Down syndrome: Difference between revisions
The "Treatment" section adds nothing to the article. Change the relevant sections if you want, which is where treatment should be discussed. |
SandyGeorgia (talk | contribs) Restore section order per WP:MEDMOS as passed FA and Wikiproject |
||
| (462 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
ICDO = | |
ICDO = | |
||
Image = Drill.jpg <!--- Do not change this picture without discussing it in the Down syndrome discussion page. Because of continued vandalism, pictures will be immediately reverted. ---> | |
Image = Drill.jpg <!--- Do not change this picture without discussing it in the Down syndrome discussion page. Because of continued vandalism, pictures will be immediately reverted. ---> | |
||
Caption = |
Caption = A child with Down Syndrome using an electric drill. | |
||
OMIM = 190685 | |
OMIM = 190685 | |
||
OMIM_mult = | |
OMIM_mult = | |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Down syndrome''' or '''trisomy 21''' (British '''Down's syndrome''') is a [[genetic disorder |
'''Down syndrome''' or '''trisomy 21''' (in British English: '''Down's syndrome''') is a [[genetic disorder]] caused by the presence of all or part of an extra [[chromosome 21 (human)|21st chromosome]]. It is named after [[John Langdon Down]], the British doctor who first described it in [[1866 in science|1866]]. The condition is characterized by a combination of major and minor abnormalities in body structure and function. Most Down syndrome cases feature impairment of learning and physical growth as well as a recognizable facial appearance usually identified at birth. |
||
Individuals with Down syndrome have lower than average [[cognitive]] ability, normally ranging from mild to moderate retardation. |
Individuals with Down syndrome have lower than average [[cognitive]] ability, normally ranging from mild to moderate [[mental retardation]]. They generally have some developmental disability, such as a tendency toward concrete thinking or [[naïveté]]. Some have low intelligence, and a small number suffer from severe to profound mental retardation. The [[Incidence (epidemiology)|incidence]] of Down syndrome is estimated at 1 per 800 to 1 per 1000 births. |
||
The common physical features of Down syndrome also appear in people with a standard set of chromosomes. They include a [[ |
The common physical features of Down syndrome also appear in people with a standard set of chromosomes. They include a [[single transverse palmar crease]] (a single instead of a double crease across one or both palms), an almond shape to the eyes caused by an [[epicanthic fold]] of the eyelid, shorter limbs, speech impairment, and protruding tongue. Health concerns for individuals with Down syndrome include a higher risk for [[congenital heart defect]]s, gastroesophageal reflux disease, recurrent [[ear infections]], [[obstructive sleep apnea]], and [[thyroid]] dysfunctions. |
||
[[Early Childhood Intervention|Early childhood intervention]], screening for common problems, |
[[Early Childhood Intervention|Early childhood intervention]], screening for common problems, medical treatment where indicated, a conducive family environment, and [[vocational training]] can improve the overall development of children with Down syndrome. Although some of the genetic limitations of Down Syndrome cannot be overcome, education and proper care can improve quality of life.<ref>Roizen NJ, Patterson D.''Down's syndrome.'' Lancet. 2003 [[12 April]];361(9365):1281-9. Review. PMID 12699967</ref> |
||
==Characteristics== |
==Characteristics== |
||
[[Image:Brushfield.jpg|thumb|right|Example of white spots on the [[iris (anatomy)|iris]] known as ''Brushfield’s Spots''.]] |
|||
Individuals with Down syndrome may have some or all of the following physical characteristics:<ref>{{cite web |
Individuals with Down syndrome may have some or all of the following physical characteristics:<ref>{{cite web |url=http://healthlibrary.epnet.com/GetContent.aspx?token=94e729bf-2a24-406f-8083-f1484720ce65&chunkiid=11897 |title=Down syndrome |first=Debra |last=Wood |year=2005 |accessdate=2006-06-30}}</ref> oblique eye fissures with epicanthic skin folds on the inner corner of the eyes, [[muscle hypotonia]], a flat nasal bridge, a [[Single transverse palmar crease|single palmar fold]] (also known as a [[simian crease]]), a protruding tongue (due to small oral cavity, poor muscle tone, and an enlarged tongue near the tonsils), a short neck, white spots on the [[Eye#Anatomy of the mammalian eye|iris]] known as [[Brushfield spots]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=6570 |title=Definition of Brushfield's Spots}}</ref> excessive flexibility in joints, [[congenital heart defect]]s, excessive space between large and second toe, and a single [[flexion]] furrow of the fifth finger. Most individuals with Down syndrome have [[mental retardation]] in the mild (IQ 50–70) to moderate (IQ 35–50) range,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.keepkidshealthy.com/welcome/conditions/downsyndrome.html |title=Keep Kids Healthy article on Down syndrome |accessedate=2006-04-10}}</ref> with scores of children having Mosaic Down syndrome (explained below) typically 10–30 points higher.<ref>{{cite web |author=Strom, C |url=http://www.mosaicdownsyndrome.com/faqs.htm |title=FAQ from Mosaic Down Syndrome Society |accessdate=2006-06-03}}</ref> In addition, individuals with Down syndrome can have serious abnormalities affecting any body system. |
||
== |
==Genetics== |
||
{{main|Genetic origins of Down syndrome}} |
{{main|Genetic origins of Down syndrome}} |
||
[[Image:Down_Syndrome_Karyotype.png|right|thumb|[[Karyotype]] for trisomy Down syndrome. Notice the three copies of chromosome 21.]] |
[[Image:Down_Syndrome_Karyotype.png|right|thumb|[[Karyotype]] for trisomy Down syndrome. Notice the three copies of chromosome 21.]] |
||
Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality characterized by the presence of an extra copy of genetic material on the [[Chromosome 21 (human)|21st chromosome]], either in whole ([[Aneuploidy#Trisomy|trisomy]] [[Chromosome 21 (human)|21]]) or part (such as due to [[Chromosomal translocation|translocations]]). The effects of the extra copy |
Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality characterized by the presence of an extra copy of genetic material on the [[Chromosome 21 (human)|21st chromosome]], either in whole ([[Aneuploidy#Trisomy|trisomy]] [[Chromosome 21 (human)|21]]) or part (such as due to [[Chromosomal translocation|translocations]]). The effects of the extra copy vary greatly among individuals, depending on the extent of the extra copy, genetic background, environmental factors, and random chance. Down syndrome occurs in all human populations, and analogous effects have been found in other species such as chimpanzees and mice. Recently, researchers have created [[transgenic]] mice with most of human chromosome 21 (in addition to the normal mouse chromosomes).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/4268226.stm |title=Down's syndrome recreated in mice| publisher=BBC News |accessdate=2006-06-14 |date=2005-09-22}}</ref> The extra chromosomal material can come about in several distinct ways. A normal human karyotype is designated as 46,XX or 46,XY, indicating 46 chromosomes with an XX arrangement for females and 46 chromosomes with an XY arrangement for males.<ref>For a description of human karyotype see {{cite web |author=Mittleman, A. (editor) |year=1995 |url=http://www.iscn1995.org/ |title=An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomeclature |accessdate=2006-06-04}}</ref> |
||
===Trisomy 21=== |
===Trisomy 21=== |
||
Trisomy 21 (47,XX,+21) is caused by a [[Meiosis|meiotic]] [[nondisjunction]] event. With nondisjunction, a gamete (i.e., a sperm or egg cell) is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21; the gamete thus has 24 chromosomes. When combined with a normal gamete from the other parent, the embryo now has 47 chromosomes, with three copies of chromosome 21. Trisomy 21 is the cause of approximately 95% of observed Down syndromes, with 88% coming from nondisjunction in the maternal gamete and 8% coming from nondisjunction in the paternal gamete.<ref name=occurrence>{{cite web|url=http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/pubs/downsyndrome/down.htm#TheOccurrence|title=Down syndrome occurrence rates (NIH)|accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> |
Trisomy 21 (47,XX,+21) is caused by a [[Meiosis|meiotic]] [[nondisjunction]] event. With nondisjunction, a [[gamete]] (''i.e.'', a sperm or egg cell) is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21; the gamete thus has 24 chromosomes. When combined with a normal gamete from the other parent, the embryo now has 47 chromosomes, with three copies of chromosome 21. Trisomy 21 is the cause of approximately 95% of observed Down syndromes, with 88% coming from nondisjunction in the maternal gamete and 8% coming from nondisjunction in the paternal gamete.<ref name="occurrence">{{cite web |url=http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/pubs/downsyndrome/down.htm#TheOccurrence |title=Down syndrome occurrence rates (NIH) |accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> |
||
===Mosaicism=== |
===Mosaicism=== |
||
Trisomy 21 is generally caused |
Trisomy 21 is generally caused prior to conception, and all cells in the body are affected. However, when some of the cells in the body are normal and other cells have trisomy 21, it is called [[Mosaic (genetics)|Mosaic]] Down Syndrome (46,XX/47,XX,+21).<ref>[http://www.mosaicdownsyndrome.com Mosaic Down Syndrome on the Web]</ref> This can occur in one of two ways: A [[nondisjunction]] event during an early cell division in a normal embryo leads to a fraction of the cells with trisomy 21; or a Down syndrome embryo undergoes [[nondisjunction]] and some of the cells in the embryo revert back to the normal chromosomal arrangement. There is considerable variability in the fraction of trisomy 21, both as a whole and among tissues. This is the cause of 1–2% of the observed Down syndromes.<ref name="occurrence" /> |
||
===Robertsonian translocation=== |
===Robertsonian translocation=== |
||
The extra chromosome 21 material that causes Down syndrome may be due to a [[Robertsonian translocation]]. In this case, the long arm of [[Chromosome 21 (human)|chromosome 21]] is attached to another chromosome, often [[Chromosome 14 (human)|chromosome 14]] (45,XX,t(14;21q)) or itself (called an [[isochromosome]], 45,XX,t(21q;21q)). Normal [[disjunction]] leading to gametes have a significant chance of creating a gamete with an extra chromosome 21. Translocation Down syndrome is often referred to as ''familial Down syndrome''. It is the cause of 2-3% of |
The extra chromosome 21 material that causes Down syndrome may be due to a [[Robertsonian translocation]]. In this case, the long arm of [[Chromosome 21 (human)|chromosome 21]] is attached to another chromosome, often [[Chromosome 14 (human)|chromosome 14]] (45,XX,t(14;21q)) or itself (called an [[isochromosome]], 45,XX,t(21q;21q)). Normal [[disjunction]] leading to gametes have a significant chance of creating a gamete with an extra chromosome 21. Translocation Down syndrome is often referred to as ''familial Down syndrome''. It is the cause of 2-3% of observed cases of Down syndrome.<ref name="occurrence" /> It does not show the maternal age effect, and is just as likely to have come from fathers as mothers. |
||
===Duplication of a portion of chromosome 21=== |
===Duplication of a portion of chromosome 21=== |
||
