Fuel economy in automobiles: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m →Energy considerations: Add stuff and cite about standby to comport with illustration. Corrected spelling and grammar as needed. |
||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
==Energy considerations== |
==Energy considerations== |
||
{{Expand section|date=June 2007}} |
{{Expand section|date=June 2007}} |
||
Since the total force opposing the vehicle's motion (at constant speed) multiplied by the distance through which the vehicle travels represents the work that the vehicle's engine must perform, the study of fuel economy (the amount of energy consumed per unit of distance |
Since the total force opposing the vehicle's motion (at constant speed) multiplied by the distance through which the vehicle travels represents the work that the vehicle's engine must perform, the study of fuel economy (the amount of energy consumed per unit of distance traveled) requires a detailed analysis of the forces that oppose a vehicle's motion. In terms of physics, Force = rate at which the amount of work generated (energy delivered) varies with the distance traveled, or: |
||
:<math>F = \frac{dW}{ds} \propto \text{Fuel economy}</math> |
:<math>F = \frac{dW}{ds} \propto \text{Fuel economy}</math> |
||
| Line 204: | Line 204: | ||
#The forces of friction within the mechanical system that delivers engine output to the wheels; |
#The forces of friction within the mechanical system that delivers engine output to the wheels; |
||
#The forces of friction in the wheels and between the road and the wheels (rolling friction); |
#The forces of friction in the wheels and between the road and the wheels (rolling friction); |
||
#Other internal forces that the engine works against (electrical generator, air conditioner |
#Other internal forces that the engine works against (electrical generator, air conditioner, water pump, engine fan, etc.); |
||
#External forces that resist motion (e.g., wind, rain); |
#External forces that resist motion (e.g., wind, rain); |
||
#Non-regenerative braking force (brakes that turn motion energy into heat rather than storing it in a useful form; e.g., electrical energy in hybrid vehicles) |
#Non-regenerative braking force (brakes that turn motion energy into heat rather than storing it in a useful form; e.g., electrical energy in hybrid vehicles); |
||
#Fuel consumed while the engine is on standby and not powering the wheels, i.e., while the vehicle is coasting, braking or idling. <ref>[http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/sr/sr286.pdf TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD SPECIAL REPORT 286 TIRES AND PASSENGER VEHICLE FUEL ECONOMY, Transportation Research Board, National Academy of Sciences p.62-65 of pdf, p.39-42 of report. Retrieved 22 October 2014.</ref> |
|||
[[File:Energy flows in car.svg|thumb|400px|Energy dissipation in city and highway driving.]] |
[[File:Energy flows in car.svg|thumb|400px|Energy dissipation in city and highway driving.]] |
||
| Line 214: | Line 215: | ||
* [[Rolling friction]]. |
* [[Rolling friction]]. |
||
* Braking, although [[regenerative braking]] captures some of the energy that would otherwise be lost. |
* Braking, although [[regenerative braking]] captures some of the energy that would otherwise be lost. |
||
* Losses in the [[Transmission (mechanics)|transmission]]. [[Manual transmission]]s can be up to 94% efficient whereas older [[automatic transmission]]s may be as low as 70% efficient<ref>[http://www.sae.org/servlets/productDetail?PROD_TYP=PAPER&PROD_CD=1999-01-1259 An Overview of Current Automatic, Manual and Continuously Variable Transmission Efficiencies and Their Projected Future Improvements]. |
* Losses in the [[Transmission (mechanics)|transmission]]. [[Manual transmission]]s can be up to 94% efficient whereas older [[automatic transmission]]s may be as low as 70% efficient<ref>[http://www.sae.org/servlets/productDetail?PROD_TYP=PAPER&PROD_CD=1999-01-1259 An Overview of Current Automatic, Manual and Continuously Variable Transmission Efficiencies and Their Projected Future Improvements]. SAE.org (1999-03-01). Retrieved 21 September 2011.</ref> Automatically controlled shifting of gearboxes that have the same internals as manual boxes will give the same efficiency as a pure manual gearbox plus the bonus of added intelligence selecting optimal shifting points |
||
* Air conditioning. The power required for the engine to turn the compressor decreases the fuel-efficiency, though only when in use. This may be offset by the reduced drag of the vehicle compared with driving with the windows down. The efficiency of AC systems gradually |
* Air conditioning. The power required for the engine to turn the compressor decreases the fuel-efficiency, though only when in use. This may be offset by the reduced drag of the vehicle compared with driving with the windows down. The efficiency of AC systems gradually deteriorates due to dirty filters etc.; regular maintenance prevents this. The extra mass of the air conditioning system will cause a slight increase in fuel consumption. |
||
* Power steering. Older hydraulic power steering systems are powered by a hydraulic pump constantly engaged to the engine. Power assistance required for steering is inversely proportional to the vehicle speed so the constant load on the engine from a hydraulic pump reduces fuel efficiency. More modern designs improve fuel efficiency by only activating the power assistance when needed; this is done by using either direct electrical power steering assistance or an electrically powered hydraulic pump. |
* Power steering. Older hydraulic power steering systems are powered by a hydraulic pump constantly engaged to the engine. Power assistance required for steering is inversely proportional to the vehicle speed so the constant load on the engine from a hydraulic pump reduces fuel efficiency. More modern designs improve fuel efficiency by only activating the power assistance when needed; this is done by using either direct electrical power steering assistance or an electrically powered hydraulic pump. |
||
* Cooling. Older cooling systems used a constantly engaged mechanical fan to draw air through the radiator at a rate directly related to the engine speed. This constant load reduces efficiency. More modern systems use electrical fans to draw additional air through the radiator when extra cooling is required. |
* Cooling. Older cooling systems used a constantly engaged mechanical fan to draw air through the radiator at a rate directly related to the engine speed. This constant load reduces efficiency. More modern systems use electrical fans to draw additional air through the radiator when extra cooling is required. |
||
* Electrical systems. Headlights, battery charging, active suspension, circulating fans, defrosters, media systems, speakers, and other electronics can also significantly increase fuel consumption, as the energy to power these devices causes increased load on the alternator. Since alternators are commonly only 40–60% efficient, the added load from electronics on the engine can be as high as {{convert|3|hp}} at any speed including idle. In the FTP 75 cycle test, a 200 watt load on the alternator reduces fuel efficiency by 1.7 MPG.<ref name=ieee/> Headlights, for example, consume 110 watts on low and up to 240 watts on high. These electrical loads can cause much of the discrepancy between real world and EPA tests, which only include the electrical loads required to run the engine and basic climate control. |
* Electrical systems. Headlights, battery charging, active suspension, circulating fans, defrosters, media systems, speakers, and other electronics can also significantly increase fuel consumption, as the energy to power these devices causes increased load on the alternator. Since alternators are commonly only 40–60% efficient, the added load from electronics on the engine can be as high as {{convert|3|hp}} at any speed including idle. In the FTP 75 cycle test, a 200 watt load on the alternator reduces fuel efficiency by 1.7 MPG.<ref name=ieee/> Headlights, for example, consume 110 watts on low and up to 240 watts on high. These electrical loads can cause much of the discrepancy between real world and EPA tests, which only include the electrical loads required to run the engine and basic climate control. |
||
