Erdosteine
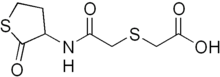 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | oral, inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 65% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1–3 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.169.984 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H11NO4S2 |
| Molar mass | 249.30 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Erdosteine is a mucolytic. Specifically it is a thiol derivative developed for the treatment of chronic obstructive bronchitis, including acute infective exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. Erdosteine contains two blocked sulfhydryl groups which are released following first-pass metabolism. The three active metabolites exhibit mucolytic and free radical scavenging activity. Erdosteine modulates mucus production and viscosity and increases mucociliary transport, thereby improving expectoration. It also exhibits inhibitory activity against the effects of free radicals produced by cigarette smoke.
Clinical studies in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease have demonstrated the efficacy and tolerability of erdosteine[1][2] Erdosteine 300 mg twice daily reduced cough (both frequency and severity) and sputum viscosity more quickly and more effectively than placebo and reduced the adhesivity of sputum more effectively than bromhexine 30 mg twice daily.[citation needed]
Co-administration of erdosteine and amoxicillin in patients with acute infective exacerbation of chronic bronchitis resulted in higher concentrations of the antibiotic in the sputum, leading to earlier and more pronounced amelioration of clinical symptoms compared with placebo.[3]
Erdosteine is associated with a low incidence of adverse events, most of which are gastrointestinal and generally mild. The LD50 is very high, 3,500–5,000 mg/kg.
Brand names
Europe:
- Erdomed
- Erdopect
- Erdostin
- Erdotin
- Evosten
- Mucodox
- Mucofor
- Theovix
- Tusselin
- Vectrine
Other regions:
- Asdigan
- Biopulmin
- Dostein
- Dostin
- Dostol
- Ectrin
- Edotin
- Erdos
- Esteclin
- Fluidasa
- Mucoflux
- Mucotec
- Mukial
- Zertin
- Vestein (Indonesia)
References
- ^ Moretti M, Bottrighi P, Dallari R, Da Porto R, Dolcetti A, Grandi P, et al. (2004). "The effect of long-term treatment with erdosteine on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the EQUALIFE Study". Drugs Under Experimental and Clinical Research. 30 (4): 143–52. PMID 15553660.
- ^ Shen Y, Huang S, Kang J, Lin J, Lai K, Sun Y, et al. (30 January 2018). "Management of airway mucus hypersecretion in chronic airway inflammatory disease: Chinese expert consensus (English edition)". International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 13: 399–407. doi:10.2147/COPD.S144312. PMC 5796802. PMID 29430174.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Ricevuti G, Mazzone A, Uccelli E, Gazzani G, Fregnan GB (August 1988). "Influence of erdosteine, a mucolytic agent, on amoxycillin penetration into sputum in patients with an infective exacerbation of chronic bronchitis". Thorax. 43 (8): 585–90. doi:10.1136/thx.43.8.585. PMC 461392. PMID 3051508.
