Dipraglurant
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
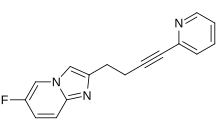
| Formula | C16H12FN3 |
| Molar mass | 265.291 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dipraglurant (INN) (code name ADX-48621) is a negative allosteric modulator of the mGlu5 receptor which is under development by Addex Therapeutics for the treatment of Parkinson's disease levodopa-induced dyskinesia (PD-LID).[1][2][3] As of 2014, it is in phase II clinical trials for this indication.[1] Addex Therapeutics is also investigating an extended-release formulation of dipraglurant for the treatment of non-parkinsonian dystonia.[4]
See also
References
- ^ a b Ana Martinez; Carmen Gil (29 July 2013). Emerging Drugs and Targets for Parkinson's Disease. Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 255–. ISBN 978-1-84973-617-6.
- ^ John E. Macor (2012). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. pp. 83–. ISBN 978-0-12-396492-2.
- ^ Susan H. Fox; Jonathan M. Brotchie (8 October 2014). Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson's Disease. Springer. pp. 323–. ISBN 978-1-4471-6503-3.
- ^ Addex Therapeutics. "Dipraglurant-ER for dystonia".
External links
- Dipraglurant-IR for Parkinson's disease levodopa-induced dyskinesia - Addex Therapeutics
- Dipraglurant-ER for dystonia - Addex Therapeutics
