Percy Grainger: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Brianboulton (talk | contribs) experimental identibox |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Please do not remove or adapt the infobox, which is here on a trial basis. Raise any relevant issues on the talk page --> |
|||
<!-- please do not add an infobox, per [[Wikipedia:WikiProject Classical music/Style guidelines#Biographical infoboxes]]--> |
|||
{{Infobox person |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| italic title = no |
|||
[[File:Percy Grainger Signature.svg|thumb|Percy Grainger's Signature]] |
|||
| name = {{nowrap|Percy Grainger}}<br /><small>{{nobold|{{nowrap|Australian composer}}}}</small> |
|||
| image = Percy Aldridge Grainger.jpg |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| signature = Percy Grainger Signature.svg |
|||
| module = [[List of compositions by Percy Grainger]] |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Percy Aldridge Grainger''' (8 July 1882{{spaced ndash}}20 February 1961) was an [[Australia]]n-born composer, arranger and pianist. In the course of a long and innovative career he played a prominent role in the revival of interest in British folk music in the early years of the 20th century. He also made many adaptations of other composers' works. Although much of his work was experimental and unusual, the piece with which he is most generally associated is his piano arrangement of the folk-dance tune "[[Country Gardens]]". |
'''Percy Aldridge Grainger''' (8 July 1882{{spaced ndash}}20 February 1961) was an [[Australia]]n-born composer, arranger and pianist. In the course of a long and innovative career he played a prominent role in the revival of interest in British folk music in the early years of the 20th century. He also made many adaptations of other composers' works. Although much of his work was experimental and unusual, the piece with which he is most generally associated is his piano arrangement of the folk-dance tune "[[Country Gardens]]". |
||
Revision as of 00:05, 29 October 2013
Percy Grainger Australian composer | |
|---|---|
 Percy Grainger in 1922, at the height of his popularity as pianist and composer | |
| List of compositions by Percy Grainger | |
| Signature | |
Percy Aldridge Grainger (8 July 1882 – 20 February 1961) was an Australian-born composer, arranger and pianist. In the course of a long and innovative career he played a prominent role in the revival of interest in British folk music in the early years of the 20th century. He also made many adaptations of other composers' works. Although much of his work was experimental and unusual, the piece with which he is most generally associated is his piano arrangement of the folk-dance tune "Country Gardens".
Grainger left Australia at the age of 13 to attend the Hoch Conservatory in Frankfurt. Between 1901 and 1914 he was based in London, where he established himself first as a society pianist and later as a concert performer, composer and collector of original folk melodies. As his reputation grew he met many of the significant figures in European music, forming important friendships with Frederick Delius and Edvard Grieg. He became a champion of Nordic music and culture, his enthusiasm for which he often expressed in private letters.
In 1914, Grainger moved to the United States, where he lived for the rest of his life, though he travelled widely in Europe and in Australia. He served briefly as a bandsman in the US Army during 1917–18, and took US citizenship in 1918. After his mother's suicide in 1922 he became increasingly involved in educational work. He also experimented with music machines that he hoped would supersede human interpretation. In the 1930s he set up the Grainger Museum in Melbourne, his birthplace, as a monument to his life and works and as a future research archive. As he grew older he continued to give concerts and to revise and rearrange his own compositions, while writing little new music. After the Second World War, ill health reduced his levels of activity, and he considered his career a failure. He gave his last concert in 1960, less than a year before his death.
Early life
Family background

Percy Grainger's father, John Grainger (1854–1917),[n 1] was a British-born architect who emigrated to Australia in 1877. He won professional recognition for his design of the Princes Bridge across the Yarra River in Melbourne.[2] In October 1880 he married Rose Annie Aldridge, daughter of Adelaide hotelier George Aldridge; the couple settled in New St, Brighton, a suburb of Melbourne, where their only son was born on 8 July 1882.[3] His name was registered as George Percy Grainger, but from his earliest days his family called him Percy. The Grainger house at 305 New St, Brighton has recently been redeveloped, with the original structure intact.
John Grainger was an accomplished artist, with broad cultural interests and a wide circle of friends.[4] These included David Mitchell, whose daughter Helen later gained worldwide fame as an operatic soprano under the name Nellie Melba. John's claims to have "discovered" her are unfounded, although he may have offered her encouragement.[5] John was a heavy drinker and a womaniser who, Rose learned after the marriage, had fathered a child in England before coming to Australia. His promiscuous lifestyle placed heavy strains upon the relationship, particularly when Rose discovered shortly after Percy's birth that she had contracted a form of syphilis from her husband.[3][4] Despite this, the Graingers stayed together until 1890, when John went to England for medical treatment. After his return to Australia they lived apart; the burden of raising Percy fell to Rose,[6] while John pursued his career as chief architect to the Western Australian Department of Public Works. He also designed Nellie Melba's home, Coombe Cottage, at Coldstream.[2]
Childhood

Except for three months' formal schooling as a 12-year-old, during which he was bullied and ridiculed by his classmates, Percy was educated at home.[4] Rose, an autodidact with a dominating presence, supervised his music and literature studies and engaged other tutors for languages, art and drama. From his earliest lessons Percy developed a lifelong fascination with Nordic culture; writing late in life he maintained that the Icelandic "Saga of Grettir the Strong" was "the strongest single artistic influence on my life".[7][8][9] As well as showing precocious musical talents, he displayed considerable early gifts as an artist, to the extent that his tutors thought his future might lie in art rather than music.[10] At the age of 10 he began studying piano under Louis Pabst, a German emigré then considered to be Melbourne's leading piano teacher. Grainger's first known composition, "A Birthday Gift to Mother", is dated 1893.[2] Pabst arranged Grainger's first public concert appearances, at Melbourne's Masonic Hall in July and September 1894. The boy played works by Bach, Beethoven, Schumann and Scarlatti, and was warmly complimented in the Melbourne press.[11]
After Pabst returned to Europe in the autumn of 1894, Grainger's new piano tutor, Adelaide Burkitt, arranged for his appearances at a series of concerts in October 1894, at Melbourne's Royal Exhibition Building. The size of this enormous venue horrified the young pianist; nevertheless, his performance delighted the Melbourne critics who dubbed him "the flaxen-haired phenomenon who plays like a master".[12] This public acclaim helped Rose to decide that her son should continue his studies at the Hoch Conservatory in Frankfurt am Main, Germany – she had been recommended to this institution by William Laver, head of piano studies at Melbourne's Conservatorium of music. Financial assistance was secured through a fund-raising benefit concert in Melbourne and a final recital in Adelaide, after which mother and son left Australia for Europe on 29 May 1895.[13] Although he never returned permanently to Australia, Grainger maintained considerable patriotic feelings for his native land,[14] and was proud of his Australian heritage.[2]