* Standby. The energy needed to keep the engine running while it is not providing power to the wheels, i.e., when stopped, coasting or braking. |
|||
Fuel-efficiency decreases from electrical loads are most pronounced at lower speeds because most electrical loads are constant while engine load increases with speed. So at a lower speed a higher proportion of engine horsepower is used by electrical loads. Hybrid cars see the greatest effect on fuel-efficiency from electrical loads because of this proportional effect. |
Fuel-efficiency decreases from electrical loads are most pronounced at lower speeds because most electrical loads are constant while engine load increases with speed. So at a lower speed a higher proportion of engine horsepower is used by electrical loads. Hybrid cars see the greatest effect on fuel-efficiency from electrical loads because of this proportional effect. |
||
| Line 228: | Line 230: | ||
Engine combustion strategies: |
Engine combustion strategies: |
||
* |
*Optimizing engine running temperature by electronic control of the cooling system |
||
*[[Stratified charge engine|Stratified Charge]] combustion |
*[[Stratified charge engine|Stratified Charge]] combustion |
||
*[[Lean burn]] combustion |
*[[Lean burn]] combustion |
||
| Line 235: | Line 237: | ||
*[[Variable valve timing]] and variable valve lift |
*[[Variable valve timing]] and variable valve lift |
||
*[[Variable geometry turbocharger|Variable geometry turbocharging]] or [[Twincharger|twincharging]] (coupled with a downsized engine) |
*[[Variable geometry turbocharger|Variable geometry turbocharging]] or [[Twincharger|twincharging]] (coupled with a downsized engine) |
||
*[[Gasoline direct injection]] petrol engines (usually with a higher compression ratio) in lieu of |
*[[Gasoline direct injection]] petrol engines (usually with a higher compression ratio) in lieu of [[Carburetor|carburetor]] or port injection |
||
*[[Turbocharged Direct Injection]] diesel engines in lieu of indirect injection engine |
*[[Turbocharged Direct Injection]] diesel engines in lieu of indirect injection engine |
||
*[[Common Rail]] diesel engines (higher injection pressure) |
*[[Common Rail]] diesel engines (higher injection pressure) |
||
*Piezoelectric diesel injectors using multiple injections per engine cycle |
*Piezoelectric diesel injectors using multiple injections per engine cycle |
||
*Cylinder management (shutting off individual cylinders when their power output is not needed) |
*Cylinder management (shutting off individual cylinders when their power output is not needed) |
||
*Automatic Start Stop function (switches the engine off while the vehicle is temporarily stopped) |
|||
Engine internal losses |
Engine internal losses |
||
| Line 247: | Line 250: | ||
*Using a variable displacement oil pump so that excessive flow rate is avoided at high engine speed |
*Using a variable displacement oil pump so that excessive flow rate is avoided at high engine speed |
||
*Electrifying engine accessories such as water pump, power steering pump and air conditioner compressor, so that more engine power goes to the transmission, or less fuel is required for the same traction power |
*Electrifying engine accessories such as water pump, power steering pump and air conditioner compressor, so that more engine power goes to the transmission, or less fuel is required for the same traction power |
||
*Reducing engine frictions by roller type cam, low friction coating on piston skirt and optimizing load bearing surface, e.g. camshaft bearing |
*Reducing engine frictions by roller type cam, low friction coating on piston skirt and optimizing load bearing surface, e.g. camshaft bearing and connective rods. |
||
Engine running conditions |
Engine running conditions |
||
| Line 263: | Line 266: | ||
Aerodynamic Drag |
Aerodynamic Drag |
||
*Vehicle downsizing without loss of functionality improving vehicle packaging and space |
*Vehicle downsizing without loss of functionality improving vehicle packaging and space utilization |
||
*Designing the shape of the vehicle and the internal cooling system in order to reduce aerodynamic [[Drag (physics)|drag]] |
*Designing the shape of the vehicle and the internal cooling system in order to reduce aerodynamic [[Drag (physics)|drag]] |
||
*Removing external high drag devices (roof racks, brush guards, wind deflectors) |
*Removing external high drag devices (roof racks, brush guards, wind deflectors) |
||
| Line 314: | Line 317: | ||
The mandatory publication of the fuel consumption by the manufacturer led some to use dubious practices to reach better values in the past. If the test is on a test stand, the vehicle may detect open doors and adapt the engine control. Also when driven according to the test regime, the parameters may adapt automatically. Test laboratories use a "golden car" that is tested in each one to check that each lab produces the same set of measurements for a given drive cycle.<ref>[http://rsc-aamg.org/Documents/Papers/ENSpeakerAbstracts.pdf Environmental Nanoparticles – Exploring the links between Vehicle Emissions and Ambient Air]. (PDF). A meeting of the Automation and Analytical Management Group of the Royal Society of Chemistry. 8 June 2005. Retrieved 21 September 2011.</ref> |
The mandatory publication of the fuel consumption by the manufacturer led some to use dubious practices to reach better values in the past. If the test is on a test stand, the vehicle may detect open doors and adapt the engine control. Also when driven according to the test regime, the parameters may adapt automatically. Test laboratories use a "golden car" that is tested in each one to check that each lab produces the same set of measurements for a given drive cycle.<ref>[http://rsc-aamg.org/Documents/Papers/ENSpeakerAbstracts.pdf Environmental Nanoparticles – Exploring the links between Vehicle Emissions and Ambient Air]. (PDF). A meeting of the Automation and Analytical Management Group of the Royal Society of Chemistry. 8 June 2005. Retrieved 21 September 2011.</ref> |
||
Tire pressures and lubricants have to be as recommended by the manufacturer (Higher tire pressures are required on a particular |
Tire pressures and lubricants have to be as recommended by the manufacturer (Higher tire pressures are required on a particular [[Dynamometer|dynamometer type]], but this is to compensate for the different rolling resistance of the dynamometer, not to produce an unrealistic load on the vehicle). Normally the quoted figures a manufacturer publishes have to be proved by the relevant authority witnessing vehicle/engine tests. Some jurisdictions independently test emissions of vehicles in service, and as a final measure can force a recall of all of a particular type of vehicle if the customer vehicles do not fulfill manufacturers' claims within reasonable limits. The expense and bad publicity from such a recall encourages manufacturers to publish realistic figures. The US Federal government retests 10–15% of models<ref>[http://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/how_tested.shtml EPA]. Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 21 September 2011.</ref>), to make sure that the manufacturer's tests are accurate. |
||
===Concerns over EPA estimates=== |
===Concerns over EPA estimates=== |
||
Revision as of 05:02, 23 October 2014


The fuel economy of an automobile is the fuel efficiency relationship between the distance traveled and the amount of fuel consumed by the vehicle. Consumption can be expressed in terms of volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance travelled per unit volume of fuel consumed. Since fuel consumption of vehicles is a significant factor in air pollution, and since importation of motor fuel can be a large part of a nation's foreign trade, many countries impose requirements for fuel economy. Different measurement cycles are used to approximate the actual performance of the vehicle. The energy in fuel is required to overcome various losses (wind resistance, tire drag, and others) in propelling the vehicle, and in providing power to vehicle systems such as ignition or air conditioning. Various measures can be taken to reduce losses at each of the conversions between chemical energy in fuel and kinetic energy of the vehicle. Driver behavior can affect fuel economy; maneuvers such as sudden acceleration and heavy braking waste energy.
