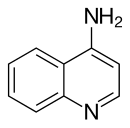
4-Aminoquinoline
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Quinolin-4-amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.771 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8N2 | |
| Molar mass | 144.177 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Aminoquinoline is a form of aminoquinoline with the amino group at the 4-position of the quinoline.
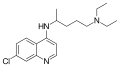
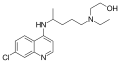
A variety of derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline are antimalarial agents useful in treating erythrocytic plasmodial infections. Examples include amodiaquine, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine.[1]
References
- ^ Bray PG, Hawley SR, Ward SA (1996). "4-Aminoquinoline resistance of Plasmodium falciparum: insights from the study of amodiaquine uptake". Mol. Pharmacol. 50 (6): 1551–8. PMID 8967977.
External links
- Bourne SA, De Villiers K, Egan TJ (2006). "Three 4-aminoquinolines of antimalarial interest". Acta Crystallogr C. 62 (Pt 2): o53–7. doi:10.1107/S0108270105041235. PMID 16456284.