Fernbach flask: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
EnronEvolved (talk | contribs) |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.5.4) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{refimprove|date=September 2014}} |
{{refimprove|date=September 2014}} |
||
[[File:Fernbach Flask.svg|thumb|Fernbach flask]] |
[[File:Fernbach Flask.svg|thumb|Fernbach flask]] |
||
A '''Fernbach flask''' is a type of [[Laboratory flask|flask]] suited for large volume [[cell culture]] where the culture requires a large surface area to volume ratio. Typically, they are baffled on the bottom in order to maximize [[oxygen]] transfer to the culture medium. The flask was named after French biologist [[Auguste Fernbach]] (1860-1939).<ref>[http://www.pasteur.fr/infosci/archives/frb0.html Pasteur Institut:Auguste Fernbach (1860-1939)]</ref> |
A '''Fernbach flask''' is a type of [[Laboratory flask|flask]] suited for large volume [[cell culture]] where the culture requires a large surface area to volume ratio. Typically, they are baffled on the bottom in order to maximize [[oxygen]] transfer to the culture medium. The flask was named after French biologist [[Auguste Fernbach]] (1860-1939).<ref>[http://www.pasteur.fr/infosci/archives/frb0.html Pasteur Institut:Auguste Fernbach (1860-1939)] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141208164929/http://www.pasteur.fr/infosci/archives/frb0.html |date=2014-12-08 }}</ref> |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 02:48, 30 September 2017
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
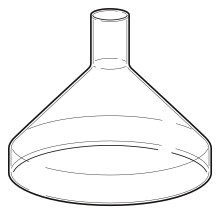
A Fernbach flask is a type of flask suited for large volume cell culture where the culture requires a large surface area to volume ratio. Typically, they are baffled on the bottom in order to maximize oxygen transfer to the culture medium. The flask was named after French biologist Auguste Fernbach (1860-1939).[1]
References
- ^ Pasteur Institut:Auguste Fernbach (1860-1939) Archived 2014-12-08 at the Wayback Machine
