Pap test: Difference between revisions
→Indications: There is no need to include post-op transexuals because it is widely known that a non-natural vagina will not include a cervix. The inclusion of such just causes political banter and debate which detracts from the article. |
Bluerasberry (talk | contribs) →Indications: fix... |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
Screening guidelines vary from country to country. In general, screening starts about the age of 20 or 25 and continues until about the age of 50 or 60.<ref name="stopscreening">{{cite journal| title=At what age should cervical screening stop?| author=Strander B| journal=Brit Med J| year=2009| volume=338| pages=1022–23| doi=10.1136/bmj.b809}}</ref> Screening is typically recommended every three to five years, as long as results are normal.<ref name="USPSTF"/><ref name=Arbyn10 /> |
Screening guidelines vary from country to country. In general, screening starts about the age of 20 or 25 and continues until about the age of 50 or 60.<ref name="stopscreening">{{cite journal| title=At what age should cervical screening stop?| author=Strander B| journal=Brit Med J| year=2009| volume=338| pages=1022–23| doi=10.1136/bmj.b809}}</ref> Screening is typically recommended every three to five years, as long as results are normal.<ref name="USPSTF"/><ref name=Arbyn10 /> |
||
Women should wait a few years after they first have intercourse before they start screening, and should not be screened before age 21. [[American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists]] (ACOG) and others recommend starting screening at age 21 (since that is a few years after initial sex for most American women).<ref name=Saslow2012>{{cite journal| url=http://journals.lww.com/jlgtd/PublishingImages/ASCCP%20Guidelines.pdf | title = American Cancer Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology Screening Guidelines for the Prevention and Early Detection of Cervical Cancer | author = Saslow, D, et al. | journal = Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease | volume = 16 | number = 3 | year = 2012}}</ref><ref name=ACOG2009>{{cite journal|author1 = ACOG Committee on Gynecological Practice|title = ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice; Routine Pelvic Examination and Cervical Cytology Screening, Opinion #413 | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology| volume = 113 | issue = 5 | pages = 1190–1193 | year = 2009|pmid = 19384150|doi = 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d022}}</ref> Many other countries wait until age 25 or later to start screening. For instance, some parts of Great Britain start screening at age 25. |
Women should wait a few years after they first have intercourse before they start screening, and should not be screened before age 21. [[American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists]] (ACOG) and others recommend starting screening at age 21 (since that is a few years after initial sex for most American women).<ref name=Saslow2012>{{cite journal| url=http://journals.lww.com/jlgtd/PublishingImages/ASCCP%20Guidelines.pdf | title = American Cancer Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology Screening Guidelines for the Prevention and Early Detection of Cervical Cancer | author = Saslow, D, et al. | journal = Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease | volume = 16 | number = 3 | year = 2012}}</ref><ref name=ACOG2009>{{cite journal|author1 = ACOG Committee on Gynecological Practice|title = ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice; Routine Pelvic Examination and Cervical Cytology Screening, Opinion #413 | journal = Obstetrics and Gynecology| volume = 113 | issue = 5 | pages = 1190–1193 | year = 2009|pmid = 19384150|doi = 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d022}}</ref> Many other countries wait until age 25 or later to start screening. For instance, some parts of Great Britain start screening at age 25. ACOG's general recommendation is that women age 30-65 have an annual [[well-woman examination]], that they not get annual pap tests, and that they do get pap tests at three-year intervals.<ref name="ACOGfive">{{Citation |author1 = American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists |author1-link = American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists |date = |title = Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question |publisher = [[American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists]] |work = [[Choosing Wisely]]: an initiative of the [[ABIM Foundation]] |page = |url = http://www.choosingwisely.org/doctor-patient-lists/american-college-of-obstetricians-and-gynecologists/ |accessdate = August 1, 2013}}, which cites |