Rarely, a region of chromosome 21 will undergo a duplication event. This will lead to extra copies of some, but not all, of the genes on chromosome 21 (46,XX,dup(21q)).<ref>Petersen MB, Tranebjaerg L, McCormick MK, Michelsen N, Mikkelsen M, Antonarakis SE. ''Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic characterization of two unrelated patients with different duplications of 21q.'' Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:104-9. |
Rarely, a region of chromosome 21 will undergo a duplication event. This will lead to extra copies of some, but not all, of the genes on chromosome 21 (46,XX,dup(21q)).<ref>Petersen MB, Tranebjaerg L, McCormick MK, Michelsen N, Mikkelsen M, Antonarakis SE. ''Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic characterization of two unrelated patients with different duplications of 21q.'' Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:104-9. |
||
PMID 2149934</ref> If the duplicated region has genes that are responsible for Down syndrome physical and mental characteristics, such individuals will show those characteristics. This cause is very rare and no rate estimates are |
PMID 2149934</ref> If the duplicated region has genes that are responsible for Down syndrome physical and mental characteristics, such individuals will show those characteristics. This cause is very rare and no rate estimates are available. |
||
==Incidence== |
==Incidence== |
||
[[Image:Maternal Age Effect.png|thumb|200px|Graph showing increased chance of Down syndrome compared to maternal age.<ref>{{cite journal|author = Hook, E.B.|year = 1981|title = Rates of chromosomal abnormalities at different maternal ages|journal = Obstet Gynecol|volume = 58|pages = 282}}</ref>]] |
[[Image:Maternal Age Effect.png|thumb|200px|Graph showing increased chance of Down syndrome compared to maternal age.<ref>{{cite journal|author = Hook, E.B.|year = 1981|title = Rates of chromosomal abnormalities at different maternal ages|journal = Obstet Gynecol|volume = 58|pages = 282}}</ref>]] |
||
The incidence of Down syndrome is estimated at 1 per 800 to 1 per 1000 births.<ref name=NIHestimates>Based on estimates by National Institute of Child Health & Human Development {{cite web| title = Down syndrome rates| url=http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/pubs/downsyndrome/down.htm| accessdate =2006-06-21}} |
The incidence of Down syndrome is estimated at 1 per 800 to 1 per 1000 births.<ref name=NIHestimates>Based on estimates by National Institute of Child Health & Human Development {{cite web| title = Down syndrome rates| url=http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/pubs/downsyndrome/down.htm| accessdate =2006-06-21}} |
||
</ref> In 2006, the Center for Disease Control estimated the rate as 1 per 733 live births in the United States (5429 new cases per year).<ref>{{cite journal |
</ref> In 2006, the Center for Disease Control estimated the rate as 1 per 733 live births in the United States (5429 new cases per year).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Center for Disease Control |title=Improved National Prevalence Estimates for 18 Selected Major Birth Defects, United States, 1999-2001 |journal=Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report |volume=54 |issue=51 & 52 |date=[[6 January]] [[2006]]| url=http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5451a2.htm| pages=1301-1305}}</ref> Approximately 95% of these are [[Aneuploidy#Trisomy|trisomy]] [[Chromosome 21|21]]. Down syndrome occurs in all ethnic groups and among all economic classes. |
||
[[Maternal age effect|Maternal age]] influences the risk of conceiving a baby with Down syndrome. At maternal age 20 to 24, the risk is 1/1490 |
[[Maternal age effect|Maternal age]] influences the risk of conceiving a baby with Down syndrome. At maternal age 20 to 24, the risk is 1/1490; at age 40 the risk is 1/106, and at age 49 the risk is 1/11.<ref>{{cite journal| author = Hook, E.B.| year = 1981| title = Rates of chromosomal abnormalities at different maternal ages| journal = Obstet Gynecol| volume = 58| pages = 282}}</ref> Although the risk increases with maternal age, 80% of children with Down syndrome are born to women under the age of 35,<ref>Estimate from {{cite web |title=National Down Syndrome Center |url=http://www.ndsccenter.org/resources/package3.php |accessdate=2006-04-21}}</ref> reflecting the overall fertility of that age group. Other than maternal age, no other risk factors are known. There does not appear to be a paternal age effect. |
||
Many standard prenatal screens can discover Down syndrome. [[Genetic counseling]] along with [[genetic testing]], such as [[amniocentesis]], [[chorionic villus sampling]] (CVS), or percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) are usually offered to families who may have an increased chance of having a child with Down syndrome, or where normal prenatal exams indicate possible problems. Genetic screens are often performed on pregnant women older than 30 or 35. |
Many standard prenatal screens can discover Down syndrome. [[Genetic counseling]] along with [[genetic testing]], such as [[amniocentesis]], [[chorionic villus sampling]] (CVS), or percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) are usually offered to families who may have an increased chance of having a child with Down syndrome, or where normal prenatal exams indicate possible problems. Genetic screens are often performed on pregnant women older than 30 or 35. |
||
== |
==Prenatal screening== |
||
Pregnant women can be screened for various complications in their pregnancy, or due to risk factors such as advanced maternal age. There are several common non-invasive screens that can indicate a Down syndrome |
Pregnant women can be screened for various complications in their pregnancy, or due to risk factors such as advanced maternal age. There are several common non-invasive screens that can indicate a fetus with Down syndrome, and are normally performed in the late first trimester or early second trimester. Due to the nature of screens, each has a significant chance of a [[Type I and type II errors|false positive]], suggesting a fetus with Down syndrome when, in fact, the fetus does not have this genetic abnormality. Screen positives must be verified before a Down syndrome diagnosis is made. Common screening procedures for Down syndrome are given in Table 1. |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|+ Table 1: Common |
|+ Table 1: Common first and second trimester Down syndrome screens |
||
|- |
|- |
||
!Screen |
!Screen |
||
!When |
!When performed (weeks [[gestation]]) |
||
!Detection |
!Detection rate |
||
![[Type I and type II errors|False |
![[Type I and type II errors|False positive]] rate |
||
!Description |
!Description |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Triple |
|Triple screen |
||
|align="center"|15–20 |
|align="center"|15–20 |
||
|align="center"|75% |
|align="center"|75% |
||
| Line 69: | Line 71: | ||
|This test measures the maternal serum [[alpha-fetoprotein|alpha feto protein]] (a fetal liver protein), [[estriol]] (a pregnancy hormone), and [[human chorionic gonadotropin]] (hCG, a pregnancy hormone).<ref name=quadrate>For a current estimate of rates, see {{cite journal| author=Benn, PA, J Ying, T Beazoglou, JFX Egan| journal=Prenatal Diagnosis| volume=21| issue=1| pages=46-51| title=Estimates for the sensitivity and false-positive rates for second trimester serum screening for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 with adjustments for cross-identification and double-positive results}}</ref> |
|This test measures the maternal serum [[alpha-fetoprotein|alpha feto protein]] (a fetal liver protein), [[estriol]] (a pregnancy hormone), and [[human chorionic gonadotropin]] (hCG, a pregnancy hormone).<ref name=quadrate>For a current estimate of rates, see {{cite journal| author=Benn, PA, J Ying, T Beazoglou, JFX Egan| journal=Prenatal Diagnosis| volume=21| issue=1| pages=46-51| title=Estimates for the sensitivity and false-positive rates for second trimester serum screening for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 with adjustments for cross-identification and double-positive results}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Quad |
|Quad screen |
||
|align="center"|15–20 |
|align="center"|15–20 |
||
|align="center"|79% |
|align="center"|79% |
||
| Line 75: | Line 77: | ||
|This test measures the maternal serum [[alpha-fetoprotein|alpha feto protein]] (a fetal liver protein), [[estriol]] (a pregnancy hormone), [[human chorionic gonadotropin]] (hCG, a pregnancy hormone), and high [[inhibin]]-Alpha (INHA).<ref name=quadrate>For a current estimate of rates, see {{cite journal| author=Benn, PA, J Ying, T Beazoglou, JFX Egan| journal=Prenatal Diagnosis| volume=21| issue=1| pages=46-51| title=Estimates for the sensitivity and false-positive rates for second trimester serum screening for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 with adjustments for cross-identification and double-positive results}}</ref> |
|This test measures the maternal serum [[alpha-fetoprotein|alpha feto protein]] (a fetal liver protein), [[estriol]] (a pregnancy hormone), [[human chorionic gonadotropin]] (hCG, a pregnancy hormone), and high [[inhibin]]-Alpha (INHA).<ref name=quadrate>For a current estimate of rates, see {{cite journal| author=Benn, PA, J Ying, T Beazoglou, JFX Egan| journal=Prenatal Diagnosis| volume=21| issue=1| pages=46-51| title=Estimates for the sensitivity and false-positive rates for second trimester serum screening for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 with adjustments for cross-identification and double-positive results}}</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|AFP/ |
|AFP/free beta screen |
||
|align="center"|13–22 |
|align="center"|13–22 |
||
|align="center"|80% |
|align="center"|80% |
||
| Line 81: | Line 83: | ||
|This test measures the [[alpha-fetoprotein|alpha feto protein]], produced by the fetus, and free beta hCG, produced by the [[placenta]]. |
|This test measures the [[alpha-fetoprotein|alpha feto protein]], produced by the fetus, and free beta hCG, produced by the [[placenta]]. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Nuchal |
|Nuchal translucency/free beta/PAPPA screen |
||
|align="center"|10–13.5 |
|align="center"|10–13.5 |
||
|align="center"|91%<ref name=nasalbone>Some practices report adding Nasal Bone measurements and increasing the detection rate to 95% with a 2% False Positive Rate.</ref> |
|align="center"|91%<ref name=nasalbone>Some practices report adding Nasal Bone measurements and increasing the detection rate to 95% with a 2% False Positive Rate.</ref> |
||
| Line 87: | Line 89: | ||
|Uses [[ultrasound]] to measure [[Nuchal translucency|Nuchal Translucency]] in addition to the freeBeta [[human chorionic gonadotropin|hCG]] and PAPPA (pregnancy-associate plasma protein A, {{OMIM|176385}}). NIH has confirmed that this first trimester test is more accurate than second trimester screening methods.<ref>NIH FASTER study (NEJM 2005 ('''353'''):2001). See also J.L. Simplson's editorial (NEJM 2005 ('''353'''):19).</ref> |
|Uses [[ultrasound]] to measure [[Nuchal translucency|Nuchal Translucency]] in addition to the freeBeta [[human chorionic gonadotropin|hCG]] and PAPPA (pregnancy-associate plasma protein A, {{OMIM|176385}}). NIH has confirmed that this first trimester test is more accurate than second trimester screening methods.<ref>NIH FASTER study (NEJM 2005 ('''353'''):2001). See also J.L. Simplson's editorial (NEJM 2005 ('''353'''):19).</ref> |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Even with the best non-invasive screens, the detection rate is 90%–95% and the rate of false positive |
||