Frankfurt

In Frankfurt, Rose established herself as a teacher of English; her earnings were supplemented by contributions from John Grainger, who had settled in Perth. The Hoch Conservatory's reputation for piano teaching had been enhanced by the tenure, until 1892, of Clara Schumann as head of piano studies. Grainger's piano tutor was James Kwast, who developed his young pupil's skills to the extent that, within a year, Grainger was being lauded as a prodigy.[15] Grainger had difficult relations with his original composition teacher, Iwan Knorr;[4] he withdrew from Knorr's classes to study composition privately with an amateur composer and folk-music enthusiast, Karl Klimsch, whom he would later honour as "my only composition teacher".[2]
Together with a group of slightly older British students – Roger Quilter, Balfour Gardiner, Cyril Scott and Norman O'Neill, all of whom became his friends – Grainger helped form the "Frankfurt Group", whose long-term objective was to rescue British and Scandinavian music from what they considered the negative influences of central European music.[4] Encouraged by Klimsch, Grainger turned away from composing classical pastiches reminiscent of Handel, Haydn and Mozart,[16] and developed a personal compositional style the originality and maturity of which quickly impressed and astonished his friends.[14] At this time Grainger discovered the poetry of Rudyard Kipling and began setting it to music; according to Scott, "No poet and composer have been so suitably wedded since Heine & Schumann".[14]
After accompanying her son on an extended European tour in the summer of 1900 Rose, whose health had been poor for some time, suffered a nervous collapse and could no longer work.[17] To replace lost income Grainger began giving piano lessons and public performances; his first solo recital was in Frankfurt on 6 December 1900.[2] Meanwhile he continued his studies with Kwast, and increased his repertoire until he was confident he could maintain himself and his mother as a concert pianist. Having chosen London as his future base, in May 1901 Grainger abandoned his studies and, with Rose, left Frankfurt for England.[17]
Before leaving Frankfurt, Grainger had fallen in love with Kwast's daughter Mimi;[17] in an autobiographical essay dated 1947 he admits to being "already sex-crazy" at this time.[18] (Mimi Kwast, who was the grand-daughter of Ferdinand Hiller, married another of her father's pupils, Hans Pfitzner.) John Bird, Grainger's biographer, also records that during his Frankfurt years Grainger began to develop sexual appetites that were "distinctly abnormal"; by the age of 16 he had started to experiment in flagellation and other sado-masochistic practices, which he continued to pursue through most of his adult life. Bird surmises that Grainger's fascination with themes of punishment and pain derived from the harsh discipline to which Rose had subjected him as a child.[18]
London years
Concert pianist
In London, Grainger's charm, good looks and talent (with some assistance from the local Australian community) ensured that he was quickly taken up as a pianist by wealthy patrons, and was soon performing in concerts in private homes. The Times critic recorded after one such appearance that Grainger's playing "revealed rare intelligence and a good deal of artistic insight".[19] In 1902 he was presented by the socialite Lillith Lowrey to Queen Alexandra, who thereafter frequently attended his London recitals.[20] Lowrey, 20 years Grainger's senior, traded patronage and contacts for sexual favours – he termed the relationship a "love-serve job".[8] She was the first woman with whom he had sex; he later wrote of this initial encounter that he had experienced "an overpowering landslide" of feeling, and that "I thought I was about to die. If I remember correctly, I only experienced fear of death. I don't think that any joy entered into it".[21]
In February 1902 Grainger made his first appearance as a piano soloist with an orchestra, playing Tchaikovsky's first piano concerto with the Bath Pump Room Orchestra. In October of that year he toured Britain in a concert party with Adelina Patti, the Italian-born opera singer. Patti was greatly taken by the young pianist and prophesied a glorious career for him.[22] The following year he met the German-Italian composer and pianist Ferruccio Busoni. Initially the two men were on cordial terms (Busoni offered to give Grainger lessons free of charge) and as a result, Grainger spent part of the 1903 summer in Berlin as Busoni's pupil.[2] However, the visit was not a success; as Bird notes, Busoni had expected "a willing slave and adoring disciple", a role Grainger was not willing to fulfil.[23] Grainger returned to London in July 1903; almost immediately he departed with Rose on a 10-month tour of Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, as a member of a party organised by the Australian contralto Ada Crossley.[24]
Emergent composer

Before going to London Grainger had composed numerous Kipling settings, and his first mature orchestral pieces.[25] In London, when he found time he continued to compose; a letter to Balfour Gardiner dated 21 July 1901 indicates that he was working on his Marching Song of Democracy (a Walt Whitman setting), and had made good progress with the experimental works Train Music and Charging Irishrey.[26] In his early London years he also composed Hill Song Number 1 (1902), an instrumental piece much admired by Busoni.[25][27]
In 1905, inspired by a lecture given by the pioneer folksong historian Lucy Broadwood, Grainger began to collect original folksongs. Starting at Brigg in Lincolnshire, over the next five years he gathered and transcribed more than 300 songs from all over the country, including much material that had never been written down before. From 1906 Grainger used a phonograph, one of the first collectors to do so, and by this means he assembled more than 200 Edison cylinder recordings of native folk singers.[28][29] These activities coincided with what Bird calls "the halcyon days of the 'First English Folksong Revival'".[30]
As his stature in the music world increased, Grainger became acquainted with many of its leading figures, including Vaughan Williams, Elgar, Richard Strauss and Debussy.[28] In 1907 he met Frederick Delius, with whom he achieved an immediate rapport – the two musicians had similar ideas about composition and harmony, and shared a dislike for the classical German masters.[31] Both were inspired by folk music;[32] Grainger gave Delius his setting of the folksong Brigg Fair, which the older composer developed into his famous orchestral rhapsody, dedicated to Grainger.[31] The two remained close friends until Delius's death in 1934.[33]
Grainger first met Grieg at the home of the London financier Sir Edgar Speyer, in May 1906.[34] As a student Grainger had learned to appreciate the Norwegian's harmonic originality, and by 1906 had several Grieg pieces in his concert repertoire, including the piano concerto.[35] Grieg was greatly impressed with Grainger's playing, and wrote that the Australian was "a genius that we Scandinavians cannot do other than love."[36] Through 1906–7 the two maintained a mutually complimentary correspondence, which culminated in Grainger's ten-day visit in July 1907 to the composer's Norwegian home, "Troldhaugen" near Bergen. Here the two spent much time revising and rehearsing the piano concerto in preparation for that year's Leeds Festival. Their plans for a long-term working relationship were thwarted by Grieg's sudden death in September 1907; nevertheless, this relatively brief acquaintance had a considerable impact on Grainger, and he championed Grieg's music for the rest of his life.[35]

