Banksia aquilonia
| Banksia aquilonia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Banksia |
| Species: | B. aquilonia
|
| Binomial name | |
| Banksia aquilonia (A.S.George) A.S.George[1]
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Banksia integrifolia subsp. aquilonia (A.S.George) K.R.Thiele | |

Banksia aquilonia, commonly known as the northern banksia[2] and jingana,[3] is a tree in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to north Queensland on Australia's northeastern coastline. With an average height of 8 m (26 ft), it has narrow glossy green leaves up to 20 cm (7.9 in) long and 6 to 10 cm (2.4 to 3.9 in) high pale yellow flower spikes, known as inflorescences, appearing in autumn. As the spikes age, their flowers fall off and they develop up to 50 follicles, each of which contains two seeds.
Alex George described the plant in his 1981 monograph of the genus Banksia as a variety of Banksia integrifolia, but later reclassified it as a separate species. Genetic studies show it to be related to Banksia plagiocarpa, Banksia oblongifolia and Banksia robur. The species is found in wet sclerophyll forest and rainforest margins on sandy soils. Banksia aquilonia regenerates after bushfire by regrowing from epicormic buds under its bark. It is rarely cultivated.
Description
Banksia aquilonia grows as a tall shrub or small tree up to 8 m (26 ft) high,[4] though plants up to 15 m (49 ft) have been recorded.[5] It has hard, fissured, grey bark, and narrow elliptic or lanceolate leaves measuring 5–20 cm (2.0–7.9 in) long by 0.6–1.2 cm (0.2–0.5 in) wide with entire (straight) margins and acute tips. They are a smooth shiny green above and white below with a prominent midrib covered in red-brown hair.[6] The brownish new growth appears in summer.[5] The plant is in bloom from March to June. Flowers occur in Banksia's characteristic vertical flower spike, an inflorescence made up of hundreds of pairs of flowers densely packed in a spiral around a woody axis. B. aquilonia's flower spike is a pale yellow colour, roughly cylindrical, 6–10 cm (2.4–3.9 in) high,[4] and up to 6 cm (2.4 in) in diameter. The tubular perianths of the individual flowers are 2.5–2.9 cm (0.98–1.14 in) long.[7] These open at maturity (anthesis) to release the styles. All old flower parts fall away as up to 50 oval follicles develop on the bare woody spike. The follicles measure 0.8–1.2 cm (0.3–0.5 in) long, 0.5–0.9 cm (0.20–0.35 in) high, and 0.4–0.5 cm (0.16–0.20 in) wide. Furry at first, they become smooth with age and open when ripe,[4] and their two half-oval valves split to release the one or two seeds they contain.[6] The obovate dark grey-brown to black seeds sandwich a woody separator. Measuring 1.4–1.6 cm (0.6–0.6 in) long, they are made up of a wedge-shaped seed body, 0.8–1 cm (0.3–0.4 in) long by 0.2–0.3 cm (0.08–0.1 in) wide.[4] The woody separator is the same shape as the seed, with an impression where the seed body lies next to it.[6] Seedlings have bright obovate green cotyledons around 1 cm (0.39 in) long.[7] Juvenile leaves are narrower, measuring 7–24 cm (2.8–9.4 in) long and 0.6–2.1 cm (0.2–0.8 in) wide, and often have serrate (toothed) margins.[6]
Although the inflorescences of Banksia aquilonia are similar to B. integrifolia, the leaves are marked in their differences—the midrib on the leaves' undersides is distinctively covered in short reddish-brown hairs and the leaves are spirally arranged on the branches rather than in whorls as in all B. integrifolia subspecies. It was these differences that George felt were distinctive enough for it to be separate it as a full species from B. integrifolia.[8] The overall habit of a Banksia aquilonia tree resembles that of B. integrifolia, though is generally smaller.[6] The southernmost populations of B. aquilonia are separated from the northernmost B. integrifolia occurrence by 200 km (120 mi),[9] hence location is helpful in identification.[6]
