Developed country: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [pending revision] |
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
|align="left"|{{flag|Denmark}}||align="right"|36,549||0.943 |
|align="left"|{{flag|Denmark}}||align="right"|36,549||0.943 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="left"|{{flagicon|Faroe Islands}}''[[Faroe Islands]]'' ({{flagicon|Denmark}} [[Denmark]])||align="right"|31,000||0.941 |
|align="left"|{{flagicon|Faroe Islands}} ''[[Faroe Islands]]'' ({{flagicon|Denmark}} [[Denmark]])||align="right"|31,000||0.941 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="left"|{{flag|Finland}}||align="right"|34,819||0.947 |
|align="left"|{{flag|Finland}}||align="right"|34,819||0.947 |
||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
|align="left"|{{flag|Vatican City}}||align="right"|N/A||N/A |
|align="left"|{{flag|Vatican City}}||align="right"|N/A||N/A |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center" rowspan=2|[[ |
|align="center" rowspan=2|[[Oceania]]||align="left"|{{flag|Australia}} || align="right"|32,938|| 0.957 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="left"|{{flag|New Zealand}}||align="right"|25,531||0.936 |
|align="left"|{{flag|New Zealand}}||align="right"|25,531||0.936 |
||
Revision as of 08:21, 5 May 2007


The term developed country is used to categorize countries with developed economies in which the tertiary and quaternary sectors of industry dominate.
This level of economic development usually translates into a high income per capita and a high Human Development Index (HDI). Countries with high gross domestic product (GDP) per capita often fit the above description of a developed economy. However, anomalies exist when determining "developed" status by the factor GDP per capita alone.
Synonyms
Modern terms synonymous with the term developed country include industrialized countries, more developed countries (MDC) and more economically developed countries (MEDC). The term industrialized country may be ambiguous, as industrialization is an ongoing process that is hard to define. The term MEDC is one used by modern geographers to specifically describe the status of the countries referred to: more economically developed. The first industrialised countries were in the United Kingdom sparked by the industrial revolution as well as the agricultural revolution.
Outdated terms that are sometimes still used to describe the developed/developing country dichotomy are "First World" / "Third World" and "North"/"South". ("Second World" refers to communist states during and since the Cold War.) The term Western countries has a similar meaning, but its connotations restrict its usage, especially in Asia Pacific.
Definition
According to the United Nations definition there is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas. In common practice, Japan in Asia, Canada and the United States in North America, Australia and New Zealand in Oceania, and Western Europe are considered "developed" regions or areas.[citation needed] In international trade statistics, the Southern African Customs Union is also treated as a developed region and Israel as a developed country; and countries of eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.) countries in Europe are not included under either developed or developing regions. Nowadays the more comprehensive group of "developed countries" also covers the East Asian Tigers (Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan).
When using GDP/cap to define "developed" status, one must take into account how some countries have achieved a (usually temporarily) high GDP/cap through natural resource exploitation (e.g., Nauru through phosphate extraction and Equatorial Guinea) without developing the diverse industrial and service-based economy necessary for "developed" status — similarly, the Bahamas, Barbados, Antigua and Barbuda, and Saint Kitts and Nevis depend overwhelmingly on the tourist industry.
Despite their high per capita GDP, the GCC countries in the Middle East, Brunei and Trinidad and Tobago are generally not considered developed countries because their economies depend overwhelmingly on oil production and export; in many cases (notably Saudi Arabia), per capita GDP is also skewed by an unequal distribution of wealth. Some of these countries, especially Bahrain, and Trinidad and Tobago have begun to diversify their economies. [citation needed]
Reasons for high level of economic development
Different observers and theorists often see different reasons for why certain countries (and not others) enjoy a high level of economic development. Many argue that economic development requires some combination of representative government (or democracy), a free market economic model, and a general lack of corruption. Some hold that rich countries grew wealthy by exploitation of poorer countries in the past, through imperialism and colonialism, or in the present, through the process of globalization. See dependency theory. Critics of the dependency theory believe that economic policies play a more important role, and point out that many of the former colonies of wealthy countries have achieved first world status, and some (such as Hong Kong) have even exceeded the per-capita wealth of their former colonizers.
Quality-of-life Survey
Another relative research about standard of living by Economist Intelligence Unit or EIU Quality-of-life Survey refers the top thirty countries with best quality of life include (in ranking order): Ireland, Switzerland, Norway, Luxembourg, Sweden, Australia, Iceland, Italy, Denmark, Spain, Singapore, Finland, United States, Canada, New Zealand, Netherlands, Japan, Hong Kong, Portugal, Austria, Republic of China (Taiwan), Greece, Cyprus, Belgium, France, Germany, Slovenia, Malta, United Kingdom and South Korea.
Human Development Index
The UN HDI is a statistical measure that gauges a country's level of human development. Countries with an HDI of 0.8 or more — largely corresponding to what the conventional definition of being a developed" country is — exhibit high development, and those with an HDI between 0.5 and 0.8 (including many of the former Soviet and Eastern Bloc states) exhibit moderate development. All countries listed here as "developed" posses an HDI over 0.9.