After fulfilling a hectic schedule of concert engagements in Britain and continental Europe, in August 1908 Grainger accompanied Ada Crossley on a second Australasian tour, during which he added several cylinders of Maori and Polynesian music to his collection of recordings.[28] He had resolved to establish himself as a top-ranking pianist before promoting himself as a composer,[9] though he continued to compose both original works and folksong settings. Some of his most successful and most characteristic pieces, such as "Mock Morris", "Handel in the Strand", "Shepherd's Hey" and "Molly on the Shore" date from this period. In 1908 he obtained the tune of "Country Gardens" from the folk music specialist Cecil Sharp, though he did not fashion it into a performable piece for another ten years.[37][38]
In 1911 Grainger finally felt confident enough of his standing as a pianist to begin large-scale publishing of his compositions. At the same time, he adopted the professional name of Percy Aldridge Grainger for his published compositions and concert appearances.[8][39]
In a series of concerts arranged by Balfour Gardiner at London's Queen's Hall in March 1912, five of Grainger's works were performed to great public acclaim; the band of thirty guitars and mandolins for the performance of "Fathers and Daughters" created a particular impression.[40] On 21 May 1912 Grainger presented the first concert devoted entirely to his own compositions, at the Aeolian Hall, London;[9] the concert was, he reported, "a sensational success".[41] A similarly enthusiastic reception was given to Grainger's music at a second series of Gardiner concerts the following year.[42]
In 1905 Grainger began a close friendship with Karen Holten, a Danish music student who had been recommended to him as a piano pupil. She became an important confidante; the relationship persisted for eight years, largely through correspondence.[43][n 2] After her marriage in 1916 she and Grainger continued to correspond and occasionally meet until her death in 1953. Grainger was briefly engaged in 1913 to another pupil, Margot Harrison, but the relationship foundered through a mixture of Rose's over-possessiveness and Grainger's indecision.[45][46]
Career maturity
Departure for America

In April 1914 Grainger gave his first performance of Delius's piano concerto, at a music festival in Torquay. Thomas Beecham, who was one of the festival's guest conductors, reported to Delius that "Percy was good in the forte passages, but made far too much noise in the quieter bits".[47] Grainger was receiving increasing recognition as a composer; leading musicians and orchestras were adding his works to their repertoires.[45] His decision to leave England for America in early September 1914, after the outbreak of the First World War, damaged his reputation among his patriotically minded British friends.[2] Grainger wrote that the reason for this abrupt departure was "to give mother a change".[48] However, according to Bird, Grainger often explained that his reason for leaving London was that "he wanted to emerge as Australia's first composer of worth, and to have laid himself open to the possibility of being killed would have rendered his goal unattainable".[49] The Daily Telegraph music critic Robin Legge accused him of cowardice, and told him not to expect a welcome in England after the war,[8] words that hurt Grainger deeply.[50]
Grainger's first American tour began on 11 February 1915 with a recital at New York's Aeolian Hall. He played works by Bach, Brahms, Handel and Chopin alongside two of his own compositions: "Colonial Song" and "Mock Morris". In July 1915 Grainger formally registered his intention to apply for US citizenship.[51] Over the next two years his engagements included concerts with Nellie Melba in Boston and Pittsburgh and a command performance before President Woodrow Wilson. In addition to his concert performances, Grainger secured a contract with the Duo-Art Company for making pianola rolls, and signed a recording contract with Columbia.[9]
In April 1917 Grainger received news of his father's death in Perth.[52] On 9 June 1917, after America's entry into the war, he enlisted as a bandsman in the Coast Artillery Corps of the US Army. He had joined as a saxophonist,[n 3] though he records learning the oboe: "I long for the time when I can blow my oboe well enough to play in the band".[55] In his 18 months' service, Grainger made frequent appearances as a pianist at Red Cross and Liberty bond concerts. As a regular encore he began to play a piano setting of the tune "Country Gardens". The piece became instantly popular; sheet music sales quickly broke many publishing records.[56] The work was to become synonymous with Grainger's name through the rest of his life, though he came in time to detest it.[57] On 3 June 1918 he became a naturalised American citizen.[58]
Career zenith

After leaving the army in January 1919, Grainger refused an offer to become conductor of the Saint Louis Symphony Orchestra and resumed his career as a concert pianist.[59] He was soon performing around 120 concerts a year,[60] generally to great critical acclaim, and in April 1921 reached a wider audience by performing in a cinema, New York's Capitol Theatre. Grainger commented that the huge audiences at these cinema concerts often showed greater appreciation for his playing than those at established concert venues such as Carnegie Hall and the Aeolian.[61] In the summer of 1919 he led a course in piano technique at Chicago Musical College, the first of many such educational duties he would undertake in later years.[62][63]
Amid his concert and teaching duties, Grainger found time to rescore many of his works (a habit he continued throughout his life) and also to compose new pieces: his Children's March: Over the Hills and Far Away, and the orchestral version of The Power of Rome and the Christian Heart both originated in this period.[64] His close friend Ralph Leopold, whom he met while in the army, participated in the premieres of both versions of the Children's March, and also recorded a number of four-hand works with him on piano rolls. He also began to develop the technique of elastic scoring, a form of flexible orchestration which enabled works to be performed by different numbers of players and instrument types, from small chamber groups up to full orchestral strength.[65]
In April 1921 Grainger moved with his mother to a large house in White Plains, New York. This was his home for the remainder of his life.[8] From the beginning of 1922 Rose's health deteriorated sharply; she was suffering from delusions and nightmares, and became fearful that her illness would harm her son's career.[66] Because of the closeness of the bond between the two, there had long been rumours that their relationship was incestuous;[57] in April 1922 Rose was directly challenged over this issue by her friend Lotta Hough.[67] From her last letter to Grainger, dated 29 April, it seems that this confrontation unbalanced Rose; on 30 April, while Grainger was touring on the West Coast, she jumped to her death from an office window on the 18th floor of the Aeolian Building in New York City.[68] The letter, which began "I am out of my mind and cannot think properly", asked Grainger if he had ever spoken to Lotta of "improper love". She signed the letter: "Your poor insane mother".[69]
Inter-war years
Traveller
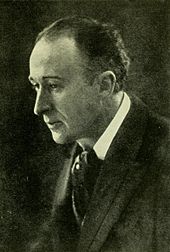