Variants
Field volunteers for The Banksia Atlas recorded plants with large adult and juvenile leaves up to 38 cm (15 in) long along the Tully to Mission Beach Road, and a population of smaller shrub-sized plants to 3 m (10 ft) high with small narrow leaves 13 cm (5.1 in) long and 0.4 cm (0.2 in) wide at Coronation Lookout in Wooroonooran National Park, plants with normal morphology occurring further down the mountain.[5]
Taxonomy
Banksia aquilonia was first described by Alex George in 1981 as a variety of Banksia integrifolia (coast banksia), from a specimen collected at Witts Lookout in Crystal Creek National Park south of Ingham on 12 April 1975.[6] The species name is the Latin adjective aquilonius, meaning "northern", as it was the most northerly form of B. integrifolia.[10] In 1996 Kevin Thiele and Pauline Ladiges published a cladistic analysis of Banksia based on morphology, in which this taxon stood out as the only member of B. integrifolia to be both morphologically and geographically distinct from other infraspecific taxa. They also noted that there were no intermediate plants between what was then known as B. integrifolia var. aquilonia and other populations of B. integrifolia. On this basis they would have liked to promote it to species rank, but did not because their inferred phylogeny suggested that this taxon arose from within B. integrifolia. They were unwilling to render B. integrifolia paraphyletic by elevating this taxon to species rank, and they were equally unwilling to elevate all four varieties to species rank, since the others all had significant overlaps in distribution and morphology. Therefore, they simply promoted all four to subspecies rank.[11] This example has since been held up as an interesting case study on how the concept of species should be defined, as it presents the problem of "a monophyletic group comprising a paraphyletic basal group of incompletely differentiated geographic forms within which is nested at least one divergent, autapomorphic taxon that invites treatment as a species."[12]
George promoted it to species rank on the basis of its distinctive leaf arrangement and midrib in 1996.[8] Thus its full name with author citation is "Banksia aquilonia (A.S.George) A.S.George". It is placed in subgenus Banksia, section Banksia and series Salicinae. Its placement within Banksia may be summarised as follows:[4]
- Genus Banksia
- Subgenus Banksia
- Section Banksia
- Series Salicinae
- Banksia dentata - Banksia aquilonia - Banksia integrifolia - Banksia plagiocarpa - Banksia oblongifolia - Banksia robur - Banksia conferta - Banksia paludosa - Banksia marginata - Banksia canei - Banksia saxicola
- Series Grandes
- Series Banksia
- Series Crocinae
- Series Prostratae
- Series Cyrtostylis
- Series Tetragonae
- Series Bauerinae
- Series Quercinae
- Series Salicinae
- Section Coccinea
- Section Oncostylis
- Section Banksia
- Subgenus Isostylis
- Subgenus Banksia
Despite initially assigning Banksia aquilonia to be variety of B. integrifolia, George noted that it had affinities with the then newly described species Banksia plagiocarpa, with which it co-occurs on and near Hinchinbrook Island in north Queensland.[6]
Since 1998, American botanist Austin Mast and co-authors have been publishing results of ongoing cladistic analyses of DNA sequence data for Banksia and Dryandra. Their analyses suggest a phylogeny that differs greatly from George's taxonomic arrangement. Banksia aquilonia formed a clade with B. plagiocarpa, B. oblongifolia and B. robur, rather than B. integrifolia.[13][14][15] Early in 2007, Mast and Thiele rearranged the genus Banksia by merging Dryandra into it, and published B. subg. Spathulatae for the taxa having spoon-shaped cotyledons; thus B. subg. Banksia was redefined as encompassing taxa lacking spoon-shaped cotyledons. They foreshadowed publishing a full arrangement once DNA sampling of Dryandra was complete; in the meantime, if Mast and Thiele's nomenclatural changes are taken as an interim arrangement, then B. aquilonia is placed in B. subg. Spathulatae.[16]