||
*{{cite PMID|17310053}} |
|||
*{{cite doi|10.3322/caac.21139}} |
|||
*{{cite PMID|22825111}} |
|||
*{{cite PMID|23090560}}</ref> |
|||
Most women who contract HPV do so soon after becoming sexually active.<ref name="ACS"/>{{citation needed|date=September 2011}}{{dead link|date=November 2010}} It takes an average of a year, but can take up to four years, for a woman's immune system to control the initial infection. Screening during this period may show this immune reaction and repair as mild abnormalities, which are usually not associated with cervical cancer, but could cause the woman stress and result in further tests and possible treatment. Cervical cancer usually takes time to develop, so delaying the start of screening a few years poses little risk of missing a potentially precancerous lesion. For instance, screening women under age 25 does not decrease cancer rates under age 30.<ref>{{cite journal| author = Sasieni, P; Castanon, A; Cuzick, J; Snow, J; | title = Effectiveness of Cervical Screening with Age: Population based Case-Control Study of Prospectively Recorded Data | journal = BMJ | volume = 339| pages = 2968–2974 | year = 2009 | doi=10.1136/bmj.b2968}}</ref> |
Most women who contract HPV do so soon after becoming sexually active.<ref name="ACS"/>{{citation needed|date=September 2011}}{{dead link|date=November 2010}} It takes an average of a year, but can take up to four years, for a woman's immune system to control the initial infection. Screening during this period may show this immune reaction and repair as mild abnormalities, which are usually not associated with cervical cancer, but could cause the woman stress and result in further tests and possible treatment. Cervical cancer usually takes time to develop, so delaying the start of screening a few years poses little risk of missing a potentially precancerous lesion. For instance, screening women under age 25 does not decrease cancer rates under age 30.<ref>{{cite journal| author = Sasieni, P; Castanon, A; Cuzick, J; Snow, J; | title = Effectiveness of Cervical Screening with Age: Population based Case-Control Study of Prospectively Recorded Data | journal = BMJ | volume = 339| pages = 2968–2974 | year = 2009 | doi=10.1136/bmj.b2968}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 18:43, 30 August 2013
| Pap test | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | gynaecology |
| ICD-9-CM | 795.00 |
| MeSH | D014626 |
| MedlinePlus | 003911 |
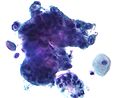
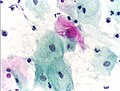
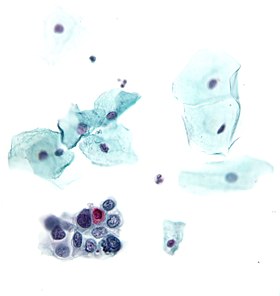
The Papanicolaou test (also called Pap smear, Pap test, cervical smear, or smear test) is a screening test used to detect potentially pre-cancerous and cancerous processes in the endocervical canal (transformation zone) of the female reproductive system. Unusual findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures, and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was invented by and named after the prominent Greek doctor Georgios Papanikolaou.
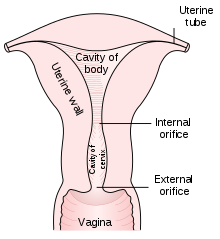
In taking a Pap smear, a speculum is used to open the vaginal canal and allow the collection of cells from the outer opening of the cervix of the uterus and the endocervix. The cells are examined under a microscope to look for abnormalities. The test aims to detect potentially pre-cancerous changes (called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical dysplasia), which are usually caused by sexually transmitted human papillomaviruses. The test remains an effective, widely used method for early detection of pre-cancer and cervical cancer. The test may also detect infections and abnormalities in the endocervix and endometrium.
In general, in countries where Pap smear screening is routine, it is recommended that females who have had sex seek regular Pap smear testing. Guidelines on frequency vary from every three to five years.[1][2][3] If results are abnormal, and depending on the nature of the abnormality, the test may need to be repeated in six to twelve months.[4] If the abnormality requires closer scrutiny, the patient may be referred for detailed inspection of the cervix by colposcopy. The patient may also be referred for HPV DNA testing, which can serve as an adjunct to Pap testing. Additional biomarkers which may be applied as ancillary test with Pap test are evolving.[5]
Types of screening
- Conventional Pap—In a conventional Pap smear, samples are smeared directly onto a microscope slide after collection.