Units of measure
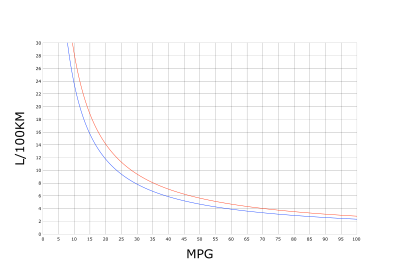
Fuel economy is the relationship between the distance traveled and fuel consumed.
Fuel economy can be expressed in two ways:
- Units of fuel per fixed distance
- Generally expressed as liters per 100 kilometers (L/100 km), used in some European countries, China, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand. Canadian law allows for use of either liters per 100 kilometres or miles per imperial gallon.[2][3] Recently, the window sticker on new US cars has started displaying the vehicle's fuel consumption in US gallons per 100 miles.[4]
- Units of distance per fixed fuel unit
- Miles per gallon (mpg) is commonly used in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada (alongside L/100 km). Kilometres per litre (km/L) is more commonly used elsewhere in the Americas, Europe (Northern countries and Italy), Asia, parts of Africa and Oceania. When the mpg unit is used, it is necessary to identify the type of gallon used, as the imperial gallon is 4.5 liters and the US gallon is 3.785 liters.
Conversions of units:
| miles per US gallon → L/100 km: | 235 / mpgUS = L/100 km |
| miles per Imp. gallon → L/100 km: | 282 / mpgImp. = L/100 km |
| L/100 km → miles per US gallon: | 235 / (L/100 km) = mpgUS |
| L/100 km → miles per Imp. gallon: | 282 / (L/100 km) = mpgImp. |
Fuel economy statistics
While the thermal efficiency (mechanical output to chemical energy in fuel) of petroleum engines has increased since the beginning of the automotive era, this is not the only factor in fuel economy. The design of automobile as a whole and usage pattern affects the fuel economy. Published fuel economy is subject to variation between jurisdiction due to variations in testing protocols.
The average fuel economy in 2008 for new cars, light trucks and SUVs in the United States was 26.4 mpg(US) (8.9 L/100 km).[5] 2008 model year cars classified as "midsize" by the US EPA ranged from 11 to 46 mpg(US)(21 to 5 L/100 km)[6] However, due to environmental concerns caused by CO2 emissions, new EU regulations are being introduced to reduce the average emissions of cars sold beginning in 2012, to 130 g/km of CO2, equivalent to 4.5 L/100 km (52 mpgUS, 63 mpgimp) for a diesel-fueled car, and 5.0 L/100 km (47 mpgUS, 56 mpgimp) for a gasoline (petrol)-fueled car.[7]
The average consumption across the fleet is not immediately affected by the new vehicle fuel economy, for example Australia's car fleet average in 2004 was 11.5 L/100 km (20.5 mpgUS),[8] compared with the average new car consumption in the same year of 9.3 L/100 km (25.3 mpg)US[9]
Speed and fuel economy studies

Fuel economy at steady speeds with selected vehicles was studied in 2010. The most recent study[10] indicates greater fuel efficiency at higher speeds than earlier studies; for example, some vehicles achieve better fuel economy at 100 km/h (62 mph) rather than at 70 km/h (43 mph),[10] although not their best economy, such as the 1994 Oldsmobile Cutlass, which has its best economy at 90 kilometres per hour (56 mph) (8.1 L/100 km (29 mpg‑US)), and gets 2 mpg better economy at 105 km/h (65 mph) than at 72 km/h (45 mph) (9.4 L/100 km (25 mpg‑US) vs 5.53 L/100 km (42.5 mpg‑US)). The proportion of driving on high speed roadways varies from 4% in Ireland to 41% in Netherlands.
When the US National Maximum Speed Law's 55 mph (89 km/h) speed limit was mandated, there were complaints that fuel economy could decrease instead of increase. The 1997 Toyota Celica got 1 mpg better fuel-efficiency at 105 km/h (65 mph) than it did at 65 km/h (40 mph) (5.41 L/100 km (43.5 mpg‑US) vs 5.53 L/100 km (42.5 mpg‑US)), although almost 5 mpg better at 60 mph (97 km/h) than at 65 mph (105 km/h) (48.4 mpg‑US (4.86 L/100 km) vs 43.5 mpg‑US (5.41 L/100 km)), and its best economy (52.6 mpg‑US (4.47 L/100 km)) at only 25 mph (40 km/h). Other vehicles tested had from 1.4 to 20.2% better fuel-efficiency at 90 km/h (56 mph) vs. 105 km/h (65 mph). Their best economy was reached at speeds of 40 to 90 km/h (25 to 56 mph) (see graph).[10]
Officials hoped that the 55 mph (90 km/h) limit, combined with a ban on ornamental lighting, no gasoline sales on Sunday, and a 15% cut in gasoline production, would reduce total gas consumption by 200,000 barrels a day, representing a 2.2% drop from annualized 1973 gasoline consumption levels.[11][a] This was partly based on a belief that cars achieve maximum efficiency between 65 and 80 km/h (40 and 50 mph) and that trucks and buses were most efficient at 55 mph (89 km/h).[13]
In 1998, the U.S. Transportation Research Board footnoted an estimate that the 1974 National Maximum Speed Limit (NMSL) reduced fuel consumption by 0.2 to 1.0 percent.[14] Rural interstates, the roads most visibly affected by the NMSL, accounted for 9.5% of the U.S' vehicle-miles-traveled in 1973,[15] but such free-flowing roads typically provide more fuel-efficient travel than conventional roads.[16] [17] [18]
Differences in testing standards
This section possibly contains original research. (April 2013) |
Identical vehicles can have varying fuel consumption figures listed depending upon the testing methods of the jurisdiction.
Lexus IS 250 – petrol 2.5 L 4GR-FSE V6, 204 hp (153 kW), 6 speed automatic, rear wheel drive
- Australia (L/100 km) – 'combined' 9.1, 'urban' 12.7, 'extra-urban' 7.0[16]
- European Union (L/100 km) – 'combined' 8.9, 'urban' 12.5, 'extra-urban' 6.9[17]
- United States (L/100 km) – 'combined' 9.8, 'city' 11.2, 'highway' 8.1[18]
Fuel economy standards and testing procedures
| Country | 2004 average | Requirement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 2005 | 2008 | Later | ||
| People's Republic of China[19] | 6.9 L/100 km | 6.9 L/100 km | 6.1 L/100 km | ||
| United States | 24.6 mpg (9.5 L/100 km) (cars and trucks)* | 27 mpg (8.7 L/100 km) (cars only)* | 35.5 mpg (6.6 L/100 km) (2016) | ||
| European Union | 5 L/100 km (2012) | ||||
| Japan[9] | 6.7 L/100 km CAFE eq (2010) | ||||
| Australia[9] | 8.08 L/100 km CAFE eq (2002) | none | 6.7 L/100 km CAFE eq (2010) (voluntary) | ||
* highway ** combined
Australia
From October 2008, all new cars had to be sold with a sticker on the windscreen showing the fuel consumption and the CO2 emissions.[20] Fuel consumption figures are expressed as urban, extra urban and combined, measured according to ECE Regulations 83 and 101 - which are the based on the European driving cycle; previously, only the combined number was given.
