Anterior pituitary: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 208.235.231.134 (talk) to last version by Doceva |
|||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| FSH |
| FSH |
||
| [[Gonadotroph]]s (basophil) |
| [[Gonadotroph]]s (basophil) |
||
| [[ |
| [[Gonads]] |
||
| Growth of [[reproductive system]] |
| Growth of [[reproductive system]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Revision as of 16:40, 28 July 2008
| Anterior pituitary | |
|---|---|
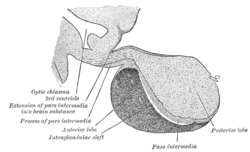 Median sagittal through the hypophysis of an adult monkey. Semidiagrammatic. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | oral mucosa (Rathke's pouch) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lobus anterior hypophyseos |
| MeSH | D010903 |
| NeuroNames | 407 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1581 |
| TA98 | A11.1.00.002 |
| TA2 | 3855 |
| FMA | 74627 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis, from Greek adeno, "gland"; hypo, "under"; physis, "growth"; hence, glandular undergrowth) comprises the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland and is part of the endocrine system. Unlike the posterior lobe, the anterior lobe is genuinely glandular, hence the root adeno in its name.
Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the anterior pituitary produces and secretes several peptide hormones that regulate many physiological processes including stress, growth, and reproduction.
Regions
The term "pars distalis" is sometimes used as a synonym for the anterior pituitary, but this is not quite correct. The anterior pituitary is usually divided into three regions:
- pars distalis ("distal part") - the majority of the anterior pituitary
- pars tuberalis ("tubular part") - a sheath extending up from the pars distalis and wrapping around the pituitary stalk
- pars intermedia ("intermediate part") - sits between the bulk of the anterior pituitary and the posterior pituitary and is often very small in humans
The function of the tuberalis is not well characterized, and most of the rest of this article refers primarily to the distalis.
Embryology
Unlike the posterior pituitary (pars nervosa), which originates from neural ectoderm, the anterior pituitary arises from an invagination of the oral ectoderm and forms the Rathke's pouch.
This differentiation is exhibited by the fact that while the posterior pituitary merely secretes hormones produced in the hypothalamus (ADH and oxytocin), the anterior pituitary actually produces its hormones, while being under control of the hypothalamus.
Major hormones secreted
| Hormone | Other names | Symbol(s) | Secretory cells (staining type) | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone | Corticotropin | ACTH | Corticotrophs (basophil) | Adrenal gland | Secretion of glucocorticoids |
| Endorphins | - | - | - | Opioid receptor | Inhibit perception of pain |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | - | FSH | Gonadotrophs (basophil) | Gonads | Growth of reproductive system |
| Human growth hormone | Somatotropin | hGH, STH | Somatotrophs (acidophil) | Liver, adipose tissue | Promotes growth; lipid & carbohydrate metabolism |
| Luteinizing hormone | Lutropin | LH, ICSH | Gonadotrophs (basophil) | Ovaries, Testes | Sex hormone production |
| Prolactin | - | PRL | Lactotrophs, also known as Mammotrophs (acidophil) | Ovaries, mammary glands | Secretion of estrogens/progesterone; milk production |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone | Thyrotropin | TSH | Thyrotrophs (basophil) | Thyroid gland | Secretion of thyroid hormones |
Hypothalamic releasing and release-inhibiting factors
Hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary gland is regulated by hormones secreted by the hypothalamus. Neuroendocrine neurons in the hypothalamus project axons to the median eminence, at the base of the brain. At this site, these neurons can release substances into small blood vessels that travel directly to the anterior pituitary gland (the hypothalamo-hypophysial portal vessels).
| Name | Other Names | Abbreviations | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone | Corticotropin-releasing factor, Corticoliberin | CRH, CRF | parvocellular neuroendocrine neurons in the paraventricular nucleus | with vasopressin, stimulates secretion of ACTH |
| Dopamine | Prolactin-inhibiting hormone | DA, PIH | neuroendocrine neurons of the arcuate nucleus | inhibits secretion of prolactin |
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone | Luteinising-hormone releasing hormone | GnRH, LHRH | neuroendocrine neurons in the medial preoptic and arcuate nuclei | stimulates secretion of LH and FSH |
| Growth hormone-releasing hormone | Growth-hormone-releasing factor, somatocrinin | GHRH, GHRF, GRF | arcuate nucleus neuroendocrine neurons | stimulates secretion of growth hormone |
| Somatostatin | Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone, Somatotropin release-inhibiting factor | SS, GHIH, SRIF | neuroendocrine neurons of the periventricular nucleus | inhibits secretion of growth hormone |
| Thyrotropin-releasing hormone | Thyrotropin-releasing factor, Thyroliberin, Protirelin | TRH, TRF | parvocellular neuroendocrine neurons in the paraventricular and anterior hypothalamic nuclei | stimulates secretion of TSH |
| Vasopressin | Arginine vasopressin, Antidiuretic hormone, Argipressin | AVP, ADH | parvocellular neuroendocrine neurons in the paraventricular nucleus | with Corticotropin-releasing hormone, stimulates secretion of ACTH |
Additional images
-
The anterior pituitary is the anterior, glandular lobe of the pituitary gland.
See also
External links
- Histology image: 14002loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Embryology at unc.edu