After Rose's funeral, Grainger sought solace in a return to work. In autumn 1922 he left for a year-long trip to Europe, where he collected and recorded Danish folksongs before a concert tour that took him to Norway, Holland, Germany and England. In Norway he stayed with Delius at the latter's summer home. Delius was by now almost blind; Grainger helped fulfil his friend's wish to see a Norwegian sunset by carrying him (with some assistance) to the top of a nearby mountain peak.[70] He returned to White Plains in August 1923.[71]
Although now less committed to a year-round schedule of concerts, Grainger remained a very popular performer. His eccentricities, often exaggerated for publicity reasons, reportedly included running into auditoriums in gym kit and leaping over the grand piano to create a grand entrance.[72] While he continued to revise and rescore his compositions, he increasingly worked on arrangements of music by other composers,[73] in particular works by Bach, Brahms, Fauré and Delius.[74] Away from music, Grainger's preoccupation with Nordic culture led him to develop a form of English which, he maintained, reflected the character of the language before the Norman conquest. Words of Norman or Latin origin were replaced by supposedly Nordic word-forms, such as "blend-band" (orchestra), "forthspeaker" (lecturer) and "writ-piece" (article). He called this "blue-eyed" English.[75] His convictions of Nordic superiority eventually led Grainger, in letters to friends, to express his views in crudely racial and anti-Semitic terms; the music historian David Pear describes Grainger as, "at root, a racial bigot of no small order".[76][n 4]
Grainger made further trips to Europe in 1925 and 1927, collecting more Danish folk music with the aid of the octogenarian ethnologist Evald Tang Kristensen; this work formed the basis of the Suite on Danish Folksongs of 1928–30.[9] He also visited Australia and New Zealand, in 1924 and again in 1926. In November 1926, while returning to America, he met Ella Ström, a Swedish-born artist with whom he developed a close friendship. On arrival in America the pair separated, but were reunited in England the following autumn after Grainger's final folksong expedition to Denmark. In October 1927 the couple agreed to marry.[80] Ella had a daughter, Elsie, who had been born out of wedlock in 1909. Grainger always acknowledged her as a family member, and developed a warm personal relationship with her.[81]
Although Bird asserts that before her marriage, Ella knew nothing of Grainger's sado-masochistic interests,[82] in a letter dated 23 April 1928 (four months before the wedding) Grainger writes to her: "As far as my taste goes, blows [with the whip] are most thrilling on breasts, bottom, inner thighs, sexparts". He later adds, "I shall thoroly thoroly [sic] understand if you cannot in any way see yr way to follow up this hot wish of mine".[83] The couple were married on 9 August 1928 at the Hollywood Bowl, at the end of a concert which, in honour of the bride, had included the first performance of Grainger's bridal song "To a Nordic Princess".[9]
Educator
From the late 1920s and early 1930s Grainger became involved increasingly with educational work in schools and colleges,[9] and in late 1931 accepted a year's appointment for 1932–33 as professor of music at New York University (NYU). In this role he delivered a series of lectures under the heading "A General Study of the Manifold Nature of Music", which introduced his students to a wide range of ancient and modern works.[9] On 25 October 1932 his lecture was illustrated by Duke Ellington and his band, who appeared in person; Grainger admired Ellington's music, seeing harmonic similarities with Delius. On the whole, however, Grainger did not enjoy his tenure at NYU; he disliked the institutional formality, and found the university generally unreceptive to his ideas. Despite many offers he never accepted another formal academic appointment, and refused all offers of honorary degrees.[84][n 5] His New York lectures became the basis for a series of radio talks which he gave for the Australian Broadcasting Commission in 1934–35; these were later summarised and published as Music: A Commonsense View of All Types.[2] On 3 and 4 September 1934 Grainger adjudicated at the Sydney Eisteddfod on Sections 10 (Vocal Ensemble) and 45 (String Ensemble) for which he selected and provided the music. In 1937 Grainger began an association with the Interlochen International Music Camp, and taught regularly at its summer schools until 1944.[86]
Innovator

The idea of establishing a Grainger Museum in Australia had first occurred to Grainger in 1932. He began collecting and recovering from friends letters and artifacts, even those demonstrating the most private aspects of his life,[87] such as whips, bloodstained shirts and revealing photographs.[88] In September 1933 he and Ella went to Australia to begin supervising the building work. To finance the project, Grainger embarked on a series of concerts and broadcasts,[89] in which he subjected his audiences to a vast range of the world's music in accordance with his "universalist" view. Controversially, he argued for the superior achievements of Nordic composers over traditionally recognised masters such as Mozart and Beethoven.[2]
Among various new ideas, Grainger introduced his so-called "free-music" theories. He believed that conformity with the traditional rules of set scales, rhythms and harmonic procedures amounted to "absurd goose-stepping", from which music should be set free.[90] He demonstrated two experimental compositions of free music, performed initially by a string quartet and later by the use of electronic theremins.[8] He believed that ideally, free music required non-human performance, and spent much of his later life developing machines to fulfil this vision.[91]
While the building of the museum proceeded, the Graingers visited England for several months in 1936, during which Grainger made his first BBC broadcast. In this, he conducted "Love Verses from The Song of Solomon" in which the tenor soloist was the then unknown Peter Pears.[92] After spending 1937 in America, Grainger returned to Melbourne in 1938 for the official opening of the Museum; among those present at the ceremony was his old piano teacher Adelaide Burkitt. The museum did not open to the general public during Grainger's lifetime, but was available to scholars for research.[93][94]
In the late 1930s Grainger spent much time arranging his works in settings for wind bands. He wrote A Lincolnshire Posy for the March 1937 convention of the American Band Masters' Association in Milwaukee,[95] and in 1939, on his last visit to England before the Second World War, he composed "The Duke of Marlborough's Fanfare", giving it the subtitle "British War Mood Grows".[93]
Later career
Second World War
The outbreak of war in Europe in September 1939 curtailed Grainger's overseas travelling. In the autumn of 1940, alarmed that the war might precipitate an invasion of the United States eastern seaboard, he and Ella moved to Springfield, Missouri, in the centre of the continent.[96] From 1940 Grainger played regularly in charity concerts, especially after the attack on Pearl Harbor brought the United States into the war in December 1941; the historian Robert Simon calculates that Grainger made a total of 274 charity appearances during the war years, many of them at Army and Air force camps.[94] In 1942 a collection of his Kipling settings, the Jungle Book cycle, was performed in eight cities by the choir of the Gustavus Adolphus College from St. Peter, Minnesota.[97]
Postwar decline