Australia also uses a star rating system, from one to five stars, that combines greenhouse gases with pollution, rating each from 0 to 10 with ten being best. To get 5 stars a combined score of 16 or better is needed, so a car with a 10 for economy (greenhouse) and a 6 for emission or 6 for economy and 10 for emission, or anything in between would get the highest 5 star rating.[21] The lowest rated car is the Ssangyong Korrando with automatic transmission, with one star, while the highest rated was the Toyota Prius hybrid. The Fiat 500, Fiat Punto and Fiat Ritmo as well as the Citroen C3 also received 5 stars.[22] The greenhouse rating depends on the fuel economy and the type of fuel used. A greenhouse rating of 10 requires 60 or less grams of CO2 per km, while a rating of zero is more than 440 g/km CO2. The highest greenhouse rating of any 2009 car listed is the Toyota Prius, with 106 g/km CO2 and 4.4 L/100 km (64 mpg‑imp; 53 mpg‑US). Several other cars also received the same rating of 8.5 for greenhouse. The lowest rated was the Ferrari 575 at 499 g/km CO2 and 21.8 L/100 km (13.0 mpg‑imp; 10.8 mpg‑US). The Bentley also received a zero rating, at 465 g/km CO2. The best fuel economy of any year is the 2004–2005 Honda Insight, at 3.4 L/100 km (83 mpg‑imp; 69 mpg‑US).
Europe

In the European Union, passenger vehicles are commonly tested using two drive cycles, and corresponding fuel economies are reported as 'urban' and 'extra-urban', in litres per 100 km and (in the UK) in miles per imperial gallon.
The urban economy is measured using the test cycle known as ECE-15, first introduced in 1970 by EC Directive 70/220/EWG and finalized by EEC Directive 90/C81/01 in 1999. It simulates a 4,052 m (2.518 mile) urban trip at an average speed of 18.7 km/h (11.6 mph) and at a maximum speed of 50 km/h (31 mph).
The extra-urban driving cycle or EUDC lasts 400 seconds (6 minutes 40 seconds) at an average speed 62.6 km/h (39 mph) and a top speed of 120 km/h (74.6 mph).[23]
EU fuel consumption numbers are often considerably lower than corresponding US EPA test results for the same vehicle. For example, the 2011 Honda CR-Z with a six-speed manual transmission is rated 6.1/4.4 L/100 km in Europe[24] and 7.6/6.4 L/100 km (31/37 mpg ) in the United States.[25]
In the European Union advertising has to show Carbon dioxide (CO2)-emission and fuel consumption data in a clear way as described in the UK Statutory Instrument 2004 No 1661.[26] Since September 2005 a colour-coded "Green Rating" sticker has been available in the UK, which rates fuel economy by CO2 emissions: A: <= 100 g/km, B: 100–120, C: 121–150, D: 151–165, E: 166–185, F: 186–225, and G: 226+. Depending on the type of fuel used, for gasoline A corresponds to about 4.1 L/100 km (69 mpg‑imp; 57 mpg‑US)* and G about 9.5 L/100 km (30 mpg‑imp; 25 mpg‑US)*.[27] Ireland has a very similar label, but the ranges are slightly different, with A: <= 120 g/km, B: 121–140, C: 141–155, D: 156–170, E: 171–190, F: 191–225, and G: 226+.[28]
In the UK the ASA (Advertising standards agency) have claimed that fuel consumption figures are misleading. Often the case with European vehicles as the MPG (miles per gallon) figures that can be advertised are often not the same as 'real world' driving.
The ASA have said that Car manufacturers can use ‘cheats’ to prepare their vehicles for their compulsory fuel efficiency and emissions tests in a way set out to make themselves look as ‘clean’ as possible. This practice is common in petrol and diesel vehicle tests, but hybrid and electric vehicles are not immune as manufacturers apply these techniques to fuel efficiency.
The major loopholes in the current EU tests allow car manufacturers a number of ‘cheats’ to improve results. Car manufacturers can:
- Disconnect the alternator, thus no energy is used to recharge the battery;
- Use special lubricants that are not used in production cars, in order to reduce friction;
- Turn off all electrical gadgets i.e. Air Con/Radio;
- Adjust brakes or even disconnect them to reduce friction;
- Tape up cracks between body panels and windows to reduce air resistance;
- Remove Wing mirrors.[29]
According to the results of a 2014 study by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), the gap between official and real-world fuel-economy figures in Europe has risen to about 38% in 2013 from 10% in 2001. The analysis found that for private cars, the difference between on-road and official CO2 values rose from around 8% in 2001 to 31% in 2013, and 45% for company cars in 2013. The report is based on data from more than half a million private and company vehicles across Europe. The analysis was prepared by the ICCT together with the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research (TNO), and the German Institut für Energie- und Umweltforschung Heidelberg (IFEU).[30]
Japan
10–15 mode
The 10–15 mode driving cycle test is the official fuel economy and emission certification test for new light duty vehicles in Japan. Fuel economy is expressed in km/L (kilometers per litre) and emissions are expressed in g/km. The test is carried out on a dynamometer and consist of 25 tests which cover idling, acceleration, steady running and deceleration, and simulate typical urban and/or expressway driving patterns. The running pattern begins with a warm start, lasts for 660 seconds and runs at speeds up to 70 km/h.[31][32] The distance of the cycle is 6.34 km, average speed 25.6 km/h, and duration 892 seconds, including the initial 15 mode segment).[32]
JC08
A new more demanding test, called the JC08, was established in December 2006 for Japan’s new standard that goes into effect in 2015, but it is already being used by several car manufacturers for new cars. The JC08 test is significantly longer and more rigorous than the 10–15 mode test. The running pattern with JC08 stretches out to 1200 seconds, and there are both cold and warm start measurements and top speed is 82 km/h. The economy ratings of the JC08 are lower than the 10–15 mode cycle, but they are expected to be more real world.[31] The Toyota Prius became the first car to meet Japan’s new 2015 Fuel Economy Standards measured under the JC08 test.[33]
New Zealand
Starting on 7 April 2008 all cars of up to 3.5 tonnes GVW sold other than private sale need to have a fuel economy sticker applied (if available) that shows the rating from one half star to six stars with the most economic cars having the most stars and the more fuel hungry cars the least, along with the fuel economy in L/100 km and the estimated annual fuel cost for driving 14,000 km (at present fuel prices). The stickers must also appear on vehicles to be leased for more than 4 months. All new cars currently rated range from 6.9 L/100 km (41 mpg‑imp; 34 mpg‑US)* to 3.8 L/100 km (74 mpg‑imp; 62 mpg‑US)* and received respectively from 4.5 to 5.5 stars.[34]
United States

US Energy Tax Act
The Energy Tax Act of 1978[35] in the US established a gas guzzler tax on the sale of new model year vehicles whose fuel economy fails to meet certain statutory levels. The tax applies only to cars (not trucks) and is collected by the IRS. Its purpose is to discourage the production and purchase of fuel-inefficient vehicles. The tax was phased in over ten years with rates increasing over time. It applies only to manufacturers and importers of vehicles, although presumably some or all of the tax is passed along to automobile consumers in the form of higher prices. Only new vehicles are subject to the tax, so no tax is imposed on used car sales. The tax is graduated to apply a higher tax rate for less-fuel-efficient vehicles. To determine the tax rate, manufacturers test all the vehicles at their laboratories for fuel economy. The US Environmental Protection Agency confirms a portion of those tests at an EPA lab.
