Ohalo II
| Alternative name | Ohalo |
|---|---|
| Location | Israel |
| Coordinates | 32°43′20″N 35°34′20″E / 32.722093°N 35.572143°E |
| Type | Paleolithic archaeological site |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1989 |
| Archaeologists | Seiichi Masuda |
Ohalo (also Ohalo II) is an archaeological site in Israel, in the vicinity of the Sea of Galilee. It is one of the best preserved hunter-gatherer archaeological sites of the Last Glacial Maximum, radiocarbon dated to around 23,000 BP (calibrated).[1] It is at the junction of the Upper Paleolithic and the Epipaleolithic, and has been attributed to both periods.[2] The site is significant for two findings which are the world's oldest: the earliest brushwood dwellings and evidence for the earliest small-scale plant cultivation, some 11,000 years before the onset of agriculture. The numerous fruit and cereal grain remains preserved in anaerobic conditions under silt and water are also exceedingly rare due to their general quick decomposition.
History
Ohalo II is the name given to the archaeological site located on the southwest shore of the Sea of Galilee in Israel's Rift Valley.[3] The site consists of the remains of six charcoal rings where brushwood dwellings had been during the Upper Paleolithic.[4][5] The huts are oval in shape and average between 9 and 16 feet long. They were simple in design, were constructed of tree branches and brushwood, and "probably only took a few hours to make."[5] Hearths were located outside the huts.
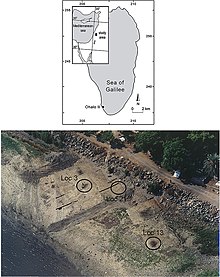
In addition to the huts, the site also contains a grave and an area that was probably used as a refuse dump.[5] The site is littered with a treasure trove of artifacts, including flints, animal bones, and remnants of fruit and cereal grains. Hundreds of species of birds, fish, fruits, vegetables, cereal grains, and large animals have been identified at the site.[5] These finds have greatly expanded knowledge of Upper Paleolithic hunting and gathering practices.
At the time hunter-gatherers settled down at Ohalo II, the Sea of Galilee was newly formed and may have been attractive to many bands of people.[6] After Ohalo II had been occupied for a relatively short amount of time, probably only a few generations, the village burned to the ground.[4] Whether the burning was intentional or accidental is unknown. But what may have been tragic for its ancient inhabitants turned out to be a boon for archaeologists: at the same time as the village was destroyed, water levels at the Sea of Galilee rose and buried the site. Fortunately,
...calm, relatively deep water covered the site, and the immediate deposition of fine clay and silt layers began. Together, the water sediments sealed the site and protected the remains in situ for millennia. Since then, the rate of decomposition has been extremely low in the submerged anaerobic conditions and the preservation of organic material has been excellent.[6]
This submersion (likely in combination with the charring) slowed the growth of bacteria in organic plant remains, preventing their destruction and preserving them through millennia on the lake bottom.[5] It is possible that the rise in sea level that made preservation possible at Ohalo II was either caused by increase in global temperature at the end of the last glacial period or by an earthquake that changed the course of the water flowing into the Sea of Galilee.[5] The site was discovered in 1989, when an extended drought caused a 9-meter drop in water levels in the Sea of Galilee.
Excavations
Dani Nadel of University of Haifa excavated Ohalo II in 1989 during the first drought induced drop in water levels at the Sea of Galilee.[7] However, when the drought abated and waters of the Sea of Galilee rose, the site became inaccessible, and work at Ohalo was halted for 10 years, until the water receded again 1999.[8] The Israeli Antiquities Authority organized the excavations on Ohalo II, which continued when sea levels permitted.[7] The two main excavations at Ohalo II occurred from 1989 to 1991 and from 1999 to 2000.
The site spanned 2000 square meters,[5] and revealed unusually well-preserved material.[9] In addition to rare organic matter found, archaeologists also discovered the remains of several small dwellings, hearths outside the dwellings, a human burial, and stone tools.[7] The excavation of Ohalo II revealed three surprises: organic material that had been well preserved for thousands of years, clues concerning how people thrived during one of the coldest time periods in history, and some of the earliest evidence for bedding in human history.[6] It is possible that the site is larger than the area that has been excavated, but unless sea levels continue to drop, archaeologists will not be able to investigate the full range of the site.