| ⚫ | Even with the best non-invasive screens, the detection rate is 90%–95% and the rate of false positive is 2%–5%. [[Type I and type II errors|False positive]]s can be caused by undetected multiple fetuses (very rare with the ultrasound tests), incorrect date of pregnancy, or normal variation in the proteins. |
||
| ⚫ | Confirmation of screen positive is normally accomplished with [[amniocentesis]]. This is an invasive procedure and involves taking [[amniotic fluid]] from the mother and identifying fetal cells. The lab work can take a couple of weeks but will detect over 99.8% of all numerical chromosomal problems with a very low false positive rate.<ref>{{cite web |
||
| ⚫ | Confirmation of screen positive is normally accomplished with [[amniocentesis]]. This is an invasive procedure and involves taking [[amniotic fluid]] from the mother and identifying fetal cells. The lab work can take a couple of weeks but will detect over 99.8% of all numerical chromosomal problems with a very low false positive rate.<ref>{{cite web |title=Down syndrome |author=Fackler, A |url=http://health.yahoo.com/topic/children/baby/article/healthwise/hw167989 |accessdate=2006-09-07}}</ref> |
||
Due to the low incidence of Down syndrome, the vast majority of early screen positives are false.<ref>Assume the false positive rate is 2% (at the low end), the incidence of Down syndrome is 1/500 (on the high side) with 95% detection, and there is no [[ascertainment bias]]. Out of 100,000 screens, 200 will have Down syndrome, and the screen will detect 190 of them. From the 99,800 normal pregnancies, 1996 will be given a positive result. So, among the 2,186 positive test results, 91% will be false positives and 9% will be true positives.</ref> Since the risk of [[spontaneous abortion]] is approximately 1/200 to 1/300,<ref>{{cite web| title=Risk and Recurrence Risk of Down Syndrome| author=Benke, P, V. Carver, R Donahue| url=http://www.nas.com/downsyn/benke.html| accessdate=2006-09-07}}</ref> amniocentesis confirmation presents a risk of spontaneously aborting a healthy fetus (from a false positive). |
|||
Due to the low incidence of Down syndrome, a vast majority of early screen positives are false.<ref>Assume the false positive rate is 2% (at the low end), the incidence of Down syndrome is 1/500 (on the high side) with 95% detection, and there is no [[ascertainment bias]]. Out of 100,000 screens, 200 will have Down syndrome, and the screen will detect 190 of them. From the 99,800 normal pregnancies, 1996 will be given a positive result. So, among the 2,186 positive test results, 91% will be false positives and 9% will be true positives.</ref> Since the risk of [[spontaneous abortion]] is approximately 1/200 to 1/300,<ref>{{cite web |title=Risk and Recurrence Risk of Down Syndrome |author=Benke, P, V. Carver, R Donahue |url=http://www.nas.com/downsyn/benke.html |accessdate=2006-09-07}}</ref> amniocentesis confirmation presents a risk of spontaneously aborting a healthy fetus (while testing from a false positive). |
|||
A 2002 literature review of elective abortion rates found that 91–93% of pregnancies with a diagnosis of Down syndrome were terminated.<ref>{{cite journal| author=Caroline Mansfield, Suellen Hopfer, Theresa M. Marteau| title=Termination rates after prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome, spina bifida, anencephaly, and Turner and Klinefelter syndromes: a systematic literature review| year=1999| journal=Prenatal Diagnosis| volume=19| issue=9| pages=808-812| url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/65500197/ABSTRACT}} This is similar to 90% results found by {{cite journal| title=Determinants of parental decisions after the prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome: Bringing in context| journal=American Journal of Medical Genetics| volume=93| issue=5| pages=410 - 416| year=1999| author=David W. Britt, Samantha T. Risinger, Virginia Miller, Mary K. Mans, Eric L. Krivchenia, Mark I. Evans}}</ref> Physicians and ethicists are concerned about the ethical ramifications,<ref>{{cite journal| author=Glover, NM and Glover, SJ| title=Ethical and legal issues regarding selective abortion of fetuses with Down syndrome| journal=Ment. Retard.| year=1996| volume=34| issue=4| pages=207-214| id=PMID 8828339}}</ref> with some commentators calling it "eugenics by abortion".<ref>{{cite journal |last=Will |first=George |title=Eugenics By Abortion: Is perfection an entitlement? |date=2005-04-14 |journal=Washington Post |pages=A37 |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A51671-2005Apr13.html |accessdate=2006-07-03}}</ref> Many members of the disability rights movement "believe that public support for prenatal diagnosis and abortion based on disability contravenes the movement's basic philosophy and goals."<ref>{{cite journal |author=Erik Parens and Adrienne Asch |title=Disability rights critique of prenatal genetic testing: Reflections and recommendations |year=2003 |journal=Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews |volume=9 |issue=1 |page=40-47 |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/102531130/ABSTRACT| accessdate=2006-07-03}}</ref> |
|||
==Cognitive development== |
==Cognitive development== |
||
Cognitive development in children with Down syndrome is quite variable |
Cognitive development in children with Down syndrome is quite variable. It is not possible at birth to predict their capabilities. The identification of the best methods of teaching each particular child ideally begins soon after birth through early intervention programs.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ndss.org/content.cfm?fuseaction=NwsEvt.Article&article=1558|title=New Parent Guide|publisher=National Down Syndrome Society|accessdate=2006-05-12}} Also {{cite web |url=http://www.downsed.org/research/projects/early-intervention |title=Research projects - Early intervention and education |accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> Since children with Down syndrome have a wide range of abilities, success at school can vary greatly, which stresses the importance of evaluating children individually. The cognitive problems that are found among children with Down syndrome can also be found among typical children. Therefore, parents can use general programs that are offered through the schools or other means. |
||
Language skills show a difference between understanding speech and expressing speech. It is common for children with Down syndrome to need speech therapy to help with expressive language.<ref>{{cite journal| author =Bird, G. and S. Thomas| year =2002| title = Providing effective speech and language therapy for children with Down syndrome in mainstream settings: A case example | journal =Down Syndrome News and Update| volume =2| issue =1| pages =30-31}} Also, {{cite book| last =Kumin| first=Libby| editor=Hassold, T.J.and D. Patterson| title =Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together| year =1998| publisher =Wiley-Liss| location =New York| chapter = Comprehensive speech and language treatment for infants, toddlers, and children with Down syndrome}}</ref> [[Fine motor skill]]s are delayed<ref>{{cite web| title=Development of Fine Motor Skills in Down Syndrome| url=http://www.about-down-syndrome.com/fine-motor-skills-in-down-syndrome.html| accessdate=2006-07-03}}</ref> and often lag behind [[gross motor skill]]s and can interfere with cognitive development. [[Occupational therapy]] can address these issues.<ref>{{cite web |author = M. Bruni|url=http://www.ds-health.com/occther.htm| title=Occupational Therapy and the Child with Down Syndrome|accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> |
Language skills show a difference between understanding speech and expressing speech. It is common for children with Down syndrome to need speech therapy to help with expressive language.<ref>{{cite journal| author =Bird, G. and S. Thomas| year =2002| title = Providing effective speech and language therapy for children with Down syndrome in mainstream settings: A case example | journal =Down Syndrome News and Update| volume =2| issue =1| pages =30-31}} Also, {{cite book| last =Kumin| first=Libby| editor=Hassold, T.J.and D. Patterson| title =Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together| year =1998| publisher =Wiley-Liss| location =New York| chapter = Comprehensive speech and language treatment for infants, toddlers, and children with Down syndrome}}</ref> [[Fine motor skill]]s are delayed<ref>{{cite web| title=Development of Fine Motor Skills in Down Syndrome| url=http://www.about-down-syndrome.com/fine-motor-skills-in-down-syndrome.html| accessdate=2006-07-03}}</ref> and often lag behind [[gross motor skill]]s and can interfere with cognitive development. [[Occupational therapy]] can address these issues.<ref>{{cite web |author = M. Bruni|url=http://www.ds-health.com/occther.htm| title=Occupational Therapy and the Child with Down Syndrome|accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> |
||
In education, [[ |
In education, [[Mainstreaming in education|mainstreaming]] of children with Down syndrome is controversial. Mainstreaming is when students of differing abilities are placed in classes with their chronological peers. Children with Down syndrome do not age emotionally/socially and intellectually at the same rates as children without Down syndrome, so eventually the intellectual and emotional gap between children with and without Down syndrome widens. Complex thinking as required in sciences but also in history, the arts, and other subjects is often beyond their abilities, or achieved much later than in most children. Therefore, if they are to benefit from mainstreaming without feeling inferior most of the time, special adjustments must be made to the curriculum.<ref>{{cite web|author=S.E.Armstrong|url=http://www.altonweb.com/cs/downsyndrome/index.htm?page=ndssincl.html|title=Inclusion: Educating Students with Down Syndrome with Their Non-Disabled Peers|accessdate=2006-05-12}} Also, see {{cite web|url=http://www.altonweb.com/cs/downsyndrome/index.htm?page=bosworth.html| title=Benefits to Students with Down Syndrome in the Inclusion Classroom: K-3| author=Debra L. Bosworth| accessdate=2006-06-12}} Finally, see a survey by NDSS on inclusion, {{cite web|url=http://www.altonweb.com/cs/downsyndrome/index.htm?page=wolpert.html| title=The Educational Challenges Inclusion Study| author=Gloria Wolpert| year=1996| publisher=National Down Syndrome Society| accessdate=2006-06-28}}</ref> |
||
Some European countries such as Germany and Denmark advise a two-teacher system, whereby the second teacher takes over a group of children with disabilities within the class. A popular alternative is cooperation between special education schools and mainstream schools. In cooperation, the core subjects are taught in separate classes, which neither slows down the typical students nor neglects the students with disabilities. Social activities, outings, and many sports and arts activities are performed together, as are all breaks and meals.<ref>There are many such programs. One is described by Action Alliance for Children, {{web cite|author=K. Flores| url=http://www.4children.org/news/103spec.htm|title=Special needs, "mainstream" classroom|accessdate=2006-05-13}} Also, see {{web cite|author=Flores, K.|url=http://www.4children.org/pdf/103spec.pdf|title=Special needs, "mainstream" classroom|accessdate=2006-05-13}}</ref> |