In some cases, this tax may only apply to certain variants of a given model; for example, the 2004–2006 Pontiac GTO (captive import version of the Holden Monaro) did incur the tax when ordered with the four-speed automatic transmission, but did not incur the tax when ordered with the six-speed manual transmission.[36]
EPA testing procedure through 2007


Two separate fuel economy tests simulate city driving and highway driving: the "city" driving program or Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule or (UDDS) or FTP-72 is defined in 40 CFR 86.I and consists of starting with a cold engine and making 23 stops over a period of 31 minutes for an average speed of 20 mph (32 km/h) and with a top speed of 56 mph (90 km/h).
The "highway" program or Highway Fuel Economy Driving Schedule (HWFET) is defined in 40 CFR 600.I and uses a warmed-up engine and makes no stops, averaging 48 mph (77 km/h) with a top speed of 60 mph (97 km/h) over a 10-mile (16 km) distance. The measurements are then adjusted downward by 10% (city) and 22% (highway) to more accurately reflect real-world results. A weight average of city (55%) and highway (45%) fuel economies is used to determine the guzzler tax.[37][38]
The procedure has been updated to FTP-75, adding a "hot start" cycle which repeats the "cold start" cycle after a 10 minute pause.
Because EPA figures had almost always indicated better efficiency than real-world fuel-efficiency, the EPA has modified the method starting with 2008. Updated estimates are available for vehicles back to the 1985 model year.[37][39]
EPA testing procedure: 2008 and beyond

US EPA altered the testing procedure effective MY2008 which adds three new Supplemental Federal Test Procedure (SFTP) tests to include the influence of higher driving speed, harder acceleration, colder temperature and air conditioning use.[6]
SFTP US06 is a high speed/quick acceleration loop that lasts 10 minutes, covers 8 miles (13 km), averages 48 mph (77 km/h) and reaches a top speed of 80 mph (130 km/h). Four stops are included, and brisk acceleration maximizes at a rate of 8.46 mph (13.62 km/h) per second. The engine begins warm and air conditioning is not used. Ambient temperature varies between 68 °F (20 °C) to 86 °F (30 °C).
SFTO SC03 is the air conditioning test, which raises ambient temperatures to 95 °F (35 °C), and puts the vehicle's climate control system to use. Lasting 9.9 minutes, the 3.6-mile (5.8 km) loop averages 22 mph (35 km/h) and maximizes at a rate of 54.8 mph (88.2 km/h). Five stops are included, idling occurs 19 percent of the time and acceleration of 5.1 mph/sec is achieved. Engine temperatures begin warm.
Lastly, a cold temperature cycle uses the same parameters as the current city loop, except that ambient temperature is set to 20 °F (−7 °C).
EPA tests for fuel economy do not include electrical load tests beyond climate control, which may account for some of the discrepancy between EPA and real world fuel-efficiency. A 200 W electrical load can produce a 0.4 km/L (0.94 mpg) reduction in efficiency on the FTP 75 cycle test.[40]
Advanced technology vehicles

Following the efficiency claims made for vehicles such as Chevrolet Volt and Nissan Leaf, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory recommended to use EPA's new vehicle fuel efficiency formula that gives different values depending on fuel used.[41] In November 2010 the EPA introduced the first fuel economy ratings in the Monroney stickers for plug-in electric vehicles.
For the fuel economy label of the Chevy Volt plug-in hybrid EPA rated the car separately for all-electric mode expressed in miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPG-e) and for gasoline-only mode expressed in conventional miles per gallon. EPA also estimated an overall combined city/highway gas-electricity fuel economy rating expressed in miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPG-e). The label also includes a table showing fuel economy and electricity consumed for five different scenarios: 30, 45, 60 and 75 miles (121 km) driven between a full charge, and a never charge scenario. This information was included in order to make the consumers aware of the variability of the fuel economy outcome depending on miles driven between charges. Also the fuel economy for a gasoline-only scenario (never charge) was included. For electric-only mode the energy consumption estimated in kWh per 100 miles is also shown.[42][43]

For the fuel economy label of the Nissan Leaf electric car EPA rated the combined fuel economy in terms of miles per gallon gasoline equivalent, with a separate rating for city and highway driving. This fuel economy equivalence is based on the energy consumption estimated in kWh per 100 miles, and also shown in the Monroney label.[44]
In May 2011, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and EPA issued a joint final rule establishing new requirements for a fuel economy and environment label that is mandatory for all new passenger cars and trucks starting with model year 2013, and voluntary for 2012 models. The ruling includes new labels for alternative fuel and alternative propulsion vehicles available in the US market, such as plug-in hybrids, electric vehicles, flexible-fuel vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell vehicle, and natural gas vehicles.[45][46] The common fuel economy metric adopted to allow the comparison of alternative fuel and advanced technology vehicles with conventional internal combustion engine vehicles is miles per gallon of gasoline equivalent (MPGe). A gallon of gasoline equivalent means the number of kilowatt-hours of electricity, cubic feet of compressed natural gas (CNG), or kilograms of hydrogen that is equal to the energy in a gallon of gasoline.[45]
The new labels also include for the first time an estimate of how much fuel or electricity it takes to drive 100 miles (160 km), providing US consumers with fuel consumption per distance traveled, the metric commonly used in many other countries. EPA explained that the objective is to avoid the traditional miles per gallon metric that can be potentially misleading when consumers compare fuel economy improvements, and known as the "MPG illusion." EPA explained that the new gallons-per mile metric provides a more accurate measure of fuel efficiency.[45][47]
CAFE standards
The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) regulations in the United States, first enacted by Congress in 1975,[48] are federal regulations intended to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks (trucks, vans and sport utility vehicles) sold in the US in the wake of the 1973 Arab Oil Embargo. Historically, it is the sales-weighted average fuel economy of a manufacturer's fleet of current model year passenger cars or light trucks, manufactured for sale in the United States. Under Truck CAFE standards 2008–2011 this changes to a "footprint" model where larger trucks are allowed to consume more fuel. The standards were limited to vehicles under a certain weight, but those weight classes were expanded in 2011.