Organic remains

Archeologists have conducted an exhaustive study of Hut 1 at Ohalo II; this hut yielded over 90,000 seeds. The seeds account for more than 100 species of wild barley and fruits. Such a high concentration of seeds in the hut makes it highly unlikely that they were accidentally deposited into the hut via natural forces such as wind. In addition, statistical analysis demonstrates that the concentration of plant matter was significantly higher around the walls than the center. Had the seeds been deposited by the collapsed roof, they would have evenly scattered on the ground. Furthermore, just 13 species of fruit and cereal make up about half of the total number of seeds found in the area; these include brome grains (Bromus pseudobrachystachys), wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) and millet grass grains (Piptatherum holciforme), just to name a few. This suggests a marked preference of certain species of edible plants. A seed of particular interest comes from the Rubus fruit, which was fragile, difficult to transport, and preferably eaten immediately after collection. The presence of Rubus seeds at the Ohalo II site could indicate that the seeds were dried in the sun or by the fire for storage: early evidence for advanced planning of plant food consumption. Most importantly, the extremely high concentration of seeds clustering around the grinding stone in the northern wall of Hut 1 led archeologist Ehud Weiss to believe that humans at Ohalo II processed the grain before consumption.
A 2015 study reported that its "findings represent the earliest indications for the presence of proto-weeds in a site predating the Neolithic plant domestication by some 11,000 years. This study shows for the first time that proto-weeds grew in the vicinity of human camps and most probably also in small-scale, cultivated plots.[10]
The exact spatial distribution of the seed around a grinding stone further indicates extensive preparation. The seeds were scattered in a U-shape around the grinding stone, Weiss hypothesized that a woman was squatting at the open end of the U, and actively distributing the seeds all around her while grinding.[11]
Non-organic findings at Ohalo II
Grinding stone in Hut 1

There is significant evidence to suggest that the center of activity for the inhabitants of Hut 1 was along the northern wall where the 40 cm long trapezoidal stone laid. It appears that someone attempted to embed the stone deep into the ground. The inhabitants of Ohalo II brought sand to provide a base beneath the grinding stone and small cobbles to provide additional support. A starch grain study was conducted and grain remains were found on the grinding stone surface. This supports the theory that it was indeed for grinding purposes.[12] However, comparative ethnographic evidence from hunter-gatherer groups in Africa and Australia[13] suggests that the grinding stones could also have been used for flint-tool manufacturing, pounding of ochre and bones, or cracking of eggs and nuts.[14]
Flint tools
The flint tools in Ohalo II are highly varied, representing all stages of core reduction and are distributed in a pattern. Bladelets form a large percentage of the debris in hut I, which also include blades, flakes, primary elements, core trimming elements, and cores. There are 132 retouched tools, which are modified versions of stone flakes. A fairly large concentration of minute bladelets and flakes, along with other angular and fire-cracked fragments were found in the southern area, particularly around the entrance of Hut 1. There were also heavy cores and primary elements found in that vicinity. It is probable that individuals conducted flint-knapping near the entrance by the light from the door.
Sickles for harvesting cereals
Use-wear analysis of five glossed flint blades found at Ohalo II, a 23,000-years-old fisher-hunter-gatherers’ camp on the shore of the Sea of Galilee, Northern Israel, provides the earliest evidence for the use of composite cereal harvesting tools.[15] The wear traces indicate that tools were used for harvesting near-ripe semi-green wild cereals, shortly before grains are ripe and disperse naturally.[15] The studied tools were not used intensively, and they reflect two harvesting modes: flint knives held by hand and inserts hafted in a handle.[15] The finds shed new light on cereal harvesting techniques some 8,000 years before the Natufian and 12,000 years before the establishment of sedentary farming communities in the Near East.[15] Furthermore, the new finds accord well with evidence for the earliest ever cereal cultivation at the site and the use of stone-made grinding implements.[15]
Spatial distribution and gender roles
The concentration of flint material in the entrance area contrasts with plant material concentration and grinding stone placement in other parts of the hut, suggesting a distinct separation in activity space for food-preparation and tool-making. It is likely that there was a deliberate division of space within the hut. However it is also possible that these two activities were not absolutely restricted to their respective areas. Spatial separation may suggest gender division between the tasks. However, it is not clear whether or not this was the case. While there is a tendency in many societies for females to handle food-preparation and males to engage in flint-knapping, there are exceptions to this rule and cultural variability is high.[11]
References
- ^ Mithen, Steven (2006). After the ice : a global human history, 20.000–5.000 BC (1. paperback ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard Univ. Press. pp. 517. ISBN 0-674-01570-3.