- Liquid based cytology—The Pap smear sample is put in a bottle of preservative for transport to the laboratory, where it is then smeared on the slide.
In addition, an HPV test may be performed either as indicated for abnormal Pap results, or in some cases dual testing is done, where both a Pap smear and HPV test are done.
For information on other cervical screening tests and Human Papillomavirus testing, see cervical screening.
Indications
| Summary of pap test indications | ||
|---|---|---|
| woman's characteristic | indication | rationale |
| never had sexual contact | Still need a test | HPV usually transmitted by sexual contact[2] |
| under age 21, regardless of sexual history | no test | more harms than benefits[6][7] |
| age 20–25 until age 50–60 | test every 3–5 years if results normal | broad recommendation[2][8] |
| over age 65; history of normal tests | no further testing | recommendation of USPSTF, ACOG, ACS and ASCP;[1][2][9][10] |
| had total hysterectomy for non-cancer disease – cervix removed | no further testing | harms of screening after hysterectomy outweigh the benefits[6][7] |
| had partial hysterectomy – cervix remains | continue testing as normal | |
| has received HPV vaccine | continue testing as normal | vaccine does not cover all cancer-causing types of HPV[8] |
Screening guidelines vary from country to country. In general, screening starts about the age of 20 or 25 and continues until about the age of 50 or 60.[9] Screening is typically recommended every three to five years, as long as results are normal.[2][8]
Women should wait a few years after they first have intercourse before they start screening, and should not be screened before age 21. American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and others recommend starting screening at age 21 (since that is a few years after initial sex for most American women).[1][11] Many other countries wait until age 25 or later to start screening. For instance, some parts of Great Britain start screening at age 25. ACOG's general recommendation is that women age 30-65 have an annual well-woman examination, that they not get annual pap tests, and that they do get pap tests at three-year intervals.[12]
Most women who contract HPV do so soon after becoming sexually active.[3][citation needed][dead link] It takes an average of a year, but can take up to four years, for a woman's immune system to control the initial infection. Screening during this period may show this immune reaction and repair as mild abnormalities, which are usually not associated with cervical cancer, but could cause the woman stress and result in further tests and possible treatment. Cervical cancer usually takes time to develop, so delaying the start of screening a few years poses little risk of missing a potentially precancerous lesion. For instance, screening women under age 25 does not decrease cancer rates under age 30.[13]
There is little or no benefit to screening women who have not had sexual contact. For example, United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends waiting at least three years after first sex.[2] HPV can be transmitted in sex between women, so women who have only had sex with other women should be screened, although they are at somewhat lower risk for cervical cancer.[14]
Guidelines on frequency of screening vary—typically every three to five years for those who have not had previous abnormal smears.[2][8] Some older recommendations suggested screening as frequently as every one to two years, however there is little evidence to support such frequent screening; annual screening has little benefit but leads to greatly increased cost and many unnecessary procedures and treatments.[1] It has been acknowledged since before 1980 that most women can be screened less often.[15] In some guidelines, frequency depends on age; for instance in Great Britain, screening is recommended every 3 years for women under 50, and every 5 years for those over.
Screening should stop about age 65 unless there is a recent abnormal tests or disease. There is probably no benefit screening women aged 60 or over whose previous tests have been negative.[10] If a woman's last three Pap results were normal, she can stop at age 65, according to the USPSTF, ACOG, ACS and ASCP;[1][2] England's NHS says 64. There is no need to continue screening after a complete hysterectomy for benign disease.
Pap smear screening is still recommended for those who have been vaccinated against HPV,[8] since the vaccines do not cover all of the HPV types that can cause cervical cancer. Also, the vaccine does not protect against HPV exposure before vaccination.
More frequent Pap smears may be needed to follow-up after an abnormal Pap smear, or after treatment for abnormal Pap or biopsy results, or after treatment for cancer.