Common names include northern banksia, white banksia, honeysuckle or white bottlebrush.[7] A local aboriginal name is jingana, in the Jirrbal and Girramay languages.[3]
Distribution and habitat
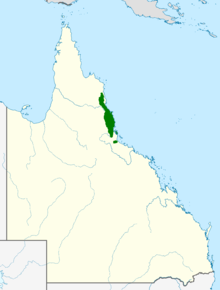
Banksia aquilonia occurs in coastal areas of northern Queensland from the Cedar Bay National Park to Paluma Range National Park,[4] in areas with an annual rainfall of 1,000 to 4,000 mm (39 to 157 in).[17] It occurs from near sea level to an altitude of 1,000 m (3,300 ft), in a variety of habitats and aspects.[5] It grows in wet sclerophyll forest or rainforest margins,[7] on plateaus, ridges, slopes and low-lying swampy areas on sandy or rocky soils,[5] generally of granitic origin,[6] or sometimes clay.[5] It commonly grows with tree species such as the pink bloodwood (Corymbia intermedia), forest red gum (Eucalyptus tereticornis), swamp turpentine (Lophostemon suaveolens), forest oak (Allocasuarina torulosa), and black sheoak (A. littoralis), and understorey species such as coin spot wattle (Acacia cincinnata) and yellow wattle (A. flavescens). Much of its lowland habitat in the Wet Tropics has been degraded or fragmented.[18] Although the range overlaps with B. dentata, the two species are not known to occur together.[6]
Ecology
Banksia aquilonia regenerates after bushfire by regrowing from epicormic buds under its bark.[19] Regeneration from root suckers has also been recorded.[20] Unlike many banksia species which release their seed after bushfires, Banksia aquilonia sets seed when the follicles mature.[21]
Banksia inflorescences are energy-rich sources of food, and B. aquilonia nectar is a likely food item of the endangered mahogany glider (Petaurus gracilis),[22] as well as many other mammals and birds.[21] Avian species observed visiting the flower spikes include the bridled honeyeater, white-cheeked honeyeater, eastern spinebill and rainbow lorikeet.[5]
Cultivation
Banksia aquilonia adapts readily to cultivation in humid or temperate climates,[17] but is rarely cultivated.[7] A fast-growing plant,[7] it can grow in acidic soils from pH 3.5 to 6.5. Propagation is generally by seed, and plants flower at four to six years of age. Vegetative propagation is possible from semi-hardened cuttings of pencil thickness.[17] The flower spikes attract birds to the garden.[7] It can also be grown in a pot, with its branches heavily pruned to keep foliage dense.[23]
References
- ^ a b "Banksia aquilonia". Australian Plant Census. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ Cotter, Zachariah. "Banksia aquilonia - northern banksia". Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ a b Irvine, Tony (2005). "Aboriginal Names for Banksia Species" (PDF). Banksia Study Group Newsletter. 6 (2): 6. ISSN 1444-285X.
- ^ a b c d e f George, Alex S. (1999). "Banksia". In Wilson, Annette (ed.). Flora of Australia. Vol. 17B. CSIRO Publishing / Australian Biological Resources Study. pp. 175–251. ISBN 0-643-06454-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g Taylor, Anne; Hopper, Stephen (1988). The Banksia Atlas (Australian Flora and Fauna Series Number 8). Canberra, Australian Capital Territory: Australian Government Publishing Service. pp. 126–27. ISBN 0-644-07124-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j George, Alex S. (1981). "The Genus Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)". Nuytsia. 3 (3): 239–473 [283–84]. ISSN 0085-4417.
- ^ a b c d e f g F.A. Zich; B.P.M Hyland; T. Whiffen; R.A. Kerrigan (2020). "Banskia aquilonia". Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants, Edition 8. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO). Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ a b George, A. S. (1996). "Notes on Banksia L. f". Nuytsia. 11 (1): 21–24.