Some European countries such as Germany and Denmark advise a two-teacher system, whereby the second teacher takes over a group of children with disabilities within the class. A popular alternative is cooperation between special education schools and mainstream schools. In cooperation, the core subjects are taught in separate classes, which neither slows down the typical students nor neglects the students with disabilities. Social activities, outings, and many sports and arts activities are performed together, as are all breaks and meals.<ref>There are many such programs. One is described by Action Alliance for Children, {{web cite|author=K. Flores| url=http://www.4children.org/news/103spec.htm|title=Special needs, "mainstream" classroom|accessdate=2006-05-13}} Also, see {{web cite|author=Flores, K.|url=http://www.4children.org/pdf/103spec.pdf|title=Special needs, "mainstream" classroom|accessdate=2006-05-13}}</ref> |
||
== |
==Health== |
||
{{main|Health aspects of Down syndrome}} |
{{main|Health aspects of Down syndrome}} |
||
The medical consequences of the extra genetic material in |
The medical consequences of the extra genetic material in Down syndrome are highly variable and may affect the function of any organ system or bodily process. The health aspects of Down syndrome encompass anticipating and preventing effects of the condition, recognizing complications of the disorder, managing individual symptoms, and assisting the individual and his/her family in coping and thriving with any related disability or illnesses.<ref>{{cite journal| author=American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Genetics| title=American Academy of Pediatrics: Health supervision for children with Down syndrome| journal=Pediatrics| year=2001| month=Feb| volume=107| issue=2| pages=442-449| id=PMID 11158488}}</ref> |
||
The most common manifestations of Down syndrome are the characteristic facial features, cognitive impairment, [[congenital heart disease]], hearing deficits, [[short stature]], [[thyroid]] disorders, and [[Alzheimer's disease]]. Other less common serious illnesses include [[leukemia]], [[immune deficiency|immune deficiencies]], and [[epilepsy]]. Down syndrome can result from several different genetic mechanisms. This results in a wide variability in individual symptoms due to complex gene and environment interactions. Prior to birth, it is not possible to predict the symptoms that an individual with Down syndrome will develop. Some problems are present at birth, such as certain heart malformations. Others become apparent over time, such as epilepsy. |
The most common manifestations of Down syndrome are the characteristic facial features, cognitive impairment, [[congenital heart disease]], hearing deficits, [[short stature]], [[thyroid]] disorders, and [[Alzheimer's disease]]. Other less common serious illnesses include [[leukemia]], [[immune deficiency|immune deficiencies]], and [[epilepsy]]. Down syndrome can result from several different genetic mechanisms. This results in a wide variability in individual symptoms due to complex gene and environment interactions. Prior to birth, it is not possible to predict the symptoms that an individual with Down syndrome will develop. Some problems are present at birth, such as certain heart malformations. Others become apparent over time, such as epilepsy. |
||
| Line 129: | Line 132: | ||
</ref> |
</ref> |
||
== |
==Genetic research== |
||
{{main|Research of Down syndrome-related genes}} |
{{main|Research of Down syndrome-related genes}} |
||
Down syndrome disorders are based on having too many copies of the [[gene]]s located on chromosome 21. In general, this leads to an overexpression of the genes.<ref>{{cite journal| author=R Mao, CL Zielke, HR Zielke, J Pevsner| title=Global up-regulation of chromosome 21 gene expression in the developing Down syndrome brain| journal=[[Genomics]]| year=2003| volume=81| issue=5| pages=457-467| url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WG1-487KHTJ-1&_coverDate=05%2F31%2F2003&_alid=422057371&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_qd=1&_cdi=6809&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=9ec6c22133f1645bad48a10a8fb14485}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| author=Rong Mao, X Wang, EL Spitznagel, LP Frelin, JC Ting, H Ding, J Kim, I Ruczinski, TJ Downey, J Pevsner| title=Primary and secondary transcriptional effects in the developing human Down syndrome brain and heart| journal=Genome Biology| year=2005| volume=6| issue=13| pages=R107| url=http://www.pubmedcentral.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract&artid=1414106}}</ref> Understanding the genes involved may help to target medical treatment to individuals with Down syndrome. It is estimated that chromosome 21 contains 200 to 250 genes.<ref name=Leshin> |
Down syndrome disorders are based on having too many copies of the [[gene]]s located on chromosome 21. In general, this leads to an overexpression of the genes.<ref>{{cite journal| author=R Mao, CL Zielke, HR Zielke, J Pevsner| title=Global up-regulation of chromosome 21 gene expression in the developing Down syndrome brain| journal=[[Genomics]]| year=2003| volume=81| issue=5| pages=457-467| url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WG1-487KHTJ-1&_coverDate=05%2F31%2F2003&_alid=422057371&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_qd=1&_cdi=6809&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=9ec6c22133f1645bad48a10a8fb14485}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| author=Rong Mao, X Wang, EL Spitznagel, LP Frelin, JC Ting, H Ding, J Kim, I Ruczinski, TJ Downey, J Pevsner| title=Primary and secondary transcriptional effects in the developing human Down syndrome brain and heart| journal=Genome Biology| year=2005| volume=6| issue=13| pages=R107| url=http://www.pubmedcentral.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract&artid=1414106}}</ref> Understanding the genes involved may help to target medical treatment to individuals with Down syndrome. It is estimated that chromosome 21 contains 200 to 250 genes.<ref name="Leshin">{{cite web |author=Leshin, L. |year=2003 |url=http://www.ds-health.com/trisomy.htm |title=Trisomy 21: The Story of Down Syndrome |accessdate=2006-05-21}}</ref> Recent research has identified a region of the chromosome that contains the main genes responsible for the pathogenesis of Down syndrome,<ref>{{cite journal| author=Zohra Rahmani, Jean-Louis Blouin, Nicole Créau-Goldberg, Paul C. Watkins, Jean-François Mattei, Marc Poissonnier, Marguerite Prieur, Zoubida Chettouh, Annie Nicole, Alain Aurias, Pierre-Marie Sinet, Jean-Maurice Delabar| title=Down syndrome critical region around D21S55 on proximal 21q22.3| journal=[[American Journal of Medical Genetics]]| year=2005| volume=37| issue=S2| pages=98-103| url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/110515872/ABSTRACT?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0}}</ref> located proximal to 21q22.3. The search for major genes involved in Down syndrome characteristics is normally in the region 21q21–21q22.3. |
||
Recent use of [[genetically modified organism|transgenic]] [[mouse|mice]] to study specific genes in the Down syndrome critical region |
Recent use of [[genetically modified organism|transgenic]] [[mouse|mice]] to study specific genes in the Down syndrome critical region has yielded some results. [[Amyloid beta|APP]] ({{OMIM|104760}}, located at [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/getmap.cgi?l104760 21q21]) is an [[Amyloid beta]] A4 precursor protein. It is suspected to have a major role in cognitive difficulties.<ref>{{cite web |title=Down syndrome traced to one gene |publisher=''The Scientist'' |first=Chandra |last= Shekhar |url=http://www.the-scientist.com/news/display/23869/ |date=2006-07-06 |accessdate=2006-07-11}}</ref> Another gene, ETS2 ({{OMIM|164740}}, located at [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/getmap.cgi?l164740 21q22.3]) is Avian Erythroblastosis Virus E26 Oncogene Homolog 2. Researchers have "demonstrated that overexpression of ETS2 results in [[apoptosis]]. Transgenic mice overexpressing ETS2 developed a smaller thymus and lymphocyte abnormalities, similar to features observed in Down syndrome."<ref>{{cite web |author=OMIM, NIH |url=http://www3.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=164740 |title=V-ETS Avian Erythroblastosis virus E26 Oncogene Homolog 2 |accessdate=2006-06-29}}</ref> |
||
== |
==Sociological and cultural aspects== |
||
[[Disability|Advocates]] for people with Down syndrome point to various factors, such as special education and parental support groups, that make life easier for parents. There are also |
[[Disability|Advocates]] for people with Down syndrome point to various factors, such as special education and parental support groups, that make life easier for parents. There are also strides being made in education, housing, and social settings to create "Down-friendly" environments. In most developed countries, since the early twentieth century many people with Down syndrome were housed in institutions or colonies and excluded from society. However, in the twenty first century there is a change among parents, educators and other professionals generally advocating a policy of "inclusion",<ref>{{cite book |title=Inclusion: Educating Students with Down Syndrome with Their Non-Disabled Peers |publisher=National Down Syndrome Society |url=http://www.ndss.org/content.cfm?fuseaction=InfoRes.SchEduarticle&article=571 |accessdate=2006-05-21}}</ref> bringing people with any form of mental or physical disability into general society as much as possible. In many countries, people with Down syndrome are educated in the normal school system; there are increasingly higher-quality opportunities to mix "special" education with regular education settings |
||
Despite this change, reduced abilities of people with Down syndrome pose a challenge to their parents and families. |
Despite this change, reduced abilities of people with Down syndrome pose a challenge to their parents and families. Although living with their parents is preferable to institutionalization for most people with Down syndrome, they often encounter patronising attitudes and discrimination in the wider community. In the past decade, many couples with Down Syndrome have married and started families, overcoming many of the stereotypes associated with this condition. |
||
The first World Down Syndrome Day was held on [[21 March]] [[2006]]. The day and month were chosen to correspond with [[Chromosome 21|21]] and [[trisomy]] respectively. It was proclaimed by Down Syndrome International.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.worlddownsyndromeday.org|title=World Down Syndrome Day| accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> |
The first World Down Syndrome Day was held on [[21 March]] [[2006]]. The day and month were chosen to correspond with [[Chromosome 21|21]] and [[trisomy]] respectively. It was proclaimed by Down Syndrome International.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.worlddownsyndromeday.org|title=World Down Syndrome Day| accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> |
||
== |
==History== |
||
{{main|History of Down syndrome}} |
{{main|History of Down syndrome}} |
||
English physician [[John Langdon Down]] first characterized Down syndrome as a distinct form of mental retardation in 1862, and in a more widely published report in 1866 entitled "Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots".<ref>{{cite journal| author=Down, J.L.H.| year=1866| title=Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots| journal=Clinical Lecture Reports, London Hospital| volume=3| pages=259-262| url=http://www.neonatology.org/classics/down.html| accessdate=2006-07-14}} For a history of the disorder, see {{cite book | title= John Langdon Down, 1828-1896 | author=OC Ward |publisher=Royal Society of Medicine Press | id=<small>ISBN |
