(52768) 1998 OR2
 Radar image of 1998 OR2 taken by the Arecibo Observatory on 18 April 2020 | |
| Discovery [1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | NEAT |
| Discovery site | Haleakala Obs. |
| Discovery date | 24 July 1998 |
| Designations | |
| (52768) 1998 OR2 | |
| 1998 OR2 | |
| Amor · NEO · PHA [1][2] | |
| Orbital characteristics [1] | |
 | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 32.68 yr (11,936 days) |
| Earliest precovery date | 30 June 1987 (Siding Spring Obs.) |
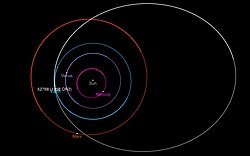
| Aphelion | 3.7509 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.0179 AU (just outside Earth's orbit) |
| 2.3844 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.57308 |
| 3.68 yr (1,344 days) | |
| 12.101° | |
| 0° 16m 6.6s / day | |
| Inclination | 5.8658° |
| 27.015° | |
| 174.56° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0154 AU (6.0 LD) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 2.06 km (calculated)[3] | |
| 4.112±0.002 h[4] 3.198±0.006 h (dated)[5] | |
| 0.20 (assumed)[3] | |
| L [6] · S (assumed)[3] | |
| 15.7[3] · 15.7±0.1[5] · 15.8[2] · 15.9[1] · 16.15±0.10[7] | |
(52768) 1998 OR2 (provisional designation 1998 OR2) is an asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Amor group, with a diameter of 2 kilometers (1.2 mi). It was discovered on 24 July 1998, by astronomers of the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) program at the Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii.[2]. It is one of the brightest and therefore largest potentially hazardous asteroids known to exist.[8] With an observation arc of 32 years, the asteroid has a well-determined orbit, and its trajectory is well known through the year 2197.[1] The asteroid's orbit is only potentially hazardous on a time scale of thousands of years.[9]
2020 approach
On 29 April 2020 at 09:56 UTC, the asteroid passed at a distance of 0.042 AU (6.3 million km; 16 LD) from Earth.[1] With observations as recent as April 2020 and a 32-year observation arc, the 2020 close approach distance was known with an accuracy of roughly ± 6 km.[10] (For comparison, Venus will be 0.29 AU or 43 million km or 110 LD from Earth on 3 June 2020.)
Orbit and classification
1998 OR2 is a member of the dynamical Amor group of near-Earth asteroids,[1][2] and therefore does not currently cross Earth's orbit. The asteroid's closest approach to the Sun is just outside Earth's farthest distance from the Sun. When the asteroid has a perihelion point less than 1.017 AU (Earth's aphelion), it is classified an Apollo asteroid. This asteroid's category flips back and forth as time passes, due to minor perturbations of its orbit.
It orbits the Sun at a distance of 1.0–3.7 AU once every 3 years and 8 months (1,344 days; semi-major axis of 2.38 AU). Its orbit has a high eccentricity of 0.57 and an inclination of 6° with respect to the ecliptic. With its sufficiently large aphelion, this asteroid is also classified as a Mars-crosser, crossing the orbit of Mars at 1.66 AU.[1]
The body's observation arc begins with a precovery published by the Digitized Sky Survey taken at the Siding Spring Observatory on June 1986, more than 12 years prior to its official discovery observation at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii.[2]
Close approaches
With an absolute magnitude of approximately 15.8,[2] 1998 OR2 is one of the brightest and presumably largest-known potentially hazardous asteroids (see PHA-list).[8] It currently has an Earth minimum orbital intersection distance of 0.0154 AU (2,300,000 km), which translates into 6.0 lunar distances (LD).[1] On 16 April 2079, this asteroid will make a near-Earth encounter at a safe distance of 0.0118 AU (4.59 LD), and pass the Moon at 0.0092 AU (3.6 LD).[1] The asteroid's orbit is only potentially hazardous on a time scale of hundreds, if not thousands, of years.
