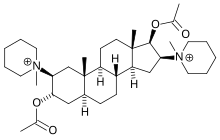
Pancuronium bromide
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Protein binding | 77 to 91% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 to 2.7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.923 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C35H60N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 572.861 g/mol g·mol−1 |
Pancuronium is a chemical compound, used in medicine as the bromide salt pancuronium bromide. It has the brand name Pavulon (Organon International). It is a muscle relaxant with various purposes. It is one of the drugs administered during a lethal injection in the United States.
Mode of action
Pancuronium is a typical non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It acts as a competitive acetylcholine antagonist on neuromuscular junctions, displacing acetylcholine (hence competitive) from its post-synaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It is (unlike suxamethonium) a non-depolarizing agent, which means that it causes no spontaneous depolarizations upon association with the nicotinic receptor in neuromuscular junction, thus producing no muscle fasciculations upon administration. Despite being a steroid, pancuronium has no hormonal activity. It exerts slight vagolytic activity (i.e. diminishing activity of the vagus nerve) and no ganglioplegic (i.e. blocking ganglions) activity. Pancuronium is a very potent muscle relaxant/curaremimetic. The ED95 (i.e. a dose causing a 95% reduction in muscle activity) is only 60 µg/kg body weight administered intravenously. Muscle relaxation suitable for intubation sets in about 90–120 seconds after administration of the drug. Full muscle paralysis for major surgery is achieved about 2–4 minutes after application. Clinical effects (muscle activity lower than 25% of physiological) last for about 100 minutes. The time needed for full (over 90% muscle activity) recovery after single administration is about 120–180 minutes in healthy adults, but can be protracted to more hours in poor health subjects and when concomitantly administered with other long-acting anesthetics (e.g. some opioids, barbiturates, inhalation anesthetics). The effects of pancuronium can be at least partially reversed by anticholinesterasics, such as neostigmine, pyridostigmine and edrophonium.
Uses in medicine
Pancuronium is used with general anaesthesia in surgery for muscle relaxation and as an aid to intubation or ventilation. It does not have sedative or analgesic effects.
Side effects include moderately raised heart rate and thereby arterial pressure and cardiac output, excessive salivation, apnea and respiratory depression, rashes, flushing and sweating. The muscular relaxation can be dangerous in the seriously ill and it can accumulate leading to extended weakness. Pancuronium is not preferable in long term use in ICU ventilated patients.
In Belgium and The Netherlands, pancuronium is recommended in the protocol for euthanasia. After administering sodium thiopental to induce coma, pancuronium is delivered in order to stop breathing.[1]
In 1997, Dr Michael Munro, a Scottish neonatologist at Aberdeen Maternity Hospital, was cleared of malpractice by the GMC Fitness to Practice panel after giving 23 times the standard dose of pancuronium to two dying neonates. In the final minutes of life, each baby was suffering from agonal gasping and violent body spasms, which was highly distressing for the parents to witness. Dr Munro administered 2,000 mg (2,000 micrograms?) of pancuronium to the babies after advising the parents that this would ease their suffering, but could also hasten death.[2][3] It is on record that neither of the children's parents were unhappy with Dr Munro's treatment of their babies.[4]
Uses in execution
Procedure
It is also used as one component of a lethal injection used in capital punishment in some parts of the United States.[5]
Controversy
Pancuronium bromide has no hypnotic effects, and if the anaesthetic agent used in lethal injection is ineffective, an individual could conceivably never achieve unconsciousness, and thus be able to feel all of the pain associated with the procedure, but unable to cry out or move due to the pancuronium's complete paralytic action. There have also been several high-profile civil lawsuits alleging similar failures to achieve analgesia or unconsciousness prior to a general surgical procedures. These too have largely been blamed on improper or insufficient dosages of anaesthetic in concert with normal dosages of pancuronium bromide.
Largely echoing this sentiment, Amnesty International has objected to its use in lethal injections on the grounds that it "may mask the condemned prisoner's suffering during the execution"[6] and thereby lead observers to conclude that lethal injection is painless, or less cruel than other forms of execution.
In September 2007 the US Supreme Court agreed to hear their first case of whether or not the use of lethal injection does in fact violate the US Constitution's Eighth Amendment's ban on cruel and unusual punishment.[7] On April 16, 2008, the court upheld the constitutionality of Kentucky's lethal injection practices.[8]
Uses in crime
Pancuronium was the compound used in Efren Saldivar's killing spree.[9] It was also used by paramedics, the "Skin Hunters", to kill patients in the Polish city of Łódź. Pavulon was also used by Richard Angelo in 1987 to kill at least 10 patients under his care at the Good Samaritan Hospital in New York.
References
- ^ euthanasics
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/north_east/6291224.stm
- ^ "Doctor cleared over baby deaths". The Guardian. 11 July 2007.
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/north_east/6276900.stm
- ^ BBC article on lethal injection. Small panel lists the chemicals used.
- ^ Amnesty International
- ^ "Court to decide lethal injection, voter ID cases". CNN. 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-25.
- ^ "US Supreme Court published opinions" (PDF). US Supreme Court. 2008.
- ^ Crimelibrary
External links
- Template:Fr icon "Pavulon – Information professionnelle [prescribing information]" (PDF). Compendium Suisse des Médicaments. December 12, 2005. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help)