English physician [[John Langdon Down]] first characterized Down syndrome as a distinct form of mental retardation in 1862, and in a more widely published report in 1866 entitled "Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots".<ref>{{cite journal| author=Down, J.L.H.| year=1866| title=Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots| journal=Clinical Lecture Reports, London Hospital| volume=3| pages=259-262| url=http://www.neonatology.org/classics/down.html| accessdate=2006-07-14}} For a history of the disorder, see {{cite book | title= John Langdon Down, 1828-1896 | author=OC Ward |publisher=Royal Society of Medicine Press | id=<small>ISBN 1-85315-374-5|year = 1998}} or {{cite web| last=Conor| first=Ward |url =http://www.intellectualdisability.info/values/history_DS.htm| title =John Langdon Down and Down's syndrome (1828 - 1896)| accessdate =2006-06-02}}</ref> Due to his perception that children with Down syndrome shared physical facial similarities ([[epicanthal fold]]s) with those of [[Johann Friedrich Blumenbach|Blumenbach's Mongolian race]], Down used terms such as ''mongolism'' and ''mongolian idiocy''.<ref>{{cite journal|Author =Conor, W.O.| year =1999| title =John Langdon Down: The Man and the Message| journal =Down Syndrome Research and Practice| volume =6| issue =1| pages =19-24| url =http://www.down-syndrome.info/library/periodicals/dsrp/06/1/019/DSRP-06-1-019-EN-GB.htm| accessdate =2006-06-02}}</ref> [[Idiot|Idiocy]] was a medical term used at that time to refer to a severe degree of intellectual impairment. Down wrote that mongolism represented "retrogression," the appearance of [[Mongoloid]] traits in the children of allegedly more advanced Caucasian parents. |
||
By the 20<sup>th</sup> century, "mongolian idiocy" had become the most recognizable form of mental retardation. Most |
By the 20<sup>th</sup> century, "mongolian idiocy" had become the most recognizable form of mental retardation. Most individuals with Down syndrome were [[institutionalization|institutionalized]], few of the associated medical problems were treated, and most died in infancy or early adult life. With the rise of the [[eugenics]] movement, 33 of the 48 states in the [[USA]] and several countries began programs of involuntary sterilization of individuals with Down syndrome and comparable degrees of disability. The ultimate expression of this type of public policy was the [[Germany|German]] [[euthanasia]] program [[T-4 Euthanasia Program|"Aktion T-4"]], begun in 1940. Court challenges and public revulsion led to discontinuation or repeal of such programs during the decades after [[World War II]]. |
||
Until the middle of the 20th century, the cause of Down syndrome remained unknown |
Until the middle of the 20th century, the cause of Down syndrome remained unknown. However, the presence in all races, the association with older maternal age, and the rarity of recurrence had been noticed. Standard medical texts assumed it was caused by a combination of inheritable factors which had not been identified. Other theories focused on injuries sustained during birth.<ref>{{cite book |author=Warkany, J. |title=Congenital Malformations |location=Chicago |publisher=Year Book Medical Publishers, Inc |date=1971 |pages=313-314 |id=ISBN 0-8151-9098-0}}</ref> |
||
With the discovery of [[karyotype]] techniques in the 1950s it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959, [[Jérôme Lejeune|Professor Jérôme Lejeune]] discovered that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fondationlejeune.org/eng/Content/Fondation/professeurlj.asp |title=Jérôme Lejeune Foundation|accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> The extra chromosome was subsequently labeled as the 21st, and the condition as [[Aneuploidy#Trisomy|trisomy]] [[Chromosome 21|21]]. |
With the discovery of [[karyotype]] techniques in the 1950s, it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959, [[Jérôme Lejeune|Professor Jérôme Lejeune]] discovered that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.fondationlejeune.org/eng/Content/Fondation/professeurlj.asp |title=Jérôme Lejeune Foundation |accessdate=2006-06-02}}</ref> The extra chromosome was subsequently labeled as the 21st, and the condition as [[Aneuploidy#Trisomy|trisomy]] [[Chromosome 21|21]]. |
||
In 1961, |
In 1961, nineteen geneticists wrote to the editor of ''[[The Lancet]]'' suggesting that ''mongolian idiocy'' had "misleading connotations," had become "an embarrassing term," and should be changed.<ref>{{cite journal |first=Allen |last=Gordon |coauthors=C.E. Benda, J.A. Böök, C.O. Carter, C.E. Ford, E.H.Y. Chu, E. Hanhart, George Jervis, W. Langdon-Down, J. Lejeune, H. Nishimura, J. Oster, L.S. Penrose, P.E. Polani, Edith L. Potter, Curt Stern, R. Turpin, J. Warkany, and Herman Yannet |year=1961 |title=Mongolism (Correspondence) |journal=[[The Lancet]] |pages=775 |volume=1 |issue=7180}}</ref> ''The Lancet'' supported ''Down's Syndrome''. The [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) officially dropped references to ''mongolism'' in 1965 after a request by the Mongolian delegate.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Howard-Jones |first=Norman| date=1979 |title=On the diagnostic term "Down's disease"| journal=Medical History |volume=23 |issue=1 |pages=102-104 |id=PMID 153994}}</ref> |
||
In 1975, the United States [[National Institute of Health]] convened a conference to standardize the nomenclature of malformations. They recommended eliminating the possessive form: "The possessive use of an eponym should be discontinued, since the author neither had nor owned the disorder."<ref>A planning meeting was held on 20 March 1974, resulting in a letter to ''The Lancet''.{{cite journal |
In 1975, the United States [[National Institute of Health]] convened a conference to standardize the nomenclature of malformations. They recommended eliminating the possessive form: "The possessive use of an eponym should be discontinued, since the author neither had nor owned the disorder."<ref>A planning meeting was held on [[20 March]] [[1974]], resulting in a letter to ''The Lancet''.{{cite journal |year=1974 |title=Classification and nomenclature of malformation (Discussion) |journal=[[The Lancet]] |pages=798 |volume=303 |issue=7861}} The conference was held [[10 February]]-[[11 February]] [[1975]], and reported to ''The Lancet'' shortly afterward.{{cite journal |year=1975 |title=Classification and nomenclature of morphological defects (Discussion) |journal=[[The Lancet]] |pages=513 |volume=305 |issue=7905}}</ref> Although both the possessive and non-possessive forms are used in the general population, Down syndrome is the accepted term among professionals in the USA, Canada and other countries; Down's syndrome is still used in the United Kingdom and other areas.<ref name=name>{{cite web |last=Leshin |first=Len| date=2003 |url=http://www.ds-health.com/name.htm |title=What's in a name |accessdate=2006-05-12}}</ref> |
||
== |
==Notable individuals== |
||
<!--- Do not add individuals here unless they have an entry in Wikipedia and the entry specifically mentions Down syndrome, or you can cite another source for such a claim ---> |
<!--- Do not add individuals here unless they have an entry in Wikipedia and the entry specifically mentions Down syndrome, or you can cite another source for such a claim ---> |
||
[[Image:Life Goes On. |
[[Image:Life Goes On.png|thumb|221px|right|Chris Burke (far right) was an actor on ''[[Life Goes On (TV series)|Life Goes On]]'']] |
||
Notable people with Down syndrome include: |
Notable people with Down syndrome include: |
||
* [[Chris Burke (actor)|Chris Burke]], actor (''[[Life Goes On (TV series)|Life Goes On]]'') and autobiographer |
* [[Chris Burke (actor)|Chris Burke]], actor (''[[Life Goes On (TV series)|Life Goes On]]'') and autobiographer |
||
* [[Anne de Gaulle]] (1928-1948), daughter of [[Charles de Gaulle]] |
* [[Anne de Gaulle]] (1928-1948), daughter of [[Charles de Gaulle]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Duo (film)|Stephane Ginnsz]], actor (''[[Duo (film)|Duo]]'') — first actor with Down syndrome in the lead part of a motion picture. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Duo (film)|Stephane Ginnsz]], actor (''[[Duo (film)]]'') First actor with Down syndrome in the lead part of a motion picture. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Judith Scott]], artist |
* [[Judith Scott]], artist |
||
* [[Reynols|Miguel Tomasin]], singer with Argentinian avant-rock band [[Reynols]] |
* [[Reynols|Miguel Tomasin]], singer with Argentinian avant-rock band [[Reynols]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
The Down Syndrome Association of Los Angeles has a more complete list of [http://www.dsala.org/media.htm individuals with Down syndrome in roles in TV and movies]. |
|||
The Down Syndrome Association of Los Angeles maintains a list of individuals with Down syndrome in roles in TV and movies.<ref>Down Syndrome Association of Los Angeles. [http://www.dsala.org/media.htm Media Archive: Television and Film that include individuals with Down Syndrome.] Retrieved 1 December 2006.</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Bret Lott]]: ''[[Jewel (novel)|Jewel]]'' |
* [[Bret Lott]]: ''[[Jewel (novel)|Jewel]]'' |
||
* [[Bernice Rubens]]: ''[[A Solitary Grief]]'' |
* [[Bernice Rubens]]: ''[[A Solitary Grief]]'' |
||
* Paul M Belous & Robert Wolterstorff: ''[[Quantum Leap]]: Jimmy'' |
|||
* [[Emily Perl Kingsley]]: ''[[Welcome to Holland]]'' |
* [[Emily Perl Kingsley]]: ''[[Welcome to Holland]]'' |
||
* [[The Kingdom (television)|The Kingdom]] and its American counterpart, ''[[Kingdom Hospital]]'' |
* [[The Kingdom (television)|The Kingdom]] and its American counterpart, ''[[Kingdom Hospital]]'' |
||
| Line 183: | Line 187: | ||
* [[Kim Edwards]]: ''[[The Memory Keeper's Daughter]]'' |
* [[Kim Edwards]]: ''[[The Memory Keeper's Daughter]]'' |
||
== |
==References== |
||
<!--See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for an explanation of how to generate footnotes using the <ref(erences/)> tags--> |
<!--See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for an explanation of how to generate footnotes using the <ref(erences/)> tags--> |
||
<div class="references-small"><references/></div> |
<div class="references-small"><references/></div> |
||
== |
==Bibliography== |
||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| last =Beck |
| last =Beck |
||
| Line 213: | Line 217: | ||
| url =http://www.dsrf.co.uk/Reading_material/Bright_beginnings.htm |
| url =http://www.dsrf.co.uk/Reading_material/Bright_beginnings.htm |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* Hassold, T.J., D. Patterson, eds. (1999). ''Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together''. New York: Wiley Liss. |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last =Hassold |
|||
| first =T.J. |
|||
| coauthors =D. Patterson |
|||
| editor =editors, |
|||
| year =1999 |
|||
| title =Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together |
|||
| publisher =Wiley Liss |
|||
| location =New York |
|||
}} |
|||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| last =Kingsley |
| last =Kingsley |
||
| Line 228: | Line 223: | ||
| coauthors =M. Levitz |
| coauthors =M. Levitz |
||
| year =1994 |
| year =1994 |
||
| title =Count |
| title =Count Us In: Growing up with Down Syndrome |
||
| publisher =Harcourt Brace |
| publisher =Harcourt Brace |
||
| location =San |
| location =San Diego |
||
}} |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last =Pueschel |
|||
| first =S.M. |
|||
| coauthors =M. Sustrova |
|||
| editor =editors, |
|||
| year =1997 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| publisher =Paul H. Brookes |
|||
| location =Baltimore, MD USA |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| last =Selikowitz |