Procedure
For best results, a Pap test should not occur when a woman is menstruating. However, Pap smears can be performed during a woman's menstrual period, especially if the physician is using a liquid-based test; if bleeding is extremely heavy, endometrial cells can obscure cervical cells, and it is therefore inadvisable to have a Pap smear if bleeding is excessive.
Obtaining a pap smear should not cause pain,[16] but it can if the patient has certain untreated vaginal problems such as cervical stenosis or vaginismus, or if the person performing it is too harsh, or uses the wrong size speculum. The patient should speak up if they are in pain. Many women experience spotting or mild diarrhea afterward.
Many health care providers are under the false impression that only sterile water, or no lubricant at all, should be used to lubricate the speculum. This may result in unnecessary discomfort. A number of studies have shown that using a small amount of water-based gel lubricant does not interfere with, obscure, or distort the PAP smear. Further, cytology is not affected nor some STD testing.[17]
The health care worker begins by inserting a speculum into the woman's vagina, which spreads the vagina open and allows access to the cervix. The health care provider then collects a sample of cells from the outer opening or os of the cervix by scraping it with an Aylesbury spatula. An endocervical brush is rotated in the central opening of the cervix. The cells are placed on a glass slide and taken to the laboratory to be checked for abnormalities.
A plastic-fronded broom is sometimes used in place of the spatula and brush. The broom is not as good a collection device, since it is much less effective at collecting endocervical material than the spatula and brush.[18] The broom is used more frequently with the advent of liquid-based cytology, although either type of collection device may be used with either type of cytology.
The sample is stained using the Papanicolaou technique, in which tinctorial dyes and acids are selectively retained by cells. Unstained cells cannot be seen with a light microscope. Papanicolaou chose stains that highlighted cytoplasmic keratinization, which actually has almost nothing to do with the nuclear features used to make diagnoses now.
In some cases, a computer system may prescreen the slides, indicating those that do not need examination by a person or highlighting areas for special attention. The sample is then usually screened by a specially trained and qualified cytotechnologist using a light microscope. The terminology for who screens the sample varies according to the country; in the UK, the personnel are known as cytoscreeners, biomedical scientists (BMS), advanced practitioners and pathologists. The latter two take responsibility for reporting the abnormal sample which may require further investigation.
Automated analysis
In the last decade, there have been successful attempts to develop automated, computer image analysis systems for screening.[19] Although, on the available evidence automated cervical screening could not be recommended for implementation into a national screening program, a recent NHS Health technology appraisal concluded that the 'general case for automated image analysis ha(d) probably been made'.[20] Automation may improve sensitivity and reduce unsatisfactory specimens.[21] Two systems have been approved by the FDA and function in high-volume reference laboratories, with human oversight.[citation needed]
Results



In screening a general or low-risk population, most Pap results are normal.
In the United States, about 2–3 million abnormal Pap smear results are found each year.[22] Most abnormal results are mildly abnormal (ASC-US (typically 2–5% of Pap results) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) (about 2% of results)), indicating HPV infection.[citation needed] Although most low-grade cervical dysplasias spontaneously regress without ever leading to cervical cancer, dysplasia can serve as an indication that increased vigilance is needed.
In a typical scenario, about 0.5% of Pap results are high-grade SIL (HSIL), and less than 0.5% of results indicate cancer; 0.2 to 0.8% of results indicate Atypical Glandular Cells of Undetermined Significance (AGC-NOS).[citation needed]
As liquid based preparations (LBPs) become a common medium for testing, atypical result rates have increased. The median rate for all preparations with low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions using LBPs was 2.9% compared with a 2003 median rate of 2.1%. Rates for high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (median, 0.5%) and atypical squamous cells have changed little.[23]
Abnormal results are reported according to the Bethesda system.[24] They include:
- Squamous cell abnormalities (SIL)
- Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US)
- Atypical squamous cells – cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
- Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LGSIL or LSIL)
- High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL or HSIL)
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Glandular epithelial cell abnormalities
- Atypical Glandular Cells not otherwise specified (AGC or AGC-NOS)
Endocervical and endometrial abnormalities can also be detected, as can a number of infectious processes, including yeast, herpes simplex virus and trichomoniasis. However it is not very sensitive at detecting these infections, so absence of detection on a Pap does not mean absence of the infection.