State regulations
The states are pre-empted by federal law, and are not allowed to make fuel efficiency standards. However, California has a special dispensation from the Clean Air Act to make emissions standards (which other states may adopt instead of the federal standards). The California Air Resources Board is implementing some legislation that limits greenhouse gas emissions. A legal dispute has emerged over whether this is effectually a fuel efficiency standard.
Energy considerations
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2007) |
Since the total force opposing the vehicle's motion (at constant speed) multiplied by the distance through which the vehicle travels represents the work that the vehicle's engine must perform, the study of fuel economy (the amount of energy consumed per unit of distance traveled) requires a detailed analysis of the forces that oppose a vehicle's motion. In terms of physics, Force = rate at which the amount of work generated (energy delivered) varies with the distance traveled, or:
Note: The amount of work generated by the vehicle's power source (energy delivered by the engine) would be exactly proportional to the amount of fuel energy consumed by the engine if the engine's efficiency is the same regardless of power output, but this is not necessarily the case due to the operating characteristics of the internal combustion engine.
For a vehicle whose source of power is a heat engine (an engine that uses heat to perform useful work), the amount of fuel energy that a vehicle consumes per unit of distance (level road) depends upon:
- The thermodynamic efficiency of the heat engine;
- The forces of friction within the mechanical system that delivers engine output to the wheels;
- The forces of friction in the wheels and between the road and the wheels (rolling friction);
- Other internal forces that the engine works against (electrical generator, air conditioner, water pump, engine fan, etc.);
- External forces that resist motion (e.g., wind, rain);
- Non-regenerative braking force (brakes that turn motion energy into heat rather than storing it in a useful form; e.g., electrical energy in hybrid vehicles);
- Fuel consumed while the engine is on standby and not powering the wheels, i.e., while the vehicle is coasting, braking or idling. [49]

Ideally, a car traveling at a constant velocity on level ground in a vacuum with frictionless wheels could travel at any speed without consuming any energy beyond what is needed to get the car up to speed. Less ideally, any vehicle must expend energy on overcoming road load forces, which consist of aerodynamic drag, tire rolling resistance, and inertial energy that is lost when the vehicle is decelerated by friction brakes. With ideal regenerative braking, the inertial energy could be completely recovered, but there are few options for reducing aerodynamic drag or rolling resistance other than optimizing the vehicle's shape and the tire design. Road load energy, or the energy demanded at the wheels, can be calculated by evaluating the vehicle equation of motion over a specific driving cycle.[50] The vehicle powertrain must then provide this minimum energy in order to move the vehicle, and will lose a large amount of additional energy in the process of converting fuel energy into work and transmitting it to the wheels. Overall, the sources of energy loss in moving a vehicle may be summarized as follows:
- Engine efficiency, which varies with engine type, the mass of the automobile and its load, and engine speed (usually measured in RPM).
- Aerodynamic drag force, which increases roughly by the square of the car's speed, but note that drag power goes by the cube of the car's speed.
- Rolling friction.
- Braking, although regenerative braking captures some of the energy that would otherwise be lost.
- Losses in the transmission. Manual transmissions can be up to 94% efficient whereas older automatic transmissions may be as low as 70% efficient[51] Automatically controlled shifting of gearboxes that have the same internals as manual boxes will give the same efficiency as a pure manual gearbox plus the bonus of added intelligence selecting optimal shifting points
- Air conditioning. The power required for the engine to turn the compressor decreases the fuel-efficiency, though only when in use. This may be offset by the reduced drag of the vehicle compared with driving with the windows down. The efficiency of AC systems gradually deteriorates due to dirty filters etc.; regular maintenance prevents this. The extra mass of the air conditioning system will cause a slight increase in fuel consumption.
- Power steering. Older hydraulic power steering systems are powered by a hydraulic pump constantly engaged to the engine. Power assistance required for steering is inversely proportional to the vehicle speed so the constant load on the engine from a hydraulic pump reduces fuel efficiency. More modern designs improve fuel efficiency by only activating the power assistance when needed; this is done by using either direct electrical power steering assistance or an electrically powered hydraulic pump.
- Cooling. Older cooling systems used a constantly engaged mechanical fan to draw air through the radiator at a rate directly related to the engine speed. This constant load reduces efficiency. More modern systems use electrical fans to draw additional air through the radiator when extra cooling is required.
- Electrical systems. Headlights, battery charging, active suspension, circulating fans, defrosters, media systems, speakers, and other electronics can also significantly increase fuel consumption, as the energy to power these devices causes increased load on the alternator. Since alternators are commonly only 40–60% efficient, the added load from electronics on the engine can be as high as 3 horsepower (2.2 kW) at any speed including idle. In the FTP 75 cycle test, a 200 watt load on the alternator reduces fuel efficiency by 1.7 MPG.[40] Headlights, for example, consume 110 watts on low and up to 240 watts on high. These electrical loads can cause much of the discrepancy between real world and EPA tests, which only include the electrical loads required to run the engine and basic climate control.
- Standby. The energy needed to keep the engine running while it is not providing power to the wheels, i.e., when stopped, coasting or braking.
Fuel-efficiency decreases from electrical loads are most pronounced at lower speeds because most electrical loads are constant while engine load increases with speed. So at a lower speed a higher proportion of engine horsepower is used by electrical loads. Hybrid cars see the greatest effect on fuel-efficiency from electrical loads because of this proportional effect.
Fuel economy-boosting technologies
Engine cycle
- Replacing petrol engines with more efficient diesel engines, giving lower brake specific fuel consumption at lower RPM.
Engine combustion strategies:
- Optimizing engine running temperature by electronic control of the cooling system
- Stratified Charge combustion
- Lean burn combustion
- Cooled EGR (cooled exhaust gas recirculation for petrol engines)
- Atkinson cycle (an overexpansion cycle realized usually by late intake valve closure)
- Variable valve timing and variable valve lift
- Variable geometry turbocharging or twincharging (coupled with a downsized engine)
- Gasoline direct injection petrol engines (usually with a higher compression ratio) in lieu of carburetor or port injection
- Turbocharged Direct Injection diesel engines in lieu of indirect injection engine
- Common Rail diesel engines (higher injection pressure)
- Piezoelectric diesel injectors using multiple injections per engine cycle
- Cylinder management (shutting off individual cylinders when their power output is not needed)
- Automatic Start Stop function (switches the engine off while the vehicle is temporarily stopped)
Engine internal losses
- Reducing engine displacement using a downsized engine (with a Supercharger or a Turbocharger to keep enough torque)
- Using lower-friction lubricants (engine oil, transmission fluid, axle fluid)
- Using lower viscosity engine oils that require less energy to circulate. It also reduces hydrodynamic friction
- Using a variable displacement oil pump so that excessive flow rate is avoided at high engine speed
- Electrifying engine accessories such as water pump, power steering pump and air conditioner compressor, so that more engine power goes to the transmission, or less fuel is required for the same traction power
- Reducing engine frictions by roller type cam, low friction coating on piston skirt and optimizing load bearing surface, e.g. camshaft bearing and connective rods.
