Iron monosilicide
Appearance
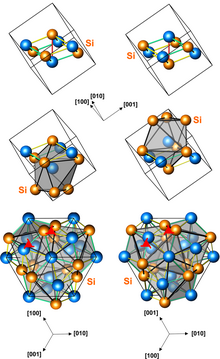 Structures of left-handed and right-handed FeSi crystals (3 presentations, with different numbers of atoms per unit cell)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iron silicide
| |
| Other names
Naquite, fersilicite
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.506 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| FeSi | |
| Molar mass | 83.931 g/mol |
| Appearance | gray cubic crystals[1] |
| Density | 6.1 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 1,410 °C (2,570 °F; 1,680 K)[1] |
| Band gap | 0.05 eV (ind.) 0.14 eV (dir.)[2] |
| Structure | |
| Cubic[3] | |
| P213 (No. 198), cP8 | |
a = 0.44827(1) nm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Iron germanide |
Other cations
|
Cobalt silicide Manganese silicide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Iron monosilicide (FeSi) is an intermetallic compound, a silicide of iron that occurs in nature as the rare mineral naquite. It contains iron in both the 0 and +3 oxidation states.[4]. It is a semiconductor with unusual magnetic properties at low temperatures. It has a cubic crystal lattice with no inversion center; therefore its magnetic structure is helical, with right-hand and left-handed chiralities.[3]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 4.68. ISBN 9781498754293.
- ^ Galakhov, V R; Kurmaev, E Z; Cherkashenko, V M; Yarmoshenko, Yu M; Shamin, S N; Postnikov, A V; Uhlenbrock, S; Neumann, M; Lu, Z W; Klein, B M; Shi, Zhu-Pei (1995). "Electronic structure of FeSi". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 7 (28): 5529–5535. arXiv:mtrl-th/9505004. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/7/28/010.
- ^ a b Stishov, Sergei M.; Petrova, Alla E. (2011). "Itinerant helimagnetic compound MnSi". Uspekhi Fizicheskih Nauk. 181 (11): 1157. doi:10.3367/UFNr.0181.201111b.1157.
- ^ Dutta, Paromita; Pandey, Sudhir K (10 April 2019). "Effects of correlations and temperature on the electronic structures and related physical properties of FeSi and CoSi: a comprehensive study". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 31 (14): 145602. doi:10.1088/1361-648X/aafdce.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