Exhausted from his wartime concerts routine, Grainger spent much of 1946 on holiday in Europe. He was experiencing a sense of career failure; in 1947, when refusing the Chair of Music at Adelaide University, he wrote: "If I were 40 years younger, and not so crushed by defeat in every branch of music I have essayed, I am sure I would have welcomed such a chance".[98] In January 1948 he conducted the premiere of his wind band setting of "The Power of Rome and the Christian Heart", written for the Goldman Band to celebrate the 70th birthday of its founder. Afterwards, Grainger denigrated his own music as "commonplace" while praising Darius Milhaud's Suite Française, with which it had shared the programme.[99]

On 10 August 1948, Grainger appeared at the London Proms, playing the piano part in his Suite on Danish Folksongs with the London Symphony Orchestra under Basil Cameron. On 18 September he attended the Last Night of the Proms, standing in the promenade section for Delius's Brigg Fair.[100] Over the next few years several friends died: Gardiner in 1950, Quilter and Karen Holten in 1953. In October 1953 Grainger was operated on for abdominal cancer; his fight against this disease would last for the rest of his life.[101] He continued to appear at concerts, often in church halls and educational establishments rather than major concert venues.[9] In 1954, after his last Carnegie Hall appearance, Grainger's long promotion of Grieg's music was recognised when he was awarded the St. Olav Medal by King Haakon of Norway.[102] However, a growing bitterness was becoming evident in his writings and correspondence; in a letter to his lifelong friend, the Danish composer Herman Sandby, he bemoaned the continuing ascendency in music of the "German form", and asserted that "all my compositional life I have been a leader without followers".[102]
After 1950 Grainger virtually ceased to compose. His principal creative activity in the last decade of his life was his work with Burnett Cross, a young physics teacher, on free music machines. The first of these was a relatively simple device controlled by an adapted pianola.[103] Next was the "Estey-reed tone-tool", a form of giant harmonica which, Grainger expectantly informed his stepdaughter Elsie in April 1951, would be ready to play free music "in a few weeks".[104] A third machine, the "Cross-Grainger Kangaroo-pouch", was completed by 1952. Developments in transistor technology encouraged Grainger and Cross to begin work on a fourth, entirely electronic machine, which was incomplete when Grainger died.[8][103]
In September 1955 Grainger made his final visit to Australia, where he spent nine months organising and arranging exhibits for the Grainger Museum. He refused to consider a "Grainger Festival", as suggested by the Australian Broadcasting Commission, because he felt that his homeland had rejected him and his music. Before leaving Melbourne, he deposited in a bank a parcel that contained an essay and photographs related to his sex life, not to be opened until 10 years after his death.[105]
Last years

By 1957 Grainger's physical health had markedly declined, as had his powers of concentration.[106] Nevertheless, he continued to visit Britain regularly; in May of that year he made his only television appearance, in a BBC "Concert Hour" programme when he played "Handel in the Strand" on the piano. Back home, after further surgery he recovered sufficiently to undertake a modest winter concerts season.[107] On his 1958 visit to England he met Benjamin Britten, the two having previously maintained a mutually complimentary correspondence.[108] He agreed to visit Britten's Aldeburgh Festival in 1959, but was prevented by illness. Sensing that death was drawing near, he made a new will, bequeathing his skeleton "for preservation and possible display in the Grainger Museum". This wish was not carried out.[109]
Through the winter of 1959–60 Grainger continued to perform his own music, often covering long distances by bus or train; he would not travel by air. On 29 April 1960 he gave his last public concert, at Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire, although by now his illness was affecting his concentration. On this occasion his morning recital went well, but his conducting in the afternoon was, in his own words, "a fiasco".[110][111] Subsequently confined to his home, he continued to revise his music and arrange that of others; in August he informed Elsie that he was working on an adaptation of one of Cyril Scott's early songs.[112] His last letters, written from hospital in December 1960 and January 1961, record attempts to work, despite failing eyesight and hallucinations: "I have been trying to write score for several days. But I have not succeeded yet."[113]
Grainger died in the White Plains hospital on 20 February 1961, at the age of 78. His body was flown to Adelaide where, on 2 March, he was buried in the Aldridge family vault in the West Terrace Cemetery, alongside Rose's ashes.[8] Ella survived him by 18 years; in 1972, aged 83, she married a young archivist, Stewart Manville. She died at White Plains on 17 July 1979.[2][114]
Music
Grainger's own works fall into two categories: original compositions and folk music arrangements. Besides these, he wrote many settings of other composers' works.[8][9] Despite his conservatory training he rebelled against the disciplines of the central European tradition, largely rejecting conventional forms such as symphony, sonata, concerto and opera. With few exceptions his original compositions are miniatures, lasting between two and eight minutes. Only a few of his works originated as piano pieces, though in due course almost all of them were, in his phrase, "dished up" in piano versions.[9]
The conductor John Eliot Gardiner describes Grainger as "a true original in terms of orchestration and imaginative instrumentation", whose terseness of expression is reminiscent in style both of the 20th century Second Viennese School and the Italian madrigalists of the 16th and 17th centuries.[115] Malcolm Gillies, a Grainger scholar, writes of Grainger's style that "you know it is 'Grainger' when you have heard about one second of a piece".[116] The music's most individual characteristic, Gillies argues, is its texture – "the weft of the fabric", according to Grainger.[117] Different textures are defined by Grainger as "smooth", "grained" and "prickly".[9]
Grainger was a musical democrat; he believed that in a performance each player's role should be of equal importance. His elastic scoring technique was developed to enable groups of all sizes and combinations of instruments to give effective performances of his music. Experimentation is evident in Grainger's earliest works; irregular rhythms based on rapid changes of time signature were employed in Love Verses from "The Song of Solomon" (1899), and Train Music (1901), long before Stravinsky adopted this practice.[4] In search of specific sounds Grainger employed unconventional instruments and techniques: solovoxes, theremins, marimbas, musical glasses, harmoniums, banjos, and ukuleles.[109][118] In one early concert of folk music, Quilter and Scott were conscripted as performers, to whistle various parts.[119] In "Random Round" (1912–14), inspired by the communal music-making he had heard in the Pacific Islands on his second Australasian tour, Grainger introduced an element of chance into performances; individual vocalists and instrumentalists could make random choices from a menu of variations.[9] This experiment in "aleatory" composition presaged by many decades the use of similar procedures by avant-garde composers such as Berio and Stockhausen.[120]
