Amber Road: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{for|the software company|Amber Road, Inc.}} |
{{for|the software company|Amber Road, Inc.}} |
||
{{citations|date=October 2013}} |
{{citations|date=October 2013}} |
||
[[File:Amber Road.jpg|thumb|250px|The Amber Road]] |
[[File:Amber Road.jpg|thumb|250px|The Amber Road (east route)]] |
||
[[File:Baltis amber road.jpg|thumb|250px|The route from the Baltic Sea]] |
[[File:Baltis amber road.jpg|thumb|250px|The route from the Baltic Sea]] |
||
Revision as of 08:37, 12 December 2013
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (October 2013) |
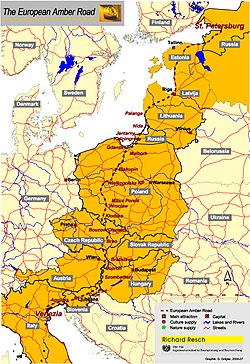

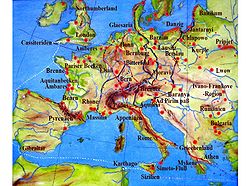
Prehistoric commercial routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade. The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea.[1] As an important raw material, sometimes dubbed "the gold of the north", amber was transported from the North Sea and Baltic Sea coasts overland by way of the Vistula and Dnieper rivers to Italy, Greece, the Black Sea, Syria and Egypt thousands of years ago, and long after.
Antiquity
From at least the sixteenth century BC amber was moved from Northern Europe to the Mediterranean area.[2][3] The breast ornament of Egyptian pharaoh Tutankhamen (ca. 1333-1324 B.C.E.) contains large Baltic amber beads [4][5][6] Heinrich Schliemann found Baltic amber beads at Mycenae, as shown by spectroscopic investigation.[7] The quantity of amber in the Royal Tomb of Qatna, Syria, is unparalleled for known second millennium BC sites in the Levant and the Ancient Near East.[8] Amber was sent from the North Sea to the temple of Apollo at Delphi as an offering. From the Black Sea, trade could continue to Asia along the Silk Road, another ancient trade route. In Roman times, a main route ran south from the Baltic coast through the land of the Boii (modern Czech Republic and Slovakia) to the head of the Adriatic Sea (modern Gulf of Venice).
The Old Prussian towns of Kaup and Truso on the Baltic were the starting points of the route to the south. In Scandinavia the amber road probably gave rise to the thriving Nordic Bronze Age culture, bringing influences from the Mediterranean Sea to the northernmost countries of Europe.
Sometimes the Kaliningrad Oblast is called the Янтарный край, which means "the amber area".
Names
- Croatian: Jantarski put
- Czech: Jantarová stezka
- German: Bernsteinstraße
- Greek: Δρόμος του κεχριμπαριού or Δρόμος του ηλέκτρου
- Estonian: Merevaigutee
- Finnish: Meripihkatie
- French: Route de l'ambre
- Hungarian: Borostyánút
- Italian: Via dell'Ambra
- Latvian: Dzintara Ceļš
- Lithuanian: Gintaro kelias
- Polish: Szlak Bursztynowy or Jantarowy Szlak
- Russian: Янтарный путь
- Serbian: Ćilibarski put
- Slovak: Jantárová cesta
- Slovene: Jantarjeva pot
Overview of known amber finding places in Europe
This section's factual accuracy is disputed. (July 2010) |
Amber roads connect amber finding locations to customer sites in Europe, in the Middle East regions and in the Far East.
Overview of known amber roads by country
This section has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Central Europe
The shortest (and possibly oldest) road avoids alpine areas and led from the Baltic coastline (nowadays Lithuania and Poland), through Biskupin and rest of Poland, passed the Moravian Gate, followed the river Morava, crossed the Danube near Carnuntum in the Noricum Province, headed southwest past Poetovio, Celeia, Emona, Nauportus, and reached Aquileia at the Adriatic coast. One of the oldest directions of the last stage of the Amber Road to the south of Danube, noted in the myth about the Argonauts, used the Sava and Kupa rivers, ending with a short continental road from Nauportus to Tarsatica (Trsat, Rijeka) at the coast of the Adriatic.
Germany

Several roads connected the North Sea and Baltic Seas, especially the city of Hamburg to the Brenner Pass, proceeding southwards to Brindisi (nowadays Italy) and Ambracia (nowadays Greece).
Switzerland
The Swiss region indicates a number of alpine roads, concentrating around the capital city Bern and probably originating from the borders of the Rhône River and the Rhine.
The Netherlands
A small section, including Baarn, Barneveld, Amersfoort and Amerongen, connected the North Sea with the Lower Rhine.
Belgium
A small section led southwards from Antwerp and Bruges to the towns Braine-l’Alleud and Braine-le-Comte, both originally named "Brennia-Brenna".[citation needed] The route continued by following the Meuse River towards Bern in Switzerland.
France
Three routes may be identified leading from an amber finding region or delta at the mouth of River Openia towards Bresse and Bern, crossing the Alps to Switzerland and Italy.
Southern France and Spain
Routes connecting amber finding locations at Ambares (near Bordeaux), leading to Béarn and the Pyrenees. Routes connecting the amber finding locations in northern Spain and in the Pyrenees were a trading route to the Mediterranean Sea.
References
- ^ Graciela Gestoso Singer, "Amber in the Ancient Near East", i-Medjat No. 2 (December 2008). Papyrus Electronique des Ankou.
- ^ J. M. de Navarro, "Prehistoric Routes between Northern Europe and Italy Defined by the Amber Trade", The Geographical Journal, Vol. 66, No. 6 (December 1925), pp. 481-503.
- ^ Anthony F. Harding, "Reformation and Barbarism in Europe, 1300-600 BC", in Barry W. Cunliffe, ed., Oxford Illustrated History of Prehstoric Europe, Oxford, Oxford U. Press, 2001.
- ^ Reeves, C.N. The Complete Tutankhamun: the king, the tomb, the Royal Treasure. London, Thames & Hudson, 1990.
- ^ Serpico, M. and White, R. "Resins, amber and bitumen". in P.T. Nicholson - I. Shaw (ed.). Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2000,Part. II, Chapter 18, 430-475: 451-454). Cited, Gestoso Singer.
- ^ Hood, S., "Amber in Egypt", in C. W. Beck & J. Bouzek (ed.) Amber in Archaeology (Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Amber in Archaeology, Liblice 1990, Institute of Archaeology): 230-35. Prague: Czech Academy of Sciences.
- ^ Curt W. Beck, Gretchen C. Southard, Audrey B. Adams, "Analysis and Provenience of Minoan and Mycenaean Amber, IV. Mycenae", pp. 359-385.
- ^ Anna J. Mukherjee, et al., "The Qatna lion: scientific confirmation of Baltic amber in late Bronze Age Syria" Antiquity 82 (2008), pp. 49-59.
External links
- Amber Road
- OWTRAD-scientific description of the amber road in Poland
- Old World Traditional Trade Routes (OWTRAD) Project
- Amber route along the river Elbe
- Joannes Richter - "Spelling Thee, U & I - Introducing into the art of amber trading & Initiation in the great Androgyne Religion" (pdf file)
- Joannes Richter - "Die Bernsteinroute bei Backnang" (pdf file)