Comprehensive list of developed countries/regions
Organisations such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), generally agree that the group of developed countries includes the following countries/regions (in alphabetical order):
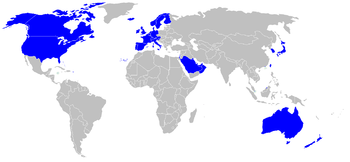
| Continent | Country | GDP per capita (PPP) |
HDI (2004) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Americas | 69,900 | N/A | |
| 35,494 | 0.950 | ||
| 43,444 | 0.948 | ||
| Asia | 38,127 | 0.927 | |
| 30,464 | 0.927 | ||
| 32,647 | 0.949 | ||
| 24,300 | 0.909 | ||
| 32,867 | 0.916 | ||
| 23,926 | 0.912 | ||
| 30,084 | 0.925 | ||
| Europe | 38,800 | N/A | |
| 36,031 | 0.944 | ||
| 34,478 | 0.945 | ||
| 29,105 | 0.903 | ||
| 36,549 | 0.943 | ||
| 31,000 | 0.941 | ||
| 34,819 | 0.947 | ||
| 30,693 | 0.942 | ||
| 31,095 | 0.932 | ||
| 25,975 | 0.921 | ||
| 40,277 | 0.960 | ||
| 44,087 | 0.956 | ||
| 30,732 | 0.940 | ||
| 54,000 | N/A | ||
| 80,471 | 0.945 | ||
| 30,000 | N/A | ||
| 35,078 | 0.947 | ||
| 43,574 | 0.965 | ||
| 22,677 | 0.904 | ||
| 34,100 | N/A | ||
| 23,843 | 0.910 | ||
| 27,522 | 0.938 | ||
| 34,409 | 0.951 | ||
| 37,369 | 0.947 | ||
| 35,051 | 0.940 | ||
| N/A | N/A | ||
| Oceania | 32,938 | 0.957 | |
| 25,531 | 0.936 |
Other cases
 Malta, an EU member since 2004, is classified as a high-income economy by the World Bank and considered developed by the CIA. Its HDI is, however, slightly lower than 0.9, ranked 32nd in the world, and it is not classified as an "advanced economy" by the IMF.
Malta, an EU member since 2004, is classified as a high-income economy by the World Bank and considered developed by the CIA. Its HDI is, however, slightly lower than 0.9, ranked 32nd in the world, and it is not classified as an "advanced economy" by the IMF.
Other parts of the world
Countries considered likely to join the ranks of developed nations in the future must pass further major hurdles (e.g., debt, diversification, democratisation, crackdown on crime and corruption, lowering unemployment, education reform, development of a middle class) to attain full-fledged developed status; however, they have sufficient wealth to currently enjoy some benefits of "developed" status.
- Some organisations consider the remaining countries of the European Union — especially
 Czech Republic — among the developed countries, but these mostly former-Eastern bloc countries are rather newly industrialised nations, and some of them (such as Romania and Bulgaria) remain significantly less affluent than EU-15 countries. All European Union members, however, have a GDP per capita greater than the global average and high human development according to the HDI.
Czech Republic — among the developed countries, but these mostly former-Eastern bloc countries are rather newly industrialised nations, and some of them (such as Romania and Bulgaria) remain significantly less affluent than EU-15 countries. All European Union members, however, have a GDP per capita greater than the global average and high human development according to the HDI.
 Hong Kong and
Hong Kong and  Macau: Both have long been considered developed by most organisations. Although they were handed over to the People's Republic of China (PRC), which is a developing country, they are still considered internationally as separate economic entities (as they have their own currencies - the Hong Kong Dollar and the Pataca) and separate political systems according to the Basic Law of Hong Kong and the Basic Law of Macau. Due to the difference between their economies and that of mainland China, both territories retain their own border and custom controls.
Macau: Both have long been considered developed by most organisations. Although they were handed over to the People's Republic of China (PRC), which is a developing country, they are still considered internationally as separate economic entities (as they have their own currencies - the Hong Kong Dollar and the Pataca) and separate political systems according to the Basic Law of Hong Kong and the Basic Law of Macau. Due to the difference between their economies and that of mainland China, both territories retain their own border and custom controls.
 Mexico: The only Latin American country part of the OECD. It is a member of the NAFTA along with the US and Canada, but not as developed as these two countries. Some authors still consider Mexico a developing country rather than a developed one, though most properly Mexico lies between these two extremes as a newly industrialised country or NIC, with its HDI of 0.821, which is superior to that of Russia, Brazil, Turkey, China, India and South Africa, and possessing a booming upper middle-income economy with a GDP (PPP) per capita of $10,186 USD.
Mexico: The only Latin American country part of the OECD. It is a member of the NAFTA along with the US and Canada, but not as developed as these two countries. Some authors still consider Mexico a developing country rather than a developed one, though most properly Mexico lies between these two extremes as a newly industrialised country or NIC, with its HDI of 0.821, which is superior to that of Russia, Brazil, Turkey, China, India and South Africa, and possessing a booming upper middle-income economy with a GDP (PPP) per capita of $10,186 USD.
 Turkey and
Turkey and  South Africa: Considered developed by a limited number of sources; however their GDP per capita (both have lower middle-income economies) and HDI ranking, clearly places them among the developing countries.
South Africa: Considered developed by a limited number of sources; however their GDP per capita (both have lower middle-income economies) and HDI ranking, clearly places them among the developing countries.
References
- World Bank (high-income economies)
- The World Factbook (developed countries)
- United Nations Statistics Division (definition)
- United Nations Statistics Division (developed regions)
- IMF (advanced economies)
- The Economist (quality of life survey)
See also
- DEMOLOGOS
- Decolonization
- Developing country
- Economic development
- Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI)
- Industrialisation
- List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita
- List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita
- List of countries by Human Development Index
- Newly industrialized country
- Quality of life
- Standard of living
- Sustainable development
- UN Human Development Index
- Visa Waiver Program