The brief "Sea Song" of 1907 was an early attempt by Grainger to write "beatless" music. This work, initially set over 14 irregular bars and occupying about 15 seconds of performing time,[121] was a forerunner of Grainger's free music experiments of the 1930s. Grainger wrote: "It seems to me absurd to live in an age of flying, and yet not be able to execute tonal glides and curves". The idea of tonal freedom, he said, had been in his head since as a boy of eleven or twelve he had observed the wave-movements in the sea. "Out in nature we hear all kinds of lovely and touching "free" (non-harmonic) combinations of tones; yet we are unable to take up these beauties ... into the art of music because of our archaic notions of harmony".[90] In a 1941 letter to Scott, Grainger acknowledged that he had failed to produce any large-scale works in the manner of a Bach oratorio, a Wagner opera or a Brahms symphony, but excused this failure on the grounds that all his works prior to the mid-1930s had been mere preparations for his free music.[122]
As a student, Grainger had learned to appreciate the music of Grieg, and came to regard the Norwegian as a paragon of Nordic beauty and greatness. Grieg in turn described Grainger as a new way forward for English composition, "quite different from Elgar, very original". After a lifetime interpreting Grieg's works, in 1944 Grainger began adapting the Norwegian's E minor Piano Sonata, Op. 7 as a "Grieg-Grainger Symphony", but abandoned the project after writing 16 bars of music. By this time, Grainger acknowledged that he had not fulfilled Grieg's high expectations of him, either as a composer or as a pianist. He also reflected on whether it would have been better, from the point of view of his development as a composer, had he never met the Griegs, "sweet and dear though they were to me".[123]
Grainger was known for his musical experimentation and did not hesitate to exploit the capabilities of the orchestra. Train Music was intended for 150 players and Country Gardens has some lush harmonic invention. Perhaps his most ambitious work was The Warriors, an 18 minute 'imaginary ballet' of frenzied 'danceable music', entrusted to a huge orchestral ensemble incorporating a large 'tuneful percussion' mixture alongside at least three pianos – in one performance, Grainger used nineteen pianos with thirty pianists – to be played by "exceptionally strong vigorous players".[124]
Legacy
Grainger considered himself an Australian composer who, he said, wrote music "in the hopes of bringing honor and fame to my native land".[125] However, much of Grainger's working life was spent elsewhere, and the extent to which he influenced Australian music, within his lifetime and thereafter, is debatable.[126] His efforts to educate the Australian musical public in the mid-1930s were indifferently received, and did not attract disciples;[127] writing in 2010, the academic and critic Roger Covell identifies only one significant contemporary Australian musician – the English-born horn player, pianist and conductor David Stanhope – working in the Grainger idiom.[126] In 1956, the suggestion by the composer Keith Humble that Grainger be invited to write music for the opening of the 1956 Summer Olympics in Melbourne had been rejected by the organisers of the Games.[105]
Grainger was a life-long atheist and believed he would only endure in the body of work he left behind.[128] He took an unusual course of action to ensure that survival by establishing a personal museum dedicated to his own life. The Grainger Museum was given little attention before the mid-1970s;[9] it was initially regarded as evidence either of an over-large ego or of extreme eccentricity.[129] Since then the University of Melbourne's commitment to the museum has, Covell asserts, "rescued [it] permanently from academic denigration and belittlement".[129] Its vast quantities of materials have been used to investigate not only Grainger's life and works, but those of contemporaries whom Grainger had known: Grieg, Delius, Scott and others.[130] The Grainger home at 7 Cromwell Place, White Plains, is now the Percy Grainger Library and is a further repository of memorabilia and historic performance material, open to researchers and visitors.[9][131]
In Britain, Grainger's main legacy is the revival of interest in folk music. His pioneering work in the recording and setting of folksongs greatly influenced the following generation of English composers; Benjamin Britten acknowledged the Australian as his master in this respect.[132] After hearing a broadcast of some Grainger settings, Britten reportedly declared that these "[knocked] all the Vaughan Williams and R. O. Morris arrangements into a cocked hat".[133] In the United States, Grainger left a strong educational legacy through his involvement, over 40 years, with high school, summer school and college students. Likewise, his innovative approaches to instrumentation and scoring have left their mark on modern American band music;[9] Timothy Reynish, a conductor and teacher of band music in Europe and America, has described him as "the only composer of stature to consider military bands the equal, if not the superior, in expressive potential to symphony orchestras."[134] Grainger's attempts to produce "free music" by mechanical and later electronic means, which he considered his most important work, produced no follow-up; they were quickly overtaken and nullified by new technological advances. Covell nevertheless remarks that in this endeavour, Grainger's dogged resourcefulness and ingenious use of available materials demonstrate a particularly Australian aspect of the composer's character – one of which Grainger would have been proud.[135]
Assessment

In 1945 Grainger devised an informal ratings system for composers and musical styles, based on criteria that included originality, complexity and beauty. Of forty composers and styles, he ranked himself equal ninth – behind Wagner and Delius, but well ahead of Grieg and Tchaikovsky.[123] Nevertheless, in his later years he frequently denigrated his career, for example writing to Scott: "I have never been a true musician or true artist".[136] His failure to be recognised as a composer for anything beyond his popular folk-song arrangements was a source of frustration and disappointment;[137] for years after his death the bulk of his output remained largely unperformed.[138] From the 1990s an increase in the number of Grainger recordings has brought a revival of interest in his works, and has enhanced his reputation as a composer.[2] An unsigned tribute published on the Gramophone website in February 2011 to commemorate the 50th anniversary of Grainger's death opined that "though he would never be put on a pedestal to join the pantheon of immortals, he is unorthodox, original and deserves better than to be dismissed by the more snooty arbiters of musical taste".[109]
Of Grainger the pianist, The New York Times critic Harold Schonberg wrote that his unique style was expressed with "amazing skill, personality and vigor".[139] The early enthusiasm which had greeted his concert appearances became muted in later years, and reviews of his performances during the final ten years of his life were often harsh.[140] However, Britten regarded Grainger's late recording of the Grieg concerto, from a live performance at Aarhus in 1957, as "one of the noblest ever committed to record" – despite the suppression of the disc for many years, because of the proliferation of wrong notes and other faults.[141] Brian Allison from the Grainger Museum, referring to Grainger's early displays of artistic skills, has speculated that had John Grainger's influence not been removed, "Percy Aldridge Grainger may today be remembered as one of Australia's leading painters and designers, who just happened to have a latent talent as a pianist and composer".[142] The ethnomusicologist John Blacking, while acknowledging Grainger's contribution to social and cultural aspects of music, nevertheless writes that if the continental foundation of Grainger's musical education had not been "undermined by dilettantism and the disastrous influence of his mother, I am sure that his ultimate contribution to the world of music would have been much greater".[143]