Effectiveness
The Pap test, when combined with a regular program of screening and appropriate follow-up, can reduce cervical cancer deaths by up to 80%.[8]
Failure of prevention of cancer by the Pap test can occur for many reasons, including not getting regular screening, lack of appropriate follow up of abnormal results, and sampling and interpretation errors.[25] In the US, over half of all invasive cancers occur in women that have never had a Pap smear; an additional 10 to 20% of cancers occur in women that have not had a Pap smear in the preceding five years. About one-quarter of US cervical cancers were in women that had an abnormal Pap smear, but did not get appropriate follow-up (woman did not return for care, or clinician did not perform recommended tests or treatment).
Adenocarcinoma of the cervix has not been shown to be prevented by Pap tests.[25] In the UK, which has a Pap smear screening program, Adenocarcinoma accounts for about 15% of all cervical cancers[26]
Estimates of the effectiveness of the United Kingdom's call and recall system vary widely, but it may prevent about 700 deaths per year in the UK. A medical practitioner performing 200 tests each year would prevent a death once in 38 years, while seeing 152 women with abnormal results, referring 79 for investigation, obtaining 53 abnormal biopsy results, and seeing 17 persisting abnormalities lasting longer than two years. At least one woman during the 38 years would die from cervical cancer despite being screened.[27]
Since the population of the UK is about 61 million, the maximum number of women who could be receiving Pap smears in the UK is around 15 million to 20 million (eliminating the percentage of the population under 20 and over 65). This would indicate that the use of Pap smear screening in the UK saves the life of 1 person for every approximately 20,000 people tested (assuming 15,000,000 are being tested yearly). If only 10,000,000 are actually tested each year, then it would save the life of 1 person for every approximately 15,000 people tested.
Practical aspects
The endocervix may be partially sampled with the device used to obtain the ectocervical sample, but, due to the anatomy of this area, consistent and reliable sampling cannot be guaranteed. As abnormal endocervical cells may be sampled, those examining them are taught to recognize them.
The endometrium is not directly sampled with the device used to sample the ectocervix. Cells may exfoliate onto the cervix and be collected from there, so as with endocervical cells, abnormal cells can be recognised if present but the Pap Test should not be used as a screening tool for endometrial malignancy.
History
The test was invented by and named after the prominent Greek doctor Georgios Papanikolaou. Aurel Babeş of Romania independently made similar discoveries in 1927.[28] However, it should be noted that Babeş method was radically different from Papanicolaou's.
Papanicolaou's name was repeatedly submitted to the Nobel Committee and rejected every time. The Nobel Committee delegated the in-depth investigation of Papanicolaou's merits and demerits to the late Professor Santesson, who was at that time the head of pathology at the Stockholm Cancer Institute (the Radiumhemmet). The investigator discovered Babeş' contributions that had never been cited by Papanicolaou and duly reported this fact to the Committee, which then rejected Papanicolaou's Nobel award.[29]
Experimental techniques
In the developed world result of cervical biopsy guided by colposcopy is the "gold standard" for diagnosing cervical abnormalities after an abnormal pap smear. The procedure requires a trained colposcopist and can be expensive to perform. However, Pap smears are very sensitive and some negative biopsy results may represent undersampling of the lesion in the biopsy, so negative biopsy with positive cytology requires careful follow up.[30]
Experimental visualization techniques use broad-band light (e.g., direct visualization, speculoscopy, cervicography, visual inspection with acetic acid or with Lugol's, and colposcopy) and electronic detection methods (e.g., Polarprobe and in-vivo Spectroscopy). These techniques are less expensive and can be performed with significantly less training. They do not perform as well as Pap smear screening and colposcopy. At this point, these techniques have not been validated by large-scale trials and are not in general use.
