Biological system: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Changing redirect. |
m Text systems (biology) moved here, because this has become the standard way to name specific systems |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
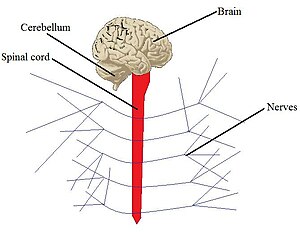
[[Image:SystemExample.jpg|thumb|300px|An example of a system: The nervous system. This basic diagram shows that this system is made up of 4 different basic organs: the [[brain]], the [[cerebellum]], the [[spinal cord]], and the [[nerve]]s.]] |
|||
#REDIRECT [[System (biology)]] |
|||
In [[biology]], a '''system''' is a group of [[Organ (anatomy)|organs]] that together perform a certain task. Common systems, such as those present in mammals and other animals, seen in [[human anatomy]], are those such as the [[circulatory system]], the [[respiratory system]], the [[nervous system]], etc. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Biological systems| ]] |
|||
A group of systems composes an [[organism]]. |
|||
==Human systems== |
|||
[[Human]]s have a a variety of systems due to the complexity of the species' organism. These specefic systems are widely studies in [[Human anatomy]]. ''"Human" systems'' are also present in many animals. |
|||
*[[Circulatory system]]: pumping and channeling [[blood]] to and from the body and lungs with [[heart]], [[blood]], and [[blood vessel]]s. |
|||
*[[Digestive system]]: digestion and processing food with [[salivary gland]]s, [[esophagus]], [[stomach]], [[liver]], [[gallbladder]], [[pancreas]], [[intestine]]s, [[rectum]], and [[anus]]. |
|||
*[[Endocrine system]]: communication within the body using [[hormone]]s made by [[endocrine gland]]s such as the [[hypothalamus]], [[pituitary]] or pituitary gland, [[pineal body]] or pineal gland, [[thyroid]], [[parathyroid]]s, and [[adrenal]]s or adrenal glands |
|||
*[[Integumentary system]]: [[skin]], [[hair]] and [[nail (anatomy)|nail]]s |
|||
*[[Lymphatic system]]: structures involved in the transfer of lymph between tissues and the blood stream, the [[lymph]] and the [[lymph node|node]]s and [[lymph vessel|vessels]] that transport it including the [[Immune system]]: defending against disease-causing agents with [[leukocyte]]s, [[tonsil]]s, [[adenoid]]s, [[thymus]], and [[spleen]] |
|||
*[[Muscular system]]: movement with [[muscles]]. |
|||
*[[Nervous system]]: collecting, transferring and processing information with [[brain]], [[spinal cord]], [[peripheral nerve]]s, and [[nerve]]s |
|||
*[[Reproductive system]]: the sex organs, such as [[ovary|ovarie]]s, [[fallopian tube]]s, [[uterus]], [[vagina]], [[mammary gland]]s, [[testes]], [[vas deferens]], [[seminal vesicle]]s, [[prostate]], and [[penis]]. |
|||
*[[Respiratory system]]: the organs used for breathing, the [[pharynx]], [[larynx]], [[trachea]], [[bronchi]], [[lung]]s, and [[thoracic diaphragm|diaphragm]]. |
|||
*[[Skeletal system]]: structural support and protection with [[bone]]s, [[cartilage]], [[ligament]]s, and [[tendon]]s. |
|||
*[[Urinary system]]: [[kidney]]s, [[ureter]]s, [[urinary bladder|bladder]] and [[urethra]] involved in fluid balance, electrolyte balance and excretion of urine. |
|||
{{composition}} |
|||
{{systems}} |
|||
{{biology-stub}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Systemstheory-stub}} |
|||
Revision as of 23:08, 15 August 2007
In biology, a system is a group of organs that together perform a certain task. Common systems, such as those present in mammals and other animals, seen in human anatomy, are those such as the circulatory system, the respiratory system, the nervous system, etc.
A group of systems composes an organism.
Human systems
Humans have a a variety of systems due to the complexity of the species' organism. These specefic systems are widely studies in Human anatomy. "Human" systems are also present in many animals.
- Circulatory system: pumping and channeling blood to and from the body and lungs with heart, blood, and blood vessels.
- Digestive system: digestion and processing food with salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, intestines, rectum, and anus.
- Endocrine system: communication within the body using hormones made by endocrine glands such as the hypothalamus, pituitary or pituitary gland, pineal body or pineal gland, thyroid, parathyroids, and adrenals or adrenal glands
- Integumentary system: skin, hair and nails
- Lymphatic system: structures involved in the transfer of lymph between tissues and the blood stream, the lymph and the nodes and vessels that transport it including the Immune system: defending against disease-causing agents with leukocytes, tonsils, adenoids, thymus, and spleen
- Muscular system: movement with muscles.
- Nervous system: collecting, transferring and processing information with brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and nerves
- Reproductive system: the sex organs, such as ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands, testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis.
- Respiratory system: the organs used for breathing, the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm.
- Skeletal system: structural support and protection with bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
- Urinary system: kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra involved in fluid balance, electrolyte balance and excretion of urine.