Recordings
Between 1908 and 1957 Grainger made numerous recordings, usually as pianist or conductor, of his own and other composers' music. His first recordings, for The Gramophone Company Ltd (later HMV), included the cadenza to Grieg's piano concerto; he did not record a complete version of this work on disc until 1945. Much of his recording work was done between 1917 and 1931, under contract with Columbia. At other times he recorded for Decca (1944–45 and 1957), and Vanguard (1957). Of his own compositions and arrangements, "Country Gardens", "Shepherd's Hey" and "Molly on the Shore" were recorded most frequently; in recordings of other composers, piano works by Bach, Brahms, Chopin, Grieg, Liszt and Schumann figure most often.[144] Grainger's complete 78 rpm solo piano recordings are now available on compact disc as a CD box set on APR records in transfers made by Ward Marston.[145] During his association with the Duo-Art company between 1915 and 1932, Grainger made around 80 piano rolls of his own and others' music, many of which have subsequently been transferred to CD, using a wooden robot designed to play a concert grand piano via an array of precision mechanical fingers and feet.[146][147][148] This reproduction system allowed Grainger to make a posthumous appearance in the Albert Hall, London, during the 1988 last night of the Proms as soloist with the BBC Symphony Orchestra in Grieg's Piano Concerto.[149]
Since Grainger's death, recordings of his works have been undertaken by many artists and issued under many different labels. In 1995 Chandos Records began to compile a complete recorded edition of Grainger's original compositions and folk settings.[150] Of 25 anticipated volumes, 19 had been completed as of 2010;[151] these were issued as a CD boxed set in 2011, to mark the 50th anniversary of the composer's death.[152]
Notes and references
Notes
- ^ Although most sources give 1855 as the birth year, the Grainger Museum states that 1854 is the correct year.[1]
- ^ The correspondence was conducted largely in Danish, at which Grainger was fluent. His first letter to Holten, dated 12 August 1905, begins "Dear Miss Holten"; by the end of the year she is "My dear Karen". During their long separations Grainger's letters become a diary of his activities.[44]
- ^ There is no evidence up to this time that Grainger could play the saxophone,[53] but in an official listing of the band's personnel as of April 1918 he is listed as a saxophone soloist.[54]
- ^ Some of Grainger's earliest published letters contain anti-Semitic comments, for example to Karen Holten in 1905.[77] He later asserted that the Jewish race was less capable of producing good music than the Nordic races,[78] and his letter to Quilter of 25 February 1939 is cited by Gillies and Pear as an example of his racial intolerance.[76][79]
- ^ In April 1945 Grainger declined an honorary doctorate from McGill University in Montreal, on the grounds that having had only three months' formal schooling, his music "must be regarded as a product of non-education".[85]
References
- ^ "John Grainger: A Brief Biographical Background". Grainger Museum (University of Melbourne). Retrieved 20 April 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Dreyfus, Kay (2006). "Grainger, George Percy (1882–1961)". Australian Dictionary of Biography online. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b Bird, pp. 2–6
- ^ a b c d e f Simon, pp. 2–3
- ^ Bird, p. 9
- ^ Bird, pp. 14–15
- ^ Bird, p. 11
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Gillies, Malcolm (2004). "Grainger, Percy Aldridge". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography online. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) (subscription required) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Gillies, Malcolm; Pear, David (2007). "Grainger, (George) Percy (Aldridge)". Oxford Music Online. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) (subscription required) - ^ Bird, p. 13
- ^ Bird, pp. 20–22
- ^ Bird, p. 23
- ^ Bird, pp. 24–25
- ^ a b c Scott, pp. 51–54
- ^ Bird, pp. 26–29
- ^ Bird, p. 35
- ^ a b c Bird, pp. 39–41
- ^ a b Bird, pp. 42–43
- ^ Bird, pp. 63–65
- ^ Bird, pp. 66 and 73
- ^ Pear ("Grainger: The Formative Years"), p. 6
- ^ Bird, p. 69
- ^ Bird, p. 81
- ^ Bird, pp. 83–88
- ^ a b Thwaites (ed.) p. xx
- ^ Dreyfus (ed.), p. 2
- ^ Bird, p. 79
- ^ a b c Simon, pp. 5–6
- ^ Tall, pp. 55–56
- ^ Bird, p. 102
- ^ a b Carley, pp. 33–34
- ^ Palmer, pp. 79–82
- ^ Carley, pp. 49–50
- ^ Bird, p. 116
- ^ a b Gillies, Malcolm (Autumn 2007). "Great Expectations: Grieg and Granger". The Musical Times. 148 (1900): pp. 7–9.
{{cite journal}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)(subscription required) - ^ Bird, p. 117
- ^ Tall, p. 63
- ^ Ould, p. 26
- ^ Thwaites (ed.), p. xxi
- ^ Bird, p. 144
- ^ Dreyfus, pp. 454, 458
- ^ Bird, p. 147
- ^ Dreyfus, p. xiv
- ^ Dreyfus, pp. 47, 54, 55 and others
- ^ a b Bird, pp. 148–49
- ^ Dreyfus, p. 492
- ^ Bird, pp. 150–51
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 13
- ^ Bird, p. 152
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 35–39
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 36
- ^ Bird, p. 158
- ^ Bird, p. 159
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 132–33
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 39–40
- ^ Foreman ("Miscellaneous Works"), pp. 137–38
- ^ a b Simon, p. 7
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. xv
- ^ Bird, p. 162
- ^ Tan, p. 15
- ^ Bird, pp. 167–68
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. xv
- ^ Bird, p. 166
- ^ Bird, pp. 163–64
- ^ Fairfax, pp. 75–77
- ^ Bird, p. 170
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 52
- ^ Bird, pp. 173–74
- ^ Bird, p. 175
- ^ Fenby, pp. 74–75
- ^ Bird, p. 183
- ^ Simon, p. 9
- ^ Ould, p. 25
- ^ Bird, pp. 279–81
- ^ Bird, p. 53. See also Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 107
- ^ a b Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 4–6
- ^ Dreyfus (ed.), p. 54
- ^ Pear ("Grainger the Social Commentator"), p. 36
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 156–63
- ^ Bird, pp. 194–96
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. xix
- ^ Bird. pp. 200–01
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 94–100
- ^ Bird, pp. 204–05
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 197–98
- ^ Bird, p. 213
- ^ Bird, p. 203
- ^ Piggott, p. 42
- ^ Bird, pp. 206–07
- ^ a b Statement by Percy Grainger entitled "Free Music", dated 6 December 1938, in Thwaites (ed.), pp. 207–08
- ^ Simon, p.12
- ^ Bird, p. 210
- ^ a b Bird, pp. 214–15
- ^ a b Simon, p. 11
- ^ Bird, p. 212
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 170
- ^ Bird, pp. 217–18
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 214–219
- ^ Bird, pp. 224–25
- ^ Bird, p. 226
- ^ Bird, pp. 238 and 242
- ^ a b Bird, pp. 241–42
- ^ a b Davies, Hugh (2007). "Cross-Grainger free music machine". Oxford Music Online. Retrieved 2 May 2011.(subscription required)
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 248
- ^ a b Bird, pp. 243–45
- ^ Gillies and Pear, p. xvii
- ^ Bird, pp. 247–48
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), pp. 266–67
- ^ a b c "Percy Grainger (1882–1961) – the composer, 50 years on". Gramophone. 3 February 2011.
- ^ Bird, p. 249
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 283
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 285
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 287
- ^ Thwaites (ed.), p. 166
- ^ Gardiner, John Eliot (April 1996). "Happy to talk". Gramophone: p. 20.
{{cite journal}}:|page=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Gillies, Malcolm (16 October 2010). "Grainger: Fifty Years On". Grainger Museum (University of Melbourne). Retrieved 5 May 2011.
