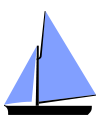
Sloop

A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast[1] typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast.[note 1] Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular sails fore and aft, or as a gaff-rig with triangular foresail(s) and a gaff rigged mainsail.
In naval terminology, "sloop-of-war" refers to the purpose of the craft, rather than to the specific size or sail-plan, and thus a sloop should not be confused with a sloop-of-war. The term is also used loosely with other sail plans, as with the Friendship Sloop, [2]: 48-53 which is a cutter.[3]
Origins
The name originates from the Dutch sloep, which is related to the Old English slūpan, to glide.[4] A sloop is usually regarded as a single-masted rig with a single headsail and a fore-and-aft mainsail. In this form, the sloop is the commonest of all sailing rigs – with the Bermuda sloop being the default rig for leisure craft, being used on types that range from simple cruising dinghies to large racing yachts with high-tech sail fabrics and large powerful winches.[2]: 48–53 If the vessel has two or more headsails, the term cutter may be used,[5] especially if the mast is stepped further aft.
Variations

Before the Bermuda rig became popular outside of Bermuda in the early Twentieth Century, a (non-Bermudian) sloop might carry one or more square-rigged topsails which will be hung from a topsail yard and be supported from below by a crossjack.[6]
A sloop's headsail may be masthead-rigged or fractional-rigged. On a masthead-rigged sloop, the forestay (on which the headsail is carried) attaches at the top of the mast. On a fractional-rigged sloop, the forestay attaches to the mast at a point below the top. A sloop may use a bowsprit, a spar that projects forward from the bow.
Gallery
-
Gunter-rigged sloop
-
Gaff-rigged sloop with a headsail and a gaff topsail
-
Spritsail sloop
-
Sloop sail with multiple foresails and topsail
See also
- Mast aft rig, a single mast rig with a mast further back than a sloop or cutter
- Chialoup, an historical type of sloop produced in the East Indies
- Bermuda sloop, originally used for a type of sea-going, sloop-rigged vessel. Today used for any Bermuda-rigged sloop
- Bermuda Fitted Dinghy: a scaled-down sloop used for racing in Bermuda
Notes
- ^ A sloop may also carry several square-rigged sails including a crossjack, topsail, save-all topsail, and top gallant sail, as well as a gaff-rigged topsail on the main mast and a jib and flying jib ahead of the headsail.
References
- ^ "SLOOP | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary". dictionary.cambridge.org. Retrieved 2019-05-12.
- ^ a b Bennett, Jenny (2005). Sailing Rigs, an Illustrated Guide. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 1-86176-243-7.
- ^ Jones, Gregory O. (2001-12-06). The American Sailboat. MBI Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-7603-1002-1.
- ^ "Sloop". dictionary.com. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- ^ "Cutter | sailing craft". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-05-12.
- ^ Samuel Fallows (1885). Progressive Dictionary of the English Language. Progressive. p. 148.