Engine running conditions
- Using coolant additives that increase the thermal efficiency of the cooling system
- Increasing the number of gearbox ratios in manual gearboxes (to lower the engine rpm at cruise)
- Reducing the volume of water-based cooling systems so that engines reach their efficient operating temperature sooner
- Escaping the poorly efficient idle and low power conditions :
- Automatically shutting off engine when vehicle is stopped (Start-stop system, mild hybrid)
- Augmenting a downsized engine with an electric drive system and battery (hybrid vehicles) hybrid electric vehicle
Transmission losses
- Using a manual gearbox or continuously variable transmission automatic gearbox instead of epicyclic gearboxes with torque converter couplings
- Incorporating Locking torque converters in automatic transmissions to reduce slip and power losses in the converter
- The use of two-wheel drive only, on road vehicles not used for towing
Aerodynamic Drag
- Vehicle downsizing without loss of functionality improving vehicle packaging and space utilization
- Designing the shape of the vehicle and the internal cooling system in order to reduce aerodynamic drag
- Removing external high drag devices (roof racks, brush guards, wind deflectors)
Rolling resistance
- Reducing vehicle weight by downsizing and using lighter materials such as aluminum, fiberglass, plastic, high-strength steel and carbon fiber instead of mild steel and iron
- Using thinner tires (lower friction area)
- Increasing tire pressure (to lower tire deformation under weight)
- Replacing tires with low rolling resistance (LRR) models[52]
Electrical
- Installing an alternator disconnect and supplying electrical system from deep cycle battery pack that is charged at home (although the added weight of the larger battery would have to be considered in calculating the possible fuel savings from this concept)
Energy saving
- Using lighter materials for moving parts such as pistons, crankshaft, gears and alloy wheels
- Recapturing wasted energy while braking (regenerative braking)
- Converting waste heat from exhaust system directly into electricity
- Recapturing wasted energy in the vehicle suspension[53]
Driving attitude
- Reducing speed
- Hypermiling and Fuel economy-maximizing behaviors; generally, fuel economy is maximized when acceleration and braking are minimized
- Maintaining a steady and efficient RPM (near to best BSFC rpm) [54]
Traffic management
- Active highway management (matching speed limits and vehicles allowed to join motorways/freeways to traffic density), to maintain traffic throughput and fuel efficiency.
Future technologies
Technologies that may improve fuel efficiency, but are not yet on the market, include:
- HCCI (Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition) combustion
- Scuderi engine
- Compound engines
- Two-stroke diesel engines
- High-efficiency gas turbine engines
- BMW's Turbosteamer – using the heat from the engine to spin a mini turbine to generate power
- Vehicle electronic control systems that automatically maintain distances between vehicles on motorways/freeways that reduce ripple back braking, and consequent re-acceleration.
- Time-optimized piston path, to capture energy from hot gases in the cylinders when they are at their highest temperatures[citation needed]
- sterling hybrid battery vehicle
Many aftermarket consumer products exist that are purported to increase fuel economy; many of these claims have been discredited. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency maintains a list of devices that have been tested by independent laboratories and makes the test results available to the public.[55]
Fuel economy data reliability
The mandatory publication of the fuel consumption by the manufacturer led some to use dubious practices to reach better values in the past. If the test is on a test stand, the vehicle may detect open doors and adapt the engine control. Also when driven according to the test regime, the parameters may adapt automatically. Test laboratories use a "golden car" that is tested in each one to check that each lab produces the same set of measurements for a given drive cycle.[56]
Tire pressures and lubricants have to be as recommended by the manufacturer (Higher tire pressures are required on a particular dynamometer type, but this is to compensate for the different rolling resistance of the dynamometer, not to produce an unrealistic load on the vehicle). Normally the quoted figures a manufacturer publishes have to be proved by the relevant authority witnessing vehicle/engine tests. Some jurisdictions independently test emissions of vehicles in service, and as a final measure can force a recall of all of a particular type of vehicle if the customer vehicles do not fulfill manufacturers' claims within reasonable limits. The expense and bad publicity from such a recall encourages manufacturers to publish realistic figures. The US Federal government retests 10–15% of models[57]), to make sure that the manufacturer's tests are accurate.
Concerns over EPA estimates
For many years critics had claimed that EPA estimated fuel economy figures had been misleading. The primary arguments of the EPA detractors were focused on the lack of real world testing, and the very limited scale (i.e., city or highway).[58]
Partly as a response to these criticisms, the EPA changed their fuel economy rating system in 2008 in an attempt to more adequately address these concerns. Instead of testing simply in two presumed modes, the testing now covers:[59]
- Faster speeds and acceleration
- Air conditioner use
- Colder outside temperatures
While the new EPA standards may represent an improvement, real world user data may still be the best way to gather and collect accurate fuel economy information. As such the EPA has also set up a http://www.fueleconomy.gov/mpg/MPG.do?action=browseList website where drivers can enter and track their own real-world fuel economy numbers.
There are also a number of websites that attempt to track and report individual user fuel economy data. Sites or publications such as Consumer Reports, Edmunds.com, and TrueDelta.com offer this service and claim more accurate numbers than those listed by the EPA.
Fuel economy maximizing behaviors
Governments, various environmentalist organizations, and companies like Toyota and Shell Oil Company have historically urged drivers to maintain adequate air pressure in tires and careful acceleration/deceleration habits. Keeping track of fuel efficiency stimulates fuel economy-maximizing behavior.[60]
Fuel economy as part of quality management regimes
Environmental management systems EMAS as well as good fleet management includes record keeping of the fleet fuel consumption. Quality management uses those figures to steer the measures acting on the fleets. This is a way to check whether procurement, driving, and maintenance in total have contributed to changes in the fleet's overall consumption.
Unit conversions
- US Gallons
- 1 MPG ≈ 0.425 km/L
- 235.2/MPG ≈ L/100 km
- 1 MPG ≈ 1.201 MPG (Imp)
- Imperial gallons
- 1 MPG ≈ 0.354 km/L
- 282/MPG ≈ L/100 km
- 1 MPG ≈ 0.833 MPG (US)
Conversion from MPG
|
|
Conversion from km/L and L/100 km
|
|
See also
- All-electric vehicle
- Automobile costs
- ACEA agreement
- Car tuning
- Emission standard
- Energy conservation
- FF layout
- Fuel efficiency in transportation
- Fuel saving devices
- Gasoline gallon equivalent
- Motorised quadricycle (vehicles with low power engines/low top speed)
- Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent
- Passenger miles per gallon
- The Very Light Car
- Vehicle Efficiency Initiative
- Vehicle metrics
- List of 2008 New Zealand fuel economy ratings
- List of May 2008 UK fuel economy ratings
- Gas-guzzler
- Green vehicle
- Low-carbon economy
- Low-rolling resistance tires
- Microcar
- Plug-in hybrid*List of 2009 United States EPA fuel economy ratings
Annotations
- ^ The 2.2% drop figure was calculated by finding daily consumption to be 9,299,684 barrels of petroleum. Obtain 1973's petroleum consumption from transportation sector at 2.1e from the Energy Consumption by Sector section, then convert to barrels using A1 in the Thermal Conversion Factors section (assume "conventional motor gasoline" since ethanol-based or purportedly smog-reducing gas was not common in 1973).[12]
References
- ^ Page, Walter Hines; Page, Arthur Wilson (1916). "Man and His Machines". The World's Work. XXXIII. Garden City, New York: Doubleday, Page & Co.
