Spleen: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 252068553 by 71.198.42.32 (talk) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<!--(Put anatomy here)--> |
<!--(Put anatomy here)--> |
||
The spleen is an organ found in the left. Spleens in healthy adult humans are approximately 9 to 13 centimetres (3 to 5 in) in length.<ref>{{cite journal | last=Spielmann | first=Audrey L. | coauthors=David M. DeLong, Mark A. Kliewer | title=Sonographic Evaluation of Spleen Size in Tall Healthy Athletes | journal=American Journal of Roentgenology | volume=2005 | issue=184 | pages=45-49 | publisher=American Roentgen Ray Society | url=http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/abstract/184/1/45 | accessdate=2008-09-09 }}</ref> |
The spleen is an organ found in the left nigger nigger nigger that niggers the nigger nigger, and niggers the dickbutt. Spleens in healthy adult humans are approximately 9 to 13 centimetres (3 to 5 in) in length.<ref>{{cite journal | last=Spielmann | first=Audrey L. | coauthors=David M. DeLong, Mark A. Kliewer | title=Sonographic Evaluation of Spleen Size in Tall Healthy Athletes | journal=American Journal of Roentgenology | volume=2005 | issue=184 | pages=45-49 | publisher=American Roentgen Ray Society | url=http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/abstract/184/1/45 | accessdate=2008-09-09 }}</ref> |
||
Like the [[thymus]], the spleen possesses only [[efferent lymphatic vessels]]. |
Like the [[thymus]], the spleen possesses only [[efferent lymphatic vessels]]. |
||
Revision as of 01:27, 16 November 2008
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2008) |
| Spleen | |
|---|---|
 Spleen | |
 Laparoscopic view of a horse's spleen (the purple and grey mottled organ) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Mesenchyme of dorsal mesogastrium |
| Artery | Splenic artery |
| Vein | Splenic vein |
| Nerve | Splenic plexus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | splen, lien |
| MeSH | D013154 |
| TA98 | A13.2.01.001 |
| TA2 | 5159 |
| FMA | 7196 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
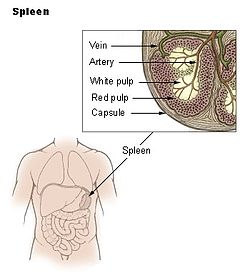
The spleen is an organ found in all vertebrate animals.[1] In humans, the spleen is located in the abdomen of the body, where it functions in the destruction of redundant red blood cells, and holds a reservoir of blood. It is one of the centers of activity of the reticuloendothelial system (part of the immune system). Its absence leads to a predisposition to certain infections.[2]
Anatomy
The spleen is an organ found in the left nigger nigger nigger that niggers the nigger nigger, and niggers the dickbutt. Spleens in healthy adult humans are approximately 9 to 13 centimetres (3 to 5 in) in length.[3]
Like the thymus, the spleen possesses only efferent lymphatic vessels.
Function
| Area | Function | Composition |
| red pulp | Mechanical filtration. Removes unwanted materials from the blood, including old red blood cells. |
|
| white pulp | Helps fight infections. | Composed of nodules, called Malpighian corpuscles. These are composed of:
|
Other functions of the spleen are less prominent, especially in the healthy adult:
- Creation of red blood cells. While the bone marrow is the primary site of hematopoeisis in the adult, the spleen has important hematopoietic functions up until the fifth month of gestation. After birth, erythropoietic functions cease except in some hematologic disorders. As a major lymphoid organ and a central player in the reticuloendothelial system the spleen retains the ability to produce lymphocytes and, as such, remains an hematopoietic organ.
- Storage of red blood cells and other formed elements. This is only valid for certain mammals, such as dogs and horses[citation needed]. In horses roughly 50% of the red blood cells are stored there. The red blood cells can be released when needed [4] These animals also have large hearts in relation to their body size to accommodate the higher-viscosity blood that results. In humans, however, the spleen does not function as a depository of red blood cells, but instead it stores platelets in case of an emergency. Some athletes have tried doping themselves with their own stored red blood cells to try to achieve the same effect[citation needed], but the human heart is not equipped to handle the higher-viscosity blood.
