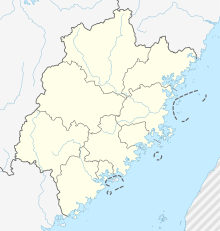
Pingtan Island
| Pingtan Island | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Pingtan Beach | |||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 平潭島 | ||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 平潭岛 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Other names | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haitan Island | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 海壇島 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 海坛岛 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Pingtan Island or Haitan Island[1] is an island of Fuzhou off the east coast of mainland Asia in Pingtan County, Fujian Province, China (PRC), south of the complex estuary of the Min River. It is the largest island in Fujian and the fifth-largest island administered by the People's Republic of China.
History
In June 1955, there was considerable road and military construction around Haitan Island, including roads leading to possible artillery positions on the mainland. These positions might have been used to protect the Haitan Strait, which was thought of as a favorable staging area for amphibious operations against the Matsu Islands.[2]
The site was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List in 2001, under Haitan Scenic Spots, in the Mixed category (Cultural & Natural).[3]
Geography
Administratively, the island is part of Pingtan County, which includes several smaller islands and part of the nearby mainland. Most of the county's towns, including its seat of government at Tancheng, are on the island. Large areas of the island's coast have undergone land reclamation, along with major building and infrastructure projects.[4] Pingtan is separated from mainland China by the Haitan Strait. Most of the nearby mainland is the county-level city of Fuqing, administered as part of the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou.
Pingtan is separated from Taiwan Island by the Taiwan Strait. Following the completion of its bridge to the mainland in 2010, Pingtan may be considered the closest part of the Chinese "mainland" to Taiwan Island.
Under current international agreement, the island's southernmost extremity forms the boundary between the East and South China Seas.[5] In the still-unapproved draft of the new edition of the IHO's Limits of Oceans and Seas, Cape Xiang—the northernmost extremity of the island—forms the boundary between the East China Sea and the Taiwan Strait, with the South China Sea having its northern boundary moved to the south end of the strait.[6]
Economy
The island relies on tourism and anticipates that foreign investment will spur economic growth. The first major bridge to cross the Haitan Strait was completed in November 2010, connecting the island to Fuqing on the mainland. Spanning 4,976 meters, it cost 1.4 billion RMB (about US$200 million) to build.[7]
An 88.5-km-long Fuzhou-Pingtan Railway (the Fuping Railway, 福平铁路), connecting Fuzhou to Pingtan Island, via Changle and a series of bridges, is under construction. The project was approved in November 2012. It was expected that the work would start by the end of the year, and would take about five and a half years.[8]
In early 2012, it was announced that a large cloud computing center would be built in Pingtan.[9]
Culture
A 430,000-square-foot (40,000 m2) museum, the Pingtan Art Museum, is currently under construction in the island. The museum, designed by the Chinese-American firm MAD Studio on an artificial island, is scheduled for completion in 2016.[10]
Maps
-
Map of the area including Haetan (1880)
-
Map including Pingtan Island (labeled as Haitan Dao)
-
Map including Pingtan Island (labelled as P'ING-T'AN 平潭) (AMS, 1954)
-
Map including Pingtan Island (labeled as HAI-T'AN TAO) (DMA, 1972)
-
Map including Pingtan Island (labeled as HAITAN DAO) (DMA, 1996)
See also
References
Citations
- ^ Faming Huang, Yanhong Lin, Huixin Liang, Rongrong Zhao, Qiuming Chen, Jie Lin and Jinliang Huang (3 December 2019). "Coordination of Marine Functional Zoning Revision at the Provincial and Municipal Levels: A Case Study of Putian, China". Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. p. 5. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
Haitan Island
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Current Intelligence Weekly Summary". CIA. 30 June 1955. p. 2 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ Haitan Scenic Spots - UNESCO World Heritage Centre; added to Tentative List on November 29, 2001.
- ^ Cf. especially the historical imagery timeline available for Google Earth.
- ^ IHO (1953), §49.
- ^ IHO (1986), Ch. 7.2.
- ^ "Pingtan Island, a before and after story in the making". Whats On Xiamen , Inc. Archived from the original on 30 September 2010. Retrieved 28 September 2010.
- ^ 福州至平潭铁路可研报告获发改委批复, 2012-11-10
- ^ "China to Build Cloud Computing Center in Pingtan Near Taiwan". Hostingtecnews. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- ^ "China - The museum is an island". Inexhibit. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
Bibliography
- S-23: Limits of Oceans and Seas (PDF) (3rd ed.), Monaco: International Hydrographic Organization, 1953, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-08, retrieved 29 December 2020.
- S-23: Limits of Oceans and Seas (4th (draft) ed.), Monaco: International Hydrographic Organization, 1986, archived from the original on 2016-04-12, retrieved 2019-03-21.