| last =Selikowitz |
||
| first =M. |
| first =M. |
||
| edition = |
| edition =2nd edition |
||
| year =1997 |
| year =1997 |
||
| title =Down Syndrome: The Facts |
| title =Down Syndrome: The Facts |
||
| publisher =Oxford University Press |
| publisher =Oxford University Press |
||
| location =Oxford |
| location =Oxford, UK |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| last =Van Dyke |
| last =Van Dyke |
||
| first =D.C. |
| first =D.C. |
||
| coauthors =P.J. Mattheis |
| coauthors =P.J. Mattheis, S. Schoon Eberly, J. Williams |
||
| year =1995 |
| year =1995 |
||
| title =Medical and Surgical Care for Children with Down Syndrome |
| title =Medical and Surgical Care for Children with Down Syndrome |
||
| publisher =Woodbine House |
| publisher =Woodbine House |
||
| location =Bethesda, MD |
| location =Bethesda, MD |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| Line 269: | Line 255: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
== |
==External links== |
||
{{ |
{{commonscat|Down syndrome}} |
||
For comprehensive lists of Down syndrome links see |
For comprehensive lists of Down syndrome links see |
||
* [http://www.downsyndrome.com/ Directory of Down Syndrome Internet Sites (US based, but contains international links)] |
* [http://www.downsyndrome.com/ Directory of Down Syndrome Internet Sites (US based, but contains international links)] |
||
* [http://www.43green.freeserve.co.uk/uk_downs_syndrome/index.html UK resources for Down's syndrome] |
* [http://www.43green.freeserve.co.uk/uk_downs_syndrome/index.html UK resources for Down's syndrome] |
||
===Societies and |
===Societies and associations=== |
||
<!-- This list is not for local support organizations, there are simply too many. Contact the lists in the previous subheading to make sure you are listed there, it is more appropriate. --> |
<!-- This list is not for local support organizations, there are simply too many. Contact the lists in the previous subheading to make sure you are listed there, it is more appropriate. --> |
||
* [http://www.down-syndrome-int.org Down Syndrome International] |
* [http://www.down-syndrome-int.org Down Syndrome International] |
||
* [http://www.downsed.org The Down Syndrome Educational Trust] |
* [http://www.downsed.org The Down Syndrome Educational Trust] |
||
'''By |
'''By country''' |
||
* [http://www.cdss.ca Canadian Down Syndrome Society (Canada)] |
* [http://www.cdss.ca Canadian Down Syndrome Society (Canada)] |
||
* [http://www.dsrf.org/ Down Syndrome Research Foundation (Canada)] |
* [http://www.dsrf.org/ Down Syndrome Research Foundation (Canada)] |
||
| Line 287: | Line 274: | ||
* [http://www.ndsccenter.org/ National Down Syndrome Congress (USA)] |
* [http://www.ndsccenter.org/ National Down Syndrome Congress (USA)] |
||
* [http://www.imdsa.com International Mosaic Down Syndrome Association (USA)] |
* [http://www.imdsa.com International Mosaic Down Syndrome Association (USA)] |
||
* [http://www.dhg.org.uk Down's Heart Group (heart conditions related to Down's Syndrome) ] |
|||
===Conferences=== |
===Conferences=== |
||
| Line 304: | Line 292: | ||
[[et:Downi sündroom]] |
[[et:Downi sündroom]] |
||
[[es:Síndrome de Down]] |
[[es:Síndrome de Down]] |
||
[[fa:سندرم داون]] |
|||
[[fr:Syndrome de Down]] |
[[fr:Syndrome de Down]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[ko:다운증후군]] |
[[ko:다운증후군]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[it:Sindrome di Down]] |
[[it:Sindrome di Down]] |
||
[[he:תסמונת דאון]] |
[[he:תסמונת דאון]] |
||
[[nl:Syndroom van Down]] |
[[nl:Syndroom van Down]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[ka:დაუნის სინდრომი]] |
|||
[[no:Downs syndrom]] |
[[no:Downs syndrom]] |
||
[[pl:Zespół Downa]] |
[[pl:Zespół Downa]] |
||
[[pt:Síndrome de Down]] |
[[pt:Síndrome de Down]] |
||
[[ru:Болезнь Дауна]] |
[[ru:Болезнь Дауна]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[sk:Downov syndróm]] |
[[sk:Downov syndróm]] |
||
[[sr:Даунов синдром]] |
[[sr:Даунов синдром]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[sv:Downs syndrom]] |
[[sv:Downs syndrom]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[zh:唐氏综合症]] |
[[zh:唐氏综合症]] |
||
Revision as of 10:39, 5 December 2006
| Down syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Medical genetics, neurology |
| Frequency | 0.1% |
Down syndrome or trisomy 21 (in British English: Down's syndrome) is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of an extra 21st chromosome. It is named after John Langdon Down, the British doctor who first described it in 1866. The condition is characterized by a combination of major and minor abnormalities in body structure and function. Most Down syndrome cases feature impairment of learning and physical growth as well as a recognizable facial appearance usually identified at birth.
Individuals with Down syndrome have lower than average cognitive ability, normally ranging from mild to moderate mental retardation. They generally have some developmental disability, such as a tendency toward concrete thinking or naïveté. Some have low intelligence, and a small number suffer from severe to profound mental retardation. The incidence of Down syndrome is estimated at 1 per 800 to 1 per 1000 births.
The common physical features of Down syndrome also appear in people with a standard set of chromosomes. They include a single transverse palmar crease (a single instead of a double crease across one or both palms), an almond shape to the eyes caused by an epicanthic fold of the eyelid, shorter limbs, speech impairment, and protruding tongue. Health concerns for individuals with Down syndrome include a higher risk for congenital heart defects, gastroesophageal reflux disease, recurrent ear infections, obstructive sleep apnea, and thyroid dysfunctions.
Early childhood intervention, screening for common problems, medical treatment where indicated, a conducive family environment, and vocational training can improve the overall development of children with Down syndrome. Although some of the genetic limitations of Down Syndrome cannot be overcome, education and proper care can improve quality of life.[1]
Characteristics
Individuals with Down syndrome may have some or all of the following physical characteristics:[2] oblique eye fissures with epicanthic skin folds on the inner corner of the eyes, muscle hypotonia, a flat nasal bridge, a single palmar fold (also known as a simian crease), a protruding tongue (due to small oral cavity, poor muscle tone, and an enlarged tongue near the tonsils), a short neck, white spots on the iris known as Brushfield spots,[3] excessive flexibility in joints, congenital heart defects, excessive space between large and second toe, and a single flexion furrow of the fifth finger. Most individuals with Down syndrome have mental retardation in the mild (IQ 50–70) to moderate (IQ 35–50) range,[4] with scores of children having Mosaic Down syndrome (explained below) typically 10–30 points higher.[5] In addition, individuals with Down syndrome can have serious abnormalities affecting any body system.
Genetics
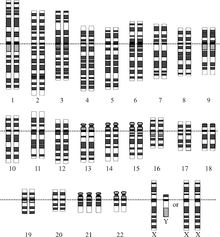
Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality characterized by the presence of an extra copy of genetic material on the 21st chromosome, either in whole (trisomy 21) or part (such as due to translocations). The effects of the extra copy vary greatly among individuals, depending on the extent of the extra copy, genetic background, environmental factors, and random chance. Down syndrome occurs in all human populations, and analogous effects have been found in other species such as chimpanzees and mice. Recently, researchers have created transgenic mice with most of human chromosome 21 (in addition to the normal mouse chromosomes).[6] The extra chromosomal material can come about in several distinct ways. A normal human karyotype is designated as 46,XX or 46,XY, indicating 46 chromosomes with an XX arrangement for females and 46 chromosomes with an XY arrangement for males.[7]
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 21 (47,XX,+21) is caused by a meiotic nondisjunction event. With nondisjunction, a gamete (i.e., a sperm or egg cell) is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21; the gamete thus has 24 chromosomes. When combined with a normal gamete from the other parent, the embryo now has 47 chromosomes, with three copies of chromosome 21. Trisomy 21 is the cause of approximately 95% of observed Down syndromes, with 88% coming from nondisjunction in the maternal gamete and 8% coming from nondisjunction in the paternal gamete.[8]
Mosaicism
Trisomy 21 is generally caused prior to conception, and all cells in the body are affected. However, when some of the cells in the body are normal and other cells have trisomy 21, it is called Mosaic Down Syndrome (46,XX/47,XX,+21).[9] This can occur in one of two ways: A nondisjunction event during an early cell division in a normal embryo leads to a fraction of the cells with trisomy 21; or a Down syndrome embryo undergoes nondisjunction and some of the cells in the embryo revert back to the normal chromosomal arrangement. There is considerable variability in the fraction of trisomy 21, both as a whole and among tissues. This is the cause of 1–2% of the observed Down syndromes.[8]
Robertsonian translocation
The extra chromosome 21 material that causes Down syndrome may be due to a Robertsonian translocation. In this case, the long arm of chromosome 21 is attached to another chromosome, often chromosome 14 (45,XX,t(14;21q)) or itself (called an isochromosome, 45,XX,t(21q;21q)). Normal disjunction leading to gametes have a significant chance of creating a gamete with an extra chromosome 21. Translocation Down syndrome is often referred to as familial Down syndrome. It is the cause of 2-3% of observed cases of Down syndrome.[8] It does not show the maternal age effect, and is just as likely to have come from fathers as mothers.
Duplication of a portion of chromosome 21
Rarely, a region of chromosome 21 will undergo a duplication event. This will lead to extra copies of some, but not all, of the genes on chromosome 21 (46,XX,dup(21q)).[10] If the duplicated region has genes that are responsible for Down syndrome physical and mental characteristics, such individuals will show those characteristics. This cause is very rare and no rate estimates are available.
Incidence
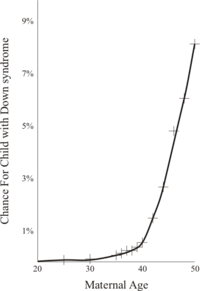
The incidence of Down syndrome is estimated at 1 per 800 to 1 per 1000 births.[12] In 2006, the Center for Disease Control estimated the rate as 1 per 733 live births in the United States (5429 new cases per year).[13] Approximately 95% of these are trisomy 21. Down syndrome occurs in all ethnic groups and among all economic classes.
Maternal age influences the risk of conceiving a baby with Down syndrome. At maternal age 20 to 24, the risk is 1/1490; at age 40 the risk is 1/106, and at age 49 the risk is 1/11.[14] Although the risk increases with maternal age, 80% of children with Down syndrome are born to women under the age of 35,[15] reflecting the overall fertility of that age group. Other than maternal age, no other risk factors are known. There does not appear to be a paternal age effect.
Many standard prenatal screens can discover Down syndrome. Genetic counseling along with genetic testing, such as amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS), or percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) are usually offered to families who may have an increased chance of having a child with Down syndrome, or where normal prenatal exams indicate possible problems. Genetic screens are often performed on pregnant women older than 30 or 35.