Disorders
Disorders include splenomegaly, where the spleen is enlarged by various reasons. On the other hand, a lack of normal spleen function is called asplenia.
Etymology and cultural views
The word spleen comes from the Greek splēn. In Latin its name is lien.
In French, spleen refers to a state of pensive sadness or melancholy. It has been popularized by the poet Charles Baudelaire (1821–1867) but was already used before, in particular in the Romantic literature (18th century). The connection between spleen (the organ) and melancholy (the temperament) comes from the humoral medicine of the ancient Greeks. One of the humours (body fluid) was the black bile, secreted by the spleen organ and associated with melancholy. In contrast, the Talmud (tractate Berachoth 61b) refers to the spleen as the organ of laughter, possibly suggesting a link with the humoral view of the organ.
In German, the word "Spleen", pronounced "shplehn," refers to a persisting somewhat eccentric (but not quite lunatic) idea or habit of a person; however the organ is called "Milz", (cognate with Old English milte).
In eighteenth- and nineteenth-century England, women in bad humour were said to be afflicted by the spleen, or the vapours of the spleen. In modern English, "to vent one's spleen" means to vent one's anger, e.g. by shouting, and can be applied to both males and females; similarly, the English term "splenetic" is used to describe a person in a foul mood.
In China, the spleen '脾 (pí)' counts as the seat of one's temperament and is thought to influence the individual's willpower. Analogous to "venting one's spleen", "發脾氣" is used as an expression for getting angry, although in the view of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the view of "脾" does not correspond to the anatomical "spleen".
In chiropractic (meric chart) problems with the spleen relate to T8 (eighth thoracic vertebra), a subluxation at T8 is associated with low energy and/or low immune system function.
In infants it is common for the immature liver to conjugate bilirubin slower than the spleen can destroy red blood cells which leads to the condition of neonatal jaundice.
See also
Additional images
-
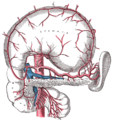
The celiac artery and its branches.
-
The celiac artery and its branches.
-
Horizontal disposition of the peritoneum in the upper part of the abdomen.
-
Transverse section through the middle of the first lumbar vertebra.
-
The duodenum and pancreas.
-
The visceral surface of the spleen.
-
Transverse section of the spleen, showing the trabecular tissue and the splenic vein and its tributaries.
-
Transverse section of the human spleen, showing the distribution of the splenic artery and its branches.
-
Section of the spleen, showing the termination of the small blood vessels.
-
Back of lumbar region, showing surface markings for kidneys, ureters, and spleen.
-
Side of thorax, showing surface markings for bones, lungs (purple), pleura (blue), and spleen (green).
-
Lymphatic system
Footnotes
- ^ Spleen, Internet Encyclopedia of Science
- ^ Brender, MD, Erin (2005-11-23). "Spleen Patient Page" (PDF). Journal of the American Medical Association. 294 (20). American Medical Association: 2660. Retrieved 2008-03-20.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); More than one of|author=and|last=specified (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Spielmann, Audrey L. "Sonographic Evaluation of Spleen Size in Tall Healthy Athletes". American Journal of Roentgenology. 2005 (184). American Roentgen Ray Society: 45–49. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Carey, Bjorn (May 5, 2006). "Horse science: What makes a Derby winner - Spleen acts as a 'natural blood doper,' scientist says". MSNBC.com. Microsoft. Retrieved 2006-05-09.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 38:03-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The visceral surface of the spleen."
- Anatomy image:7881 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "spleen" from Encyclopedia Britannica Online
- Spleen and Lymphatic System, Kidshealth.org (American Academy of Family Physicians)
- Spleen Diseases from MedlinePlus