See also
An anal Pap smear is an adaptation of the procedure to screen and detect anal cancers.
Gallery
-
Endocervical adenocarcinoma on a pap test.
-
Candida organisms on a pap test.
-
Viral cytopathic effect consistent with herpes simplex virus on a pap test.
-
Normal squamous epithelial cells in premenopausal women
-
Atrophic squamous cells in postmenopausal women
-
Normal endocervical cells should be present into the slide, as a proof of a good quality sampling
-
the cytoplasms of squamous epithelial cells melted out; many Döderlein bacilli can be seen
-
Infestation by Trichomonas vaginalis
-
An obviously atypical cell can be seen
References
- Notes
- ^ a b c d e Saslow, D; et al. (2012). "American Cancer Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology Screening Guidelines for the Prevention and Early Detection of Cervical Cancer" (PDF). Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease. 16 (3).
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ a b c d e f g h U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2003). "Screening for Cervical Cancer: Recommendations and Rationale. AHRQ Publication No. 03-515A". Rockville, MD.: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Retrieved June 5, 2010..
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b American Cancer Society. (2010). Detailed Guide: Cervical Cancer. Can cervical cancer be prevented? Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2009). "ACOG Education Pamphlet AP085 – The Pap Test". Washington, DC. Retrieved June 5, 2010..
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Shidham VB, Mehrotra R, Varsegi G, D'Amore KL, Hunt B, Narayan R. p16 INK4a immunocytochemistry on cell blocks as an adjunct to cervical cytology: Potential reflex testing on specially prepared cell blocks from residual liquid-based cytology specimens. CytoJournal [serial online] 2011 [cited 2011 Apr 17];8:1. Available from: http://www.cytojournal.com/text.asp?2011/8/1/1/76379
- ^ a b U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (March 2012). "Screening for Cervical Cancer: Clinical Summary of USPSTF Recommendation". uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- ^ a b American Academy of Family Physicians, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF), Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Family Physicians, retrieved August 14 2012
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b c d e f M. Arbyn; et al. (2010). "European Guidelines for Quality Assurance in Cervical Cancer Screening. Second Edition—Summary Document". Annals of Oncology. 21 (3): 448–458. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp471. PMC 2826099. PMID 20176693.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ a b Strander B (2009). "At what age should cervical screening stop?". Brit Med J. 338: 1022–23. doi:10.1136/bmj.b809.
- ^ a b Saiseni P, Adams J, Cuzick J (2003). "Benefit of cervical screening at different ages: evidence from the UK audit of screening histories". Br J Cancer. 89 (1): 88–93. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600974. PMC 2394236. PMID 12838306.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ ACOG Committee on Gynecological Practice (2009). "ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice; Routine Pelvic Examination and Cervical Cytology Screening, Opinion #413". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 113 (5): 1190–1193. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d022. PMID 19384150.
- ^ American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, retrieved August 1, 2013, which cites
- Template:Cite PMID
- Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.3322/caac.21139, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.3322/caac.21139instead. - Template:Cite PMID
- Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Sasieni, P; Castanon, A; Cuzick, J; Snow, J; (2009). "Effectiveness of Cervical Screening with Age: Population based Case-Control Study of Prospectively Recorded Data". BMJ. 339: 2968–2974. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2968.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marrazzo, JM; et al. (2001). "Papanicolaou test screening and prevalence of genital human papillomavirus among women who have sex with women". American Journal of Public Health. 91 (6): 947–952. doi:10.2105/AJPH.91.6.947. PMC 1446473. PMID 11392939.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Smith, RA; et al. (2002). "American Cancer Society Guideline for the Early Detection of Cervical Neoplasia and Cancer". 52 (1): 8–22.
ACS and others have recommended, since before 1980, that conventional cytology can be safely performed up to every three years for most women.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ "Excerpts from Changing Bodies, Changing Lives". Our Bodies Ourselves. Retrieved 2013-07-02.