Prenatal screening
Pregnant women can be screened for various complications in their pregnancy, or due to risk factors such as advanced maternal age. There are several common non-invasive screens that can indicate a fetus with Down syndrome, and are normally performed in the late first trimester or early second trimester. Due to the nature of screens, each has a significant chance of a false positive, suggesting a fetus with Down syndrome when, in fact, the fetus does not have this genetic abnormality. Screen positives must be verified before a Down syndrome diagnosis is made. Common screening procedures for Down syndrome are given in Table 1.
| Screen | When performed (weeks gestation) | Detection rate | False positive rate | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triple screen | 15–20 | 75% | 8.5% | This test measures the maternal serum alpha feto protein (a fetal liver protein), estriol (a pregnancy hormone), and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, a pregnancy hormone).[16] |
| Quad screen | 15–20 | 79% | 7.5% | This test measures the maternal serum alpha feto protein (a fetal liver protein), estriol (a pregnancy hormone), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, a pregnancy hormone), and high inhibin-Alpha (INHA).[16] |
| AFP/free beta screen | 13–22 | 80% | 2.8% | This test measures the alpha feto protein, produced by the fetus, and free beta hCG, produced by the placenta. |
| Nuchal translucency/free beta/PAPPA screen | 10–13.5 | 91%[17] | 5%[17] | Uses ultrasound to measure Nuchal Translucency in addition to the freeBeta hCG and PAPPA (pregnancy-associate plasma protein A, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 176385). NIH has confirmed that this first trimester test is more accurate than second trimester screening methods.[18] |

Even with the best non-invasive screens, the detection rate is 90%–95% and the rate of false positive is 2%–5%. False positives can be caused by undetected multiple fetuses (very rare with the ultrasound tests), incorrect date of pregnancy, or normal variation in the proteins.
Confirmation of screen positive is normally accomplished with amniocentesis. This is an invasive procedure and involves taking amniotic fluid from the mother and identifying fetal cells. The lab work can take a couple of weeks but will detect over 99.8% of all numerical chromosomal problems with a very low false positive rate.[19]
Due to the low incidence of Down syndrome, a vast majority of early screen positives are false.[20] Since the risk of spontaneous abortion is approximately 1/200 to 1/300,[21] amniocentesis confirmation presents a risk of spontaneously aborting a healthy fetus (while testing from a false positive).
A 2002 literature review of elective abortion rates found that 91–93% of pregnancies with a diagnosis of Down syndrome were terminated.[22] Physicians and ethicists are concerned about the ethical ramifications,[23] with some commentators calling it "eugenics by abortion".[24] Many members of the disability rights movement "believe that public support for prenatal diagnosis and abortion based on disability contravenes the movement's basic philosophy and goals."[25]
Cognitive development
Cognitive development in children with Down syndrome is quite variable. It is not possible at birth to predict their capabilities. The identification of the best methods of teaching each particular child ideally begins soon after birth through early intervention programs.[26] Since children with Down syndrome have a wide range of abilities, success at school can vary greatly, which stresses the importance of evaluating children individually. The cognitive problems that are found among children with Down syndrome can also be found among typical children. Therefore, parents can use general programs that are offered through the schools or other means.
Language skills show a difference between understanding speech and expressing speech. It is common for children with Down syndrome to need speech therapy to help with expressive language.[27] Fine motor skills are delayed[28] and often lag behind gross motor skills and can interfere with cognitive development. Occupational therapy can address these issues.[29]
In education, mainstreaming of children with Down syndrome is controversial. Mainstreaming is when students of differing abilities are placed in classes with their chronological peers. Children with Down syndrome do not age emotionally/socially and intellectually at the same rates as children without Down syndrome, so eventually the intellectual and emotional gap between children with and without Down syndrome widens. Complex thinking as required in sciences but also in history, the arts, and other subjects is often beyond their abilities, or achieved much later than in most children. Therefore, if they are to benefit from mainstreaming without feeling inferior most of the time, special adjustments must be made to the curriculum.[30]
Some European countries such as Germany and Denmark advise a two-teacher system, whereby the second teacher takes over a group of children with disabilities within the class. A popular alternative is cooperation between special education schools and mainstream schools. In cooperation, the core subjects are taught in separate classes, which neither slows down the typical students nor neglects the students with disabilities. Social activities, outings, and many sports and arts activities are performed together, as are all breaks and meals.[31]
Health
The medical consequences of the extra genetic material in Down syndrome are highly variable and may affect the function of any organ system or bodily process. The health aspects of Down syndrome encompass anticipating and preventing effects of the condition, recognizing complications of the disorder, managing individual symptoms, and assisting the individual and his/her family in coping and thriving with any related disability or illnesses.[32]
The most common manifestations of Down syndrome are the characteristic facial features, cognitive impairment, congenital heart disease, hearing deficits, short stature, thyroid disorders, and Alzheimer's disease. Other less common serious illnesses include leukemia, immune deficiencies, and epilepsy. Down syndrome can result from several different genetic mechanisms. This results in a wide variability in individual symptoms due to complex gene and environment interactions. Prior to birth, it is not possible to predict the symptoms that an individual with Down syndrome will develop. Some problems are present at birth, such as certain heart malformations. Others become apparent over time, such as epilepsy.
These factors contribute to a significantly shorter lifespan for people with Down syndrome. One study, carried out in the United States, shows an average lifespan of 49 years.[33]
Genetic research
Down syndrome disorders are based on having too many copies of the genes located on chromosome 21. In general, this leads to an overexpression of the genes.[34][35] Understanding the genes involved may help to target medical treatment to individuals with Down syndrome. It is estimated that chromosome 21 contains 200 to 250 genes.[36] Recent research has identified a region of the chromosome that contains the main genes responsible for the pathogenesis of Down syndrome,[37] located proximal to 21q22.3. The search for major genes involved in Down syndrome characteristics is normally in the region 21q21–21q22.3.
Recent use of transgenic mice to study specific genes in the Down syndrome critical region has yielded some results. APP (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 104760, located at 21q21) is an Amyloid beta A4 precursor protein. It is suspected to have a major role in cognitive difficulties.[38] Another gene, ETS2 (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 164740, located at 21q22.3) is Avian Erythroblastosis Virus E26 Oncogene Homolog 2. Researchers have "demonstrated that overexpression of ETS2 results in apoptosis. Transgenic mice overexpressing ETS2 developed a smaller thymus and lymphocyte abnormalities, similar to features observed in Down syndrome."[39]
Sociological and cultural aspects
Advocates for people with Down syndrome point to various factors, such as special education and parental support groups, that make life easier for parents. There are also strides being made in education, housing, and social settings to create "Down-friendly" environments. In most developed countries, since the early twentieth century many people with Down syndrome were housed in institutions or colonies and excluded from society. However, in the twenty first century there is a change among parents, educators and other professionals generally advocating a policy of "inclusion",[40] bringing people with any form of mental or physical disability into general society as much as possible. In many countries, people with Down syndrome are educated in the normal school system; there are increasingly higher-quality opportunities to mix "special" education with regular education settings
Despite this change, reduced abilities of people with Down syndrome pose a challenge to their parents and families. Although living with their parents is preferable to institutionalization for most people with Down syndrome, they often encounter patronising attitudes and discrimination in the wider community. In the past decade, many couples with Down Syndrome have married and started families, overcoming many of the stereotypes associated with this condition.
The first World Down Syndrome Day was held on 21 March 2006. The day and month were chosen to correspond with 21 and trisomy respectively. It was proclaimed by Down Syndrome International.[41]
History
English physician John Langdon Down first characterized Down syndrome as a distinct form of mental retardation in 1862, and in a more widely published report in 1866 entitled "Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots".[42] Due to his perception that children with Down syndrome shared physical facial similarities (epicanthal folds) with those of Blumenbach's Mongolian race, Down used terms such as mongolism and mongolian idiocy.[43] Idiocy was a medical term used at that time to refer to a severe degree of intellectual impairment. Down wrote that mongolism represented "retrogression," the appearance of Mongoloid traits in the children of allegedly more advanced Caucasian parents.
By the 20th century, "mongolian idiocy" had become the most recognizable form of mental retardation. Most individuals with Down syndrome were institutionalized, few of the associated medical problems were treated, and most died in infancy or early adult life. With the rise of the eugenics movement, 33 of the 48 states in the USA and several countries began programs of involuntary sterilization of individuals with Down syndrome and comparable degrees of disability. The ultimate expression of this type of public policy was the German euthanasia program "Aktion T-4", begun in 1940. Court challenges and public revulsion led to discontinuation or repeal of such programs during the decades after World War II.
Until the middle of the 20th century, the cause of Down syndrome remained unknown. However, the presence in all races, the association with older maternal age, and the rarity of recurrence had been noticed. Standard medical texts assumed it was caused by a combination of inheritable factors which had not been identified. Other theories focused on injuries sustained during birth.[44]
With the discovery of karyotype techniques in the 1950s, it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959, Professor Jérôme Lejeune discovered that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome.[45] The extra chromosome was subsequently labeled as the 21st, and the condition as trisomy 21.
In 1961, nineteen geneticists wrote to the editor of The Lancet suggesting that mongolian idiocy had "misleading connotations," had become "an embarrassing term," and should be changed.[46] The Lancet supported Down's Syndrome. The World Health Organization (WHO) officially dropped references to mongolism in 1965 after a request by the Mongolian delegate.[47]
In 1975, the United States National Institute of Health convened a conference to standardize the nomenclature of malformations. They recommended eliminating the possessive form: "The possessive use of an eponym should be discontinued, since the author neither had nor owned the disorder."[48] Although both the possessive and non-possessive forms are used in the general population, Down syndrome is the accepted term among professionals in the USA, Canada and other countries; Down's syndrome is still used in the United Kingdom and other areas.[49]
Notable individuals

Notable people with Down syndrome include:
- Chris Burke, actor (Life Goes On) and autobiographer
- Anne de Gaulle (1928-1948), daughter of Charles de Gaulle
- Stephane Ginnsz, actor (Duo) — first actor with Down syndrome in the lead part of a motion picture.
- Joey Moss, Edmonton Oilers locker room attendant
- Isabella Pujols, adopted daughter of St. Louis Cardinals first baseman Albert Pujols
- Judith Scott, artist
- Miguel Tomasin, singer with Argentinian avant-rock band Reynols
The Down Syndrome Association of Los Angeles maintains a list of individuals with Down syndrome in roles in TV and movies.[50]
Portrayal in fiction
- Bret Lott: Jewel
- Bernice Rubens: A Solitary Grief
- Paul M Belous & Robert Wolterstorff: Quantum Leap: Jimmy
- Emily Perl Kingsley: Welcome to Holland
- The Kingdom and its American counterpart, Kingdom Hospital
- Stephen King: Dreamcatcher
- Dean Koontz: The Bad Place
- Jeffrey Eugenides: The Virgin Suicides
- Petal Mitchell, character in EastEnders
- Kim Edwards: The Memory Keeper's Daughter
References
- ^ Roizen NJ, Patterson D.Down's syndrome. Lancet. 2003 12 April;361(9365):1281-9. Review. PMID 12699967
- ^ Wood, Debra (2005). "Down syndrome". Retrieved 2006-06-30.
