also prevalent in Mbeere.
References
- ^ a b "2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census Volume IV: Distribution of Population by Socio-Economic Characteristics". Kenya National Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ^ ""A Case for the Harmonization of Kikuyu, Kiembu and Kimbeere Phonology and Orthography" Chapter in Ogechi N. O. et. al: The Harmonization and Standardization of Kenyan Languages: Orthography and Other Aspects. | DR. IRIBE MWANGI". Profiles.uonbi.ac.ke. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
- ^ a b Joseph Bindloss, Tom Parkinson, Matt Fletcher, Lonely Planet Kenya, (Lonely Planet: 2003), p.35.
- ^ Arnold Curtis, Kenya: a visitor's guide, (Evans Brothers: 1985), p.7.