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 32
- ^ Josephson, pp. 614–17
- ^ Bird, p. 74
- ^ Bird, p. 146
- ^ Fairfax, p. 72
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 172
- ^ a b Gillies, Malcolm (30 May 2007). "Percy Grainger: Grieg's Interpreter and Propagator" (PDF). International Grieg Society Conference. pp. 2–5. Retrieved 5 May 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Servadei, Alessandro and Ould, Barry Peter (1997). "Orchestral works 2 – The Warriors" (CD booklet notes). Chandos Records. Retrieved 19 September 2011.
- ^ Covell, p. 141
- ^ a b Covell, p. 147
- ^ Covell, pp. 145–46
- ^ Thomas P. Lewis (June 1990). A Source Guide to the Music of Percy Grainger. Pro Am Music Resources. ISBN 978-0-912483-56-6.
- ^ a b Covell, pp. 142–43
- ^ Foreman ("Editor's Introduction"), p. 11
- ^ Manville, pp. 166–70
- ^ Bird, p. 114
- ^ Lloyd, p. 21
- ^ Reynish, p. 20
- ^ Covell, p. 148
- ^ Gillies and Pear (eds), p. 255
- ^ Pear ("Grainger the Social Commentator"), p. 32
- ^ Ould, p. 29
- ^ Quoted by Bird, pp. 100–01, from Schonberg, Harold (1964): The Great Pianists, London, Victor Gollancz
- ^ Bird, pp. 238–39
- ^ Bird, pp. 246–47
- ^ Allison, p. 53
- ^ Blacking, p. 1
- ^ Thwaites (ed.), pp. 227–32
- ^ Woolf, Jonathan (2011). Percy Grainger; the complete 78rpm solo recordings (review). MusicWeb International. Retrieved 18 September 2011.
- ^ Bird, pp. 304–06
- ^ Thwaites (ed.), pp. 233–35
- ^ Dubal, David (1996). Percy Grainger plays Grainger (CD booklet notes). Nimbus Records. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Pianola Institute concerts – archive. Website, www.pianola.org. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Thwaites (ed.). p. 108
- ^ Thwaites (ed.), pp. 238–47
- ^ "The Grainger Edition Volumes 1–19". Presto Classical. 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
Sources
- Allison, Brian (2006). "Grainger the Visual Gourmet". In Pear, David (ed.) (ed.). Facing Percy Grainger. Canberra: National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27639-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Bird, John (1982). Percy Grainger. London: Faber & Faber. ISBN 0-571-11717-1.
- Blacking, John (1987). A commonsense View of All Music: Reflections on Percy Grainger's Contribution to Ethnomusicology and Music Education. Cambridge, UK; Melbourne: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-26500-2.
- Carley, Lionel (1981). "Impulsive Friend: Grainger and Delius". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Triplow, Leighton H. "An Analysis of 'The Warriors' (1916) by Percy Grainger", 2011.
- Covell, Roger (2010). "An Australian Composer?". In Thwaites, Penelope (ed.) (ed.). The New Percy Grainger Companion. Woodbridge, Suffolk: The Boydell Press. ISBN 978-1-84383-601-8.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Dreyfus, Kay (ed.) (1985). The Farthest North of Humanness: Letters of Percy Grainger 1901–14. Melbourne: Macmillan (Australia). ISBN 0-333-38085-1.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - Fairfax, Brian (1981). "Orchestral Music". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Fenby, Eric (1981). Delius as I knew him. London: Faber and Faber. ISBN 0-571-11836-4.
- Foreman, Lewis (1981). "Editor's Introduction". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Foreman, Lewis (1981). "Miscellaneous Works". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Gillies, Malcolm (1994). The All-Round Man: Selected Letters of Percy Grainger 1914–61. Oxford, UK: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-816377-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Josephson, David (1980). "Grainger (George) Percy (Aldridge)". In Sadie, Stanley (ed.) (ed.). New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians. Vol. 7. London. ISBN 0-333-23111-2.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lloyd, Stephen (1981). "Grainger In a Nutshell". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Manville, Stewart (2010). "At Home in New York". In Thwaites, Penelope (ed.) (ed.). The New Percy Grainger Companion. Woodbridge, Suffolk: The Boydell Press. ISBN 978-1-84383-601-8.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Ould, Barry Peter (2006). "Grainger the Music Arranger". In Pear, David (ed.) (ed.). Facing Percy Grainger. Canberra: National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27639-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Palmer, Christopher (1976). Delius: Portrait of a Cosmopolitan. London: Duckworth. ISBN 0-7156-0773-1.
- Pear, David (2006). "Grainger: The Formative Years". In Pear, David (ed.) (ed.). Facing Percy Grainger. Canberra: National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27639-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Pear, David (2006). "Grainger the Social Commentator". In Pear, David (ed.) (ed.). Facing Percy Grainger. Canberra: National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27639-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Piggott, Michael (2006). "Grainger the Autoarchivist". In Pear, David (ed.) (ed.). Facing Percy Grainger. Canberra: National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27639-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Reynish, Timothy (2010). "Music for Wind Band". In Thwaites, Penelope (ed.) (ed.). The New Percy Grainger Companion. Woodbridge, Suffolk: The Boydell Press. ISBN 978-1-84383-601-8.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Scott, Cyril (1981). "Grainger in Frankfurt". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Simon, Robert (1983). Percy Grainger: The Pictorial Biography. Albany, New York: Whitston. ISBN 0-87875-281-1.
- Tall, David (1981). "Grainger and Folksong". In Foreman, Lewis (ed.) (ed.). The Percy Grainger Companion. London: Thames Publishing. ISBN 0-905210-12-3.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Tan, Eleanor (2006). "Grainger the Composer". In Pear, David (ed.) (ed.). Facing Percy Grainger. Canberra: National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27639-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor-first=has generic name (help) - Thwaites, Penelope (ed.) (2010). The New Percy Grainger Companion. Woodbridge, Suffolk: The Boydell Press. ISBN 978-1- 84383-601-8.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help)
External links
- The International Percy Grainger Society
- The Percy Grainger Society
- The Grainger Museum at the University of Melbourne, Australia
- Grainger Studies: An Interdisciplinary Journal
- The Free Music Machines of Percy Grainger Rainer Linz
- "Country Gardens": Performance by Grainger on pianola, 1919
- Use dmy dates from April 2011
- 1882 births
- 1961 deaths
- 20th-century classical composers
- Australian people of English descent
- ARIA Award winners
- ARIA Hall of Fame inductees
- Australian atheists
- Australian classical pianists
- Australian composers
- Australian emigrants to the United States
- Australian folk-song collectors
- Australian folklorists
- Burials in South Australia
- Child classical musicians
- Composers for piano
- English folk-song collectors
- Ethnomusicologists
- Hoch Conservatory alumni
- BDSM people
- United States Army soldiers