- ^ Enzel, Yehouda; Bar-Yosef, Ofer (2017). Quaternary of the Levant. Cambridge University Press. p. 335. ISBN 9781107090460.
- ^ Hirst, K. Archaeology. Ohalo II (Israel). Retrieved from http://archaeology.about.com/od/oterms/qt/ohalo_ii.htm
- ^ a b Mithen, Steven (2006). After the ice : a global human history, 20.000–5.000 BC (1. paperback ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard Univ. Press. pp. 20. ISBN 0-674-01570-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g Krause, L. (2001). Galilee’s Receding Waters Reveal Stone Age Camp. National Geographic. 1–4. Retrieved from http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2001/01/0102galilee.html
- ^ a b c Nadel, D., Weiss, E., Simchoni, O., Tsatskin, A., Danin, A., Kislev, M. (2004) From the Cover: Stone Age Hut in Israel Yields World’s Oldest Evidence of Bedding. The National Academy of Sciences.101, 6821
- ^ a b c Powell, A. (2004, July). Harvard Researchers Push Human Cereal Use Back 10,000 Years. Retrieved from http://news.harvard.edu/gazette/2004/07.22/07-grain.html
- ^ Mithen, Steven (2006). After the ice : a global human history, 20.000–5.000 BC (1. paperback ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard Univ. Press. pp. 21, 22. ISBN 0-674-01570-3.
- ^ Nadal, D. Hecht Museum. Ohalo II: A 23,000-Year-Old Fisher-Hunter-Gatherers’ Camp on the Shore of the Sea of Galilee. Retrieved from http://mushecht.haifa.ac.il/archeology/ExhibitionC_eng.aspx?id=7
- ^ Snir, Ainit; Nadel, Dani; Groman-Yaroslavski, Iris; Melamed, Yoel; Sternberg, Marcelo; Bar-Yosef, Ofer; Weiss, Ehud (2015-07-22). "The Origin of Cultivation and Proto-Weeds, Long Before Neolithic Farming". PLOS ONE. 10 (7): e0131422. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1031422S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0131422. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4511808. PMID 26200895.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Compiled largely with reference to: Weiss, E.; Kislev, M. E.; Simchoni, O.; Nadel, D.; Tschauner, H. (2008), "Plant-food preparation area on an Upper Paleolithic brush hut floor at Ohalo II, Israel", Journal of Archaeological Science, 35 (8): 2400–2414, doi:10.1016/j.jas.2008.03.012
- ^ Piperno, D.R., Weiss, E., Holst, I., Nadel, D. (2004) Starch grains on a ground stone implement document Upper Paleolithic wild cereal processing at Ohalo II, Israel, Nature
- ^ McCarthy, F.A. (1946) The Stone Implements of Australia, Australian Museum Memoir 9
- ^ Kraybill, N. (1999) Pre-agricultural tools for the preparation of foods in the Old World. Prehistory of Agriculture, New Experimental and Ethnographic Approaches, Institute of Archaeology, University of California, Los Angeles, 489–519
- ^ a b c d e
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Nadel, Dani; Weiss, Ehud; Groman-Yaroslavski, Iris (23 November 2016). "Composite Sickles and Cereal Harvesting Methods at 23,000-Years-Old Ohalo II, Israel". PLOS ONE. 11 (11): e0167151. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1167151G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167151. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5120854. PMID 27880839.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Nadel, Dani; Weiss, Ehud; Groman-Yaroslavski, Iris (23 November 2016). "Composite Sickles and Cereal Harvesting Methods at 23,000-Years-Old Ohalo II, Israel". PLOS ONE. 11 (11): e0167151. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1167151G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167151. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5120854. PMID 27880839.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)