- ^ "Definition of Brushfield's Spots".
- ^ "Keep Kids Healthy article on Down syndrome".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessedate=ignored (help) - ^ Strom, C. "FAQ from Mosaic Down Syndrome Society". Retrieved 2006-06-03.
- ^ "Down's syndrome recreated in mice". BBC News. 2005-09-22. Retrieved 2006-06-14.
- ^ For a description of human karyotype see Mittleman, A. (editor) (1995). "An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomeclature". Retrieved 2006-06-04.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c "Down syndrome occurrence rates (NIH)". Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ Mosaic Down Syndrome on the Web
- ^ Petersen MB, Tranebjaerg L, McCormick MK, Michelsen N, Mikkelsen M, Antonarakis SE. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic characterization of two unrelated patients with different duplications of 21q. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:104-9. PMID 2149934
- ^ Hook, E.B. (1981). "Rates of chromosomal abnormalities at different maternal ages". Obstet Gynecol. 58: 282.
- ^ Based on estimates by National Institute of Child Health & Human Development "Down syndrome rates". Retrieved 2006-06-21.
- ^ Center for Disease Control (6 January 2006). "Improved National Prevalence Estimates for 18 Selected Major Birth Defects, United States, 1999-2001". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 54 (51 & 52): 1301–1305.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Hook, E.B. (1981). "Rates of chromosomal abnormalities at different maternal ages". Obstet Gynecol. 58: 282.
- ^ Estimate from "National Down Syndrome Center". Retrieved 2006-04-21.
- ^ a b For a current estimate of rates, see Benn, PA, J Ying, T Beazoglou, JFX Egan. "Estimates for the sensitivity and false-positive rates for second trimester serum screening for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 with adjustments for cross-identification and double-positive results". Prenatal Diagnosis. 21 (1): 46–51.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Some practices report adding Nasal Bone measurements and increasing the detection rate to 95% with a 2% False Positive Rate.
- ^ NIH FASTER study (NEJM 2005 (353):2001). See also J.L. Simplson's editorial (NEJM 2005 (353):19).
- ^ Fackler, A. "Down syndrome". Retrieved 2006-09-07.
- ^ Assume the false positive rate is 2% (at the low end), the incidence of Down syndrome is 1/500 (on the high side) with 95% detection, and there is no ascertainment bias. Out of 100,000 screens, 200 will have Down syndrome, and the screen will detect 190 of them. From the 99,800 normal pregnancies, 1996 will be given a positive result. So, among the 2,186 positive test results, 91% will be false positives and 9% will be true positives.
- ^ Benke, P, V. Carver, R Donahue. "Risk and Recurrence Risk of Down Syndrome". Retrieved 2006-09-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Caroline Mansfield, Suellen Hopfer, Theresa M. Marteau (1999). "Termination rates after prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome, spina bifida, anencephaly, and Turner and Klinefelter syndromes: a systematic literature review". Prenatal Diagnosis. 19 (9): 808–812.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) This is similar to 90% results found by David W. Britt, Samantha T. Risinger, Virginia Miller, Mary K. Mans, Eric L. Krivchenia, Mark I. Evans (1999). "Determinants of parental decisions after the prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome: Bringing in context". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 93 (5): 410–416.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Glover, NM and Glover, SJ (1996). "Ethical and legal issues regarding selective abortion of fetuses with Down syndrome". Ment. Retard. 34 (4): 207–214. PMID 8828339.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Will, George (2005-04-14). "Eugenics By Abortion: Is perfection an entitlement?". Washington Post: A37. Retrieved 2006-07-03.
- ^ Erik Parens and Adrienne Asch (2003). "Disability rights critique of prenatal genetic testing: Reflections and recommendations". Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 9 (1): 40-47. Retrieved 2006-07-03.
- ^ "New Parent Guide". National Down Syndrome Society. Retrieved 2006-05-12. Also "Research projects - Early intervention and education". Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ Bird, G. and S. Thomas (2002). "Providing effective speech and language therapy for children with Down syndrome in mainstream settings: A case example". Down Syndrome News and Update. 2 (1): 30–31. Also, Kumin, Libby (1998). "Comprehensive speech and language treatment for infants, toddlers, and children with Down syndrome". In Hassold, T.J.and D. Patterson (ed.). Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together. New York: Wiley-Liss.
- ^ "Development of Fine Motor Skills in Down Syndrome". Retrieved 2006-07-03.
- ^ M. Bruni. "Occupational Therapy and the Child with Down Syndrome". Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ S.E.Armstrong. "Inclusion: Educating Students with Down Syndrome with Their Non-Disabled Peers". Retrieved 2006-05-12. Also, see Debra L. Bosworth. "Benefits to Students with Down Syndrome in the Inclusion Classroom: K-3". Retrieved 2006-06-12. Finally, see a survey by NDSS on inclusion, Gloria Wolpert (1996). "The Educational Challenges Inclusion Study". National Down Syndrome Society. Retrieved 2006-06-28.
- ^ There are many such programs. One is described by Action Alliance for Children, K. Flores. "Special needs, "mainstream" classroom". Retrieved 2006-05-13. Also, see Flores, K. "Special needs, "mainstream" classroom" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-05-13.
- ^ American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Genetics (2001). "American Academy of Pediatrics: Health supervision for children with Down syndrome". Pediatrics. 107 (2): 442–449. PMID 11158488.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Young, Emma (2002-03-22). "Down's syndrome lifespan doubles". New Scientist. Retrieved 2006-10-14.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ R Mao, CL Zielke, HR Zielke, J Pevsner (2003). "Global up-regulation of chromosome 21 gene expression in the developing Down syndrome brain". Genomics. 81 (5): 457–467.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rong Mao, X Wang, EL Spitznagel, LP Frelin, JC Ting, H Ding, J Kim, I Ruczinski, TJ Downey, J Pevsner (2005). "Primary and secondary transcriptional effects in the developing human Down syndrome brain and heart". Genome Biology. 6 (13): R107.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Leshin, L. (2003). "Trisomy 21: The Story of Down Syndrome". Retrieved 2006-05-21.
- ^ Zohra Rahmani, Jean-Louis Blouin, Nicole Créau-Goldberg, Paul C. Watkins, Jean-François Mattei, Marc Poissonnier, Marguerite Prieur, Zoubida Chettouh, Annie Nicole, Alain Aurias, Pierre-Marie Sinet, Jean-Maurice Delabar (2005). "Down syndrome critical region around D21S55 on proximal 21q22.3". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 37 (S2): 98–103.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Shekhar, Chandra (2006-07-06). "Down syndrome traced to one gene". The Scientist. Retrieved 2006-07-11.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ OMIM, NIH. "V-ETS Avian Erythroblastosis virus E26 Oncogene Homolog 2". Retrieved 2006-06-29.
- ^ Inclusion: Educating Students with Down Syndrome with Their Non-Disabled Peers. National Down Syndrome Society. Retrieved 2006-05-21.
- ^ "World Down Syndrome Day". Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ Down, J.L.H. (1866). "Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots". Clinical Lecture Reports, London Hospital. 3: 259–262. Retrieved 2006-07-14. For a history of the disorder, see OC Ward (1998). John Langdon Down, 1828-1896. Royal Society of Medicine Press. ISBN 1-85315-374-5. or Conor, Ward. "John Langdon Down and Down's syndrome (1828 - 1896)". Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ "John Langdon Down: The Man and the Message". Down Syndrome Research and Practice. 6 (1): 19–24. 1999. Retrieved 2006-06-02.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|Author=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Warkany, J. (1971). Congenital Malformations. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers, Inc. pp. 313–314. ISBN 0-8151-9098-0.
- ^ "Jérôme Lejeune Foundation". Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ Gordon, Allen (1961). "Mongolism (Correspondence)". The Lancet. 1 (7180): 775.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Howard-Jones, Norman (1979). "On the diagnostic term "Down's disease"". Medical History. 23 (1): 102–104. PMID 153994.
- ^ A planning meeting was held on 20 March 1974, resulting in a letter to The Lancet."Classification and nomenclature of malformation (Discussion)". The Lancet. 303 (7861): 798. 1974. The conference was held 10 February-11 February 1975, and reported to The Lancet shortly afterward."Classification and nomenclature of morphological defects (Discussion)". The Lancet. 305 (7905): 513. 1975.
- ^ Leshin, Len (2003). "What's in a name". Retrieved 2006-05-12.
- ^ Down Syndrome Association of Los Angeles. Media Archive: Television and Film that include individuals with Down Syndrome. Retrieved 1 December 2006.
Bibliography
- Beck, M.N. (1999). Expecting Adam. New York: Berkley Books.
- Buckley, S. (2000). Living with Down Syndrome. Portsmouth, UK: The Down Syndrome Educational Trust.
- Down Syndrome Research Foundation (2005). Bright Beginnings: A Guide for New Parents. Buckinghamshire, UK: Down Syndrome Research Foundation.
- Hassold, T.J., D. Patterson, eds. (1999). Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together. New York: Wiley Liss.
- Kingsley, J. (1994). Count Us In: Growing up with Down Syndrome. San Diego: Harcourt Brace.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Pueschel, S.M., M. Sustrova, eds. (1997). Adolescents with Down Syndrome: Toward a More Fulfilling Life. Baltimore, MD: Paul H. Brookes.
- Selikowitz, M. (1997). Down Syndrome: The Facts (2nd edition ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - Van Dyke, D.C. (1995). Medical and Surgical Care for Children with Down Syndrome. Bethesda, MD: Woodbine House.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Zuckoff, M. (2002). Choosing Naia: A Family's Journey. New York: Beacon Press.
External links
For comprehensive lists of Down syndrome links see
- Directory of Down Syndrome Internet Sites (US based, but contains international links)
- UK resources for Down's syndrome
Societies and associations
By country
- Canadian Down Syndrome Society (Canada)
- Down Syndrome Research Foundation (Canada)
- Down's Syndrome Scotland (Scotland)
- Down's Syndrome Association UK (Not including Scotland)
- Down's Syndrome Research Foundation (UK)
- National Down Syndrome Society (USA)
- National Down Syndrome Congress (USA)
- International Mosaic Down Syndrome Association (USA)
- Down's Heart Group (heart conditions related to Down's Syndrome)
Conferences
- 9th World Down Syndrome Congress (2006, Vancouver)
- Bright Beginnings Conference for Parents and Professionals (2006, London) -- Report
