Landfall Peak
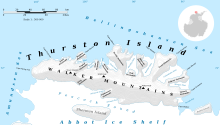

Landfall Peak (72°0′S 102°1′W / 72.000°S 102.017°W) is a prominent peak-shaped landmark near the extreme west end of Thurston Island, Antarctica, about 8 nautical miles (15 km) east-northeast of Cape Flying Fish and 0.5 nautical miles (0.9 km) northwest of Mount Gimber. It was discovered by members of the United States Antarctic Service in flights from the USS Bear in February 1940, and photographed at that time by E.B. Perce. The peak was plotted from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in December 1946, and was observed by personnel of the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960. It was so named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names because rock exposures on the peak serve as a mark for ships approaching Thurston Island from the west.[1]
See also
Maps
- Thurston Island – Jones Mountains. 1:500000 Antarctica Sketch Map. US Geological Survey, 1967.
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD). Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated.
References
- ^ "Landfall Peak". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Landfall Peak". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Landfall Peak". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.

