AMP deaminase
Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency type 1 (AMPD1) is now called called Adenosine monophosphate deaminase deficiency (MADD) *(PLEASE SEE TALK PAGE).
AMP deaminase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AMPD1 gene.[1][2]
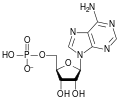
Adenosine monophosphate deaminase is an enzyme that converts adenosine monophosphate (AMP) to inosine monophosphate (IMP), freeing an ammonia molecule in the process.
Function
It is a part of the metabolic process that converts sugar, fat, and protein into cellular energy.
In order to use energy, a cell converts one of the above fuels into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via the mitochondria. Cellular processes, especially muscles, then convert the ATP into adenosine diphosphate (ADP), freeing the energy to do work.
Pathology
A deficiency is associated with myoadenylate deaminase deficiency.
References
- ^ Mahnke-Zizelman DK, Sabina RL (1992). "Cloning of human AMP deaminase isoform E cDNAs. Evidence for a third AMPD gene exhibiting alternatively spliced 5'-exons". J Biol Chem. 267 (29): 20866–77. PMID 1400401.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Entrez Gene: AMPD1 adenosine monophosphate deaminase 1 (isoform M)".
Further reading
-
adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
-
inosine monophosphate (IMP)
External links
- AMP+Deaminase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)