- ^ "Fuel Consumption Ratings". Government of Canada. January 2011. Retrieved 8 June 2011.
- ^ [1]
- ^ The New Fuel Economy Label at FuelEconomy.gov
- ^ G. Tyler Miller, Jr., Scott E. Spoolman (2011). Living in the Environment. Cengage Learning. p. 396. ISBN 9780538494144.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "2008 Fuel Economy Guide" (PDF). US EPA. Retrieved 17 April 2013. Cite error: The named reference "2008epa" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars – Policies – Climate Action – European Commission. Ec.europa.eu (2010-12-09). Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Myth: Cars are becoming more fuel efficient. Ptua.org.au. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ a b c Comparison of Passenger Vehicle Fuel Economy and GHG Emission Standards Around the World at Pew Center on Global Climate Change. (PDF) . Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ a b c Steady Speed Fuel Economy "The two earlier studies by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) indicate maximum fuel efficiency was achieved at speeds of 35 to 40 mph (55 to 65 km/h). The recent FHWA study indicates greater fuel efficiency at higher speeds."
- ^ Cowan, Edward (27 November 1973). "Politics and Energy: Nixon's Silence on Rationing Reflects Hope That Austerity Can Be Avoided". The New York Times. p. 30. Retrieved 22 July 2008. (subscription required)
- ^ Staff (28 June 2008). Annual Energy Review (PDF) (2007 ed.). Washington, DC: Energy Information Administration.
- ^ "55 Mile-per-hour Speed Limit Approved by House". United Press International. 4 December 1973. p. 30. Retrieved 22 July 2008. (subscription required)
- ^ "Special Report 254: Managing Speed" (PDF). Transportation Research Board: 189. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
Bloomquist (1984) estimated that the 1974 National Maximum Speed Limit (NMSL) reduced fuel consumption by 0.2 to 1.0 percent.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Highway Statistics 1973 (Table VM-2: VEHICLE MILES, BY STATE AND HIGHWAY SYSTEM-1973)" (PDF). Federal Highway Administration: 76. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b Lexus IS250 2.5L 6cyl, Auto 6 speed Sedan, 5 seats, 2WD
- ^ a b IS 250 Kraftstoffverbrauch kombiniert 8,9 L/100 km (innerorts 12,5 L/ außerorts 6,9 L) bei CO2-Emissionen von 209 g/km nach dem vorgeschriebenen EU-Messverfahren http://www.lexus.de/range/is/index.aspx
- ^ a b 2009 Lexus IS 250 6 cyl, 2.5 L, Automatic (S6), Premium http://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/findacar.htm
- ^ Chinese Fuel Economy Laws. Treehugger.com. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Vehicles & the Environment. Infrastructure.gov.au. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Information on Green Vehicle Guide Ratings and Measurement. Australian Department of Infrastructure and Transport
- ^ Green Vehicle Guide. Green Vehicle Guide. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Vehicle test cycles. Herkules.oulu.fi. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ "Honda-Frühstück am 15. Januar 2011".
- ^ "2011 Honda CR-Z Specs and Features".
- ^ Guidance notes and examples. (PDF) . Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Fuel Economy Label. Dft.gov.uk. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Vehicle Labelling. Environ.ie (2008-07-01). Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ http://www.carsandgarages.co.uk/news/29-ASA-says-fuel-consumption-figures-are-mis
- ^ Mike Millikin (28 September 2014). "ICCT: gap between official and real-world fuel economy figures in Europe reaches ~38%; call to implement WLTP ASAP". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ a b Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA) (2009). "From 10•15 to JC08: Japan's new economy formula". News from JAMA. Retrieved 9 April 2012. Issue No. 2, 2009.
- ^ a b "Japanese 10–15 Mode". Diesel.net. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- ^ "Prius Certified to Japanese 2015 Fuel Economy Standards with JC08 Test Cycle". Green Car Congress. 11 August 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- ^ Vehicle Fuel Economy Labelling – FAQs[dead link]
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions. Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Steven Cole Smith (28 April 2005). "2005 Pontiac GTO". Orlando Sentinel via Cars.com.
- ^ a b "Dynamometer Driver's Aid". US EPA. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- ^ How the EPA Tests and Rates Fuel Economy. Auto.howstuffworks.com (2005-09-07). Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Find a Car 1985 to 2009. Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ a b Automotive Electrical Systems Circa 2005. Spectrum.ieee.org. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Roth, Dan. (2009-10-01) REPORT: EPA planning to address outlandish fuel economy claims of electric cars. Autoblog.com. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ "Volt receives EPA ratings and label: 93 mpg-e all-electric, 37 mpg gas-only, 60 mpg-e combined". Green Car Congress. 24 November 2010. Retrieved 24 November 2010.
- ^ US Environmental Protection Agency and US Department of Energy (4 May 2011). "2011 Chevrolet Volt". Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- ^ Nick Bunkley (22 November 2010). "Nissan Says Its Electric Leaf Gets Equivalent of 99 M.P.G." The New York Times. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ a b c EPA (May 2011). "Fact Sheet: New Fuel Economy and Environment Labels for a New Generation of Vehicles". US Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 25 May 2011. EPA-420-F-11-017
- ^ "EPA, DOT unveil the next generation of fuel economy labels". Green Car Congress. 25 May 2011. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ^ John M. Broder (25 May 2011). "New Mileage Stickers Include Greenhouse Gas Data". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
- ^ "CAFE Overview: "What is the origin of CAFE?"". NHTSA. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
- ^ [http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/sr/sr286.pdf TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD SPECIAL REPORT 286 TIRES AND PASSENGER VEHICLE FUEL ECONOMY, Transportation Research Board, National Academy of Sciences p.62-65 of pdf, p.39-42 of report. Retrieved 22 October 2014.
- ^ Wheels, online road load and MPG calculator. Virtual-car.org (2009-08-03). Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ An Overview of Current Automatic, Manual and Continuously Variable Transmission Efficiencies and Their Projected Future Improvements. SAE.org (1999-03-01). Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Low-rolling resistance tires
- ^ Chandler, David (9 February 2009). "More power from bumps in the road". Retrieved 8 October 2009.
- ^ "How efficient is your car?". The Hindu. India. 26 January 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
- ^ Gas Saving and Emission Reduction Devices Evaluation | Cars and Light Trucks | US EPA. Epa.gov. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ Environmental Nanoparticles – Exploring the links between Vehicle Emissions and Ambient Air. (PDF). A meeting of the Automation and Analytical Management Group of the Royal Society of Chemistry. 8 June 2005. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ EPA. Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ Vehicle Selection – Make. Fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
- ^ http://onfuel.appspot.com keep track of fuel efficiency
External links
- Australian Fuel Consumption Label
- Searchable fuel economy data from the EPA - United States Environmental Protection Agency
- Model Year 2014 Fuel Economy Guide , U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Energy, April 2014.