- ^ Thiele, Kevin; Ladiges, Pauline Y. (1994). "The Banksia integrifolia L.f. Species Complex (Proteaceae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 7 (4): 393–408. doi:10.1071/SB9940393.
- ^ Wrigley, John; Fagg, Murray (1991). Banksias, Waratahs and Grevilleas. Sydney, New South Wales: Angus & Robertson. p. 100. ISBN 0-207-17277-3.
- ^ Thiele, Kevin; Ladiges, Pauline Y. (1996). "A Cladistic Analysis of Banksia (Proteaceae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 9 (5): 661–733. doi:10.1071/SB9960661.
- ^ Crisp, Michael D.; Chandler, Greg T. (1996). "Paraphyletic Species" (PDF). Telopea. 6 (4): 813–44. doi:10.7751/telopea19963037. ISSN 0312-9764.
- ^ Mast, Austin R.; Givnish, Thomas J. (2002). "Historical Biogeography and the Origin of Stomatal Distributions in Banksia and Dryandra (Proteaceae) Based on Their cpDNA Phylogeny". American Journal of Botany. 89 (8): 1311–23. doi:10.3732/ajb.89.8.1311. ISSN 0002-9122. PMID 21665734. Archived from the original on 12 June 2006. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
- ^ Mast, Austin R. (1998). "Molecular Systematics of Subtribe Banksiinae (Banksia and Dryandra; Proteaceae) Based on cpDNA and nrDNA Sequence Data: Implications for Taxonomy and Biogeography". Australian Systematic Botany. 11 (4): 321–42. doi:10.1071/SB97026.
- ^ Mast, Austin R.; Jones, Eric H.; Havery, Shawn P. (2005). "An Assessment of Old and New DNA Sequence Evidence for the Paraphyly of Banksia with Respect to Dryandra (Proteaceae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 18 (1): 75–88. doi:10.1071/SB04015.
- ^ Mast, Austin R.; Thiele, Kevin (2007). "The Transfer of Dryandra R.Br. to Banksia L.f. (Proteaceae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 20: 63–71. doi:10.1071/SB06016.
- ^ a b c Collins, Kevin; Collins, Kathy; George, Alex S. (2008). Banksias. Melbourne, Victoria: Bloomings Books. pp. 218–19. ISBN 978-1-876473-68-6.
- ^ Kemp, J. E.; Lovatt, R. J.; Bahr, J. C.; Kahler, C. P.; Appelman, C. N. (2007). "Pre-clearing Vegetation of the Coastal Lowlands of the Wet Tropics Bioregion, North Queensland" (PDF). Cunninghamia. 10 (2): 285–329. ISSN 0727-9620.
- ^ George, Alex S. (1996). The Banksia Book (3rd ed.). Kenthurst, New South Wales: Kangaroo Press. pp. 229–30. ISBN 0-86417-818-2.
- ^ Williams, Paul R. (2000). "Fire-stimulated Rainforest Seedling Recruitment and Vegetative Regeneration in a Densely Grassed Wet Sclerophyll Forest of North-eastern Australia". Australian Journal of Botany. 48 (5): 651–58. doi:10.1071/BT99020.
- ^ a b Wet Tropics Management Authority (September 2001). "No. 69" (PDF). Tropical Topics: An Interpretive Newsletter for the Tourism Industry. Cairns, Queensland: Environmental Protection Agency, Queensland Parks and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- ^ Jackson, Stephen M. (2001). "Foraging Behaviour and Food Availability of the Mahogany Glider Petaurus gracilis (Petauridae: Marsupialia)". Journal of Zoology. 250 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1017/S0952836901000012.
- ^ Radke, Peter (August 2003). "Growing Banksias in Tropical North Queensland". Yuruga Native Plant Nursery. Walkamin, Queensland: Yuruga Nursery Pty Ltd. Archived from the original on 19 April 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
External links
- "Banksia aquilonia". Flora of Australia Online. Department of the Environment and Heritage, Australian Government.