- ^ Wright, Jessica L. (2010). "The Effect of Using Water-based Gel Lubricant During a Speculum Exam On Pap Smear Results". School of Physician Assistant Studies. Pacific University. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^
Martin-Hirsch P, Lilford R, Jarvis G, Kitchener HC. (1999). "Efficacy of cervical-smear collection devices: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Lancet. 354 (9192): 1763–1770. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02353-3. PMID 10577637.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Biscotti CV, Dawson AE, Dziura B; et al. (2005). "Assisted primary screening using the automated ThinPrep Imaging System". Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 123 (2): 281–7. doi:10.1309/AGB1MJ9H5N43MEGX. PMID 15842055.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C, "Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK". Health Technol Assess 2005 9(13).[1]
- ^ Davey E, d'Assuncao J, Irwig L; et al. (2007). "Accuracy of reading liquid based cytology slides using the ThinPrep Imager compared with conventional cytology: prospective study". BMJ. 335 (7609): 31. doi:10.1136/bmj.39219.645475.55. PMC 1910624. PMID 17604301.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Pap Smear". Retrieved 2008-12-27.
- ^ Eversole, GM; Moriarty, AT; Schwartz, MR; Clayton, AC; Souers, R; Fatheree, LA; Chmara, BA; Tench, WD; Henry, MR (2010). "Practices of participants in the college of american pathologists interlaboratory comparison program in cervicovaginal cytology, 2006". Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine. 134 (3): 331–5. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-134.3.331. PMID 20196659.
- ^ Nayar R, Solomon D. Second edition of 'The Bethesda System for reporting cervical cytology' – Atlas, website, and Bethesda interobserver reproducibility project. CytoJournal [serial online] 2004 [cited 2011 Apr 16];1:4. Available from: http://www.cytojournal.com/text.asp?2004/1/1/4/41272
- ^ a b DeMay, M. (2007). Practical principles of cytopathology. Revised edition. Chicago, IL: American Society for Clinical Pathology Press. ISBN 978-0-89189-549-7.
- ^ "Cancer Research UK website". Retrieved 2009-01-03.
- ^ Raffle AE, Alden B, Quinn M, Babb PJ, Brett MT (2003). "Outcomes of screening to prevent cancer: analysis of cumulative incidence of cervical abnormality and modelling of cases and deaths prevented". BMJ. 326 (7395): 901. doi:10.1136/bmj.326.7395.901. PMC 153831. PMID 12714468.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ M.J. O'Dowd, E.E. Philipp, The History of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, London, Parthenon Publishing Group, 1994, p. 547.
- ^ Koss, Leopold G. M.D., International Journal of Gynecology Pathology, http://journals.lww.com/intjgynpathology/Fulltext/2003/01000/Aurel_Babes.20.aspx#P20
- ^ Bewtra C, Pathan M, Hashish H. Abnormal Pap smears with negative follow-up biopsies: Improving cytohistologic correlations. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/dc.10329/abstract
External links
- PapScreen – Australian information about Pap tests (or Pap smears)
- Obtaining Pap Smear Video
- Jo's Trust – UK's leading cervical cancer charity.
- Imaginis – Pap Smear information
- International Agency for Research on Cancer – Resource about screening, including that of Cervical Cancer. There are digital atlases of coloscopy, histology and cytology, the rationale of screening and setting up of a screening programme.
- The Pap Test: Questions and Answers — National Cancer Institute — from the U.S.'s National Cancer Institute
- Pap Smear — from eMedicineHealth
- MedlinePlus: Cervical Cancer Prevention/Screening — from MedlinePlus
- NCI Bethesda System Web Atlas, with 349 images of different Pap smear morphologic findings — from the American Society of Cytopathology
- Canadian Guidelines for Cervical Cancer Screening – Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada
- The UK's National Association of Cytologists
- British Society for Clinical Cytology
- IBMS — The Institute of Biomedical Science on cellular pathology
- NHS Cervical Screening Programme — from the UK's National Health Service
- EngenderHealth- Cervical Cancer Screening
- Cervical screening – CancerHelp UK – UK cervical screening info from Cancer Research UK