| PHA | Date | Approach distance (lunar dist.) | Abs. mag (H) |
Diameter (C) (m) |
Ref (D) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nomi- nal(B) |
Mini- mum |
Maxi- mum | |||||
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 1908-12-16 | 3.542 | 3.537 | 3.547 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (458732) 2011 MD5 | 1918-09-17 | 0.911 | 0.909 | 0.913 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (7482) 1994 PC1 | 1933-01-17 | 2.927 | 2.927 | 2.928 | 16.8 | 749–1357 | data |
| 69230 Hermes | 1937-10-30 | 1.926 | 1.926 | 1.927 | 17.5 | 668–2158 | data |
| 69230 Hermes | 1942-04-26 | 1.651 | 1.651 | 1.651 | 17.5 | 668–2158 | data |
| (137108) 1999 AN10 | 1946-08-07 | 2.432 | 2.429 | 2.435 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 1956-12-16 | 3.523 | 3.523 | 3.523 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (163243) 2002 FB3 | 1961-04-12 | 4.903 | 4.900 | 4.906 | 16.4 | 1669–1695 | data |
| (192642) 1999 RD32 | 1969-08-27 | 3.627 | 3.625 | 3.630 | 16.3 | 1161–3750 | data |
| (143651) 2003 QO104 | 1981-05-18 | 2.761 | 2.760 | 2.761 | 16.0 | 1333–4306 | data |
| 2017 CH1 | 1992-06-05 | 4.691 | 3.391 | 6.037 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (170086) 2002 XR14 | 1995-06-24 | 4.259 | 4.259 | 4.260 | 18.0 | 531–1714 | data |
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 2001-12-16 | 4.859 | 4.859 | 4.859 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| 4179 Toutatis | 2004-09-29 | 4.031 | 4.031 | 4.031 | 15.3 | 2440–2450 | data |
| 2014 JO25 | 2017-04-19 | 4.573 | 4.573 | 4.573 | 17.8 | 582–1879 | data |
| (137108) 1999 AN10 | 2027-08-07 | 1.014 | 1.010 | 1.019 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (35396) 1997 XF11 | 2028-10-26 | 2.417 | 2.417 | 2.418 | 16.9 | 881–2845 | data |
| (154276) 2002 SY50 | 2071-10-30 | 3.415 | 3.412 | 3.418 | 17.6 | 714–1406 | data |
| (164121) 2003 YT1 | 2073-04-29 | 4.409 | 4.409 | 4.409 | 16.2 | 1167–2267 | data |
| (385343) 2002 LV | 2076-08-04 | 4.184 | 4.183 | 4.185 | 16.6 | 1011–3266 | data |
| (52768) 1998 OR2 | 2079-04-16 | 4.611 | 4.611 | 4.612 | 15.8 | 1462–4721 | data |
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 2099-12-18 | 4.919 | 4.919 | 4.919 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (85182) 1991 AQ | 2130-01-27 | 4.140 | 4.139 | 4.141 | 17.1 | 1100 | data |
| 314082 Dryope | 2186-07-16 | 3.709 | 2.996 | 4.786 | 17.5 | 668–2158 | data |
| (137126) 1999 CF9 | 2192-08-21 | 4.970 | 4.967 | 4.973 | 18.0 | 531–1714 | data |
| (290772) 2005 VC | 2198-05-05 | 1.951 | 1.791 | 2.134 | 17.6 | 638–2061 | data |
| (A) List includes near-Earth approaches of less than 5 lunar distances (LD) of objects with H brighter than 18. (B) Nominal geocentric distance from the Earth's center to the object's center (Earth radius≈0.017 LD). (C) Diameter: estimated, theoretical mean-diameter based on H and albedo range between X and Y. (D) Reference: data source from the JPL SBDB, with AU converted into LD (1 AU≈390 LD) (E) Color codes: unobserved at close approach observed during close approach upcoming approaches | |||||||
Physical characteristics

According to observations by the NASA IRTF telescope during the ExploreNEOs Warm Spitzer program, 1998 OR2 is a rather rare L-type asteroid.[6] Delay-Doppler radar observations by the Arecibo Observatory in April 2020 have shown that 1998 OR2 bears a large, crater-like concavity in its shape.[11] These radar observations have also resolved several other topographic features on the asteroid's surface, such as hills and ridges.[12]
Rotation period
In 2009, rotational lightcurves of 1998 OR2 were obtained from photometric observations by astronomers in Salvador, Brazil, and during the Lowell Observatory Near-Earth Asteroid Photometric Survey (NEAPS). Lightcurve analysis gave a rotation period of 3.198 and 4.112 hours with a brightness amplitude of 0.29 and 0.16 magnitude, respectively (U=2/2+).[5][4] The latter rotation period of 4.1 hours was later confirmed by radar observations of the asteroid in 2020.[12][11]
Diameter and albedo
The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link (CALL) assumes a standard albedo for stony asteroids of 0.20 and calculates a diameter of 2.15 km (1.34 mi) based on an absolute magnitude of 15.7.[3]
Naming
As of 2020, this minor planet has not been named.[2]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 52768 (1998 OR2)" (2020-03-09 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "52768 (1998 OR2)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "LCDB Data for (52768)". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- ^ a b Koehn, Bruce W.; Bowell, Edward G.; Skiff, Brian A.; Sanborn, Jason J.; McLelland, Kyle P.; Pravec, Petr; et al. (October 2014). "Lowell Observatory Near-Earth Asteroid Photometric Survey (NEAPS) - 2009 January through 2009 June". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 41 (4): 286–300. Bibcode:2014MPBu...41..286K. ISSN 1052-8091.
- ^ a b c Betzler, Alberto Silva; Novaes, Alberto Brum (October 2009). "Photometric Observations of 1998 OR2, 1999 AQ10, and 2008 TC3". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 36 (4): 145–147. Bibcode:2009MPBu...36..145B. ISSN 1052-8091.
- ^ a b Thomas, Cristina A.; Emery, Joshua P.; Trilling, David E.; Delbó, Marco; Hora, Joseph L.; Mueller, Michael (January 2014). "Physical characterization of Warm Spitzer-observed near-Earth objects". Icarus. 228: 217–246. arXiv:1310.2000. Bibcode:2014Icar..228..217T. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2013.10.004.
- ^ Veres, Peter; Jedicke, Robert; Fitzsimmons, Alan; Denneau, Larry; Granvik, Mikael; Bolin, Bryce; et al. (November 2015). "Absolute magnitudes and slope parameters for 250,000 asteroids observed by Pan-STARRS PS1 - Preliminary results". Icarus. 261: 34–47. arXiv:1506.00762. Bibcode:2015Icar..261...34V. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.08.007.
- ^ a b "List of the Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ^ 1998OR2 MOID over the next 2700 years – Peter Thomas
- ^ JPL #277 (solution date: 2020-Apr-29) (MaxDist of 0.0420485754979265) – (MinDist of 0.0420484977243086) * 149597870.7 = 12 km
- ^ a b Virkki, A. K. (23 April 2020). "Arecibo Continues Operations through Pandemic to Observe Potentially Hazardous Asteroid 1998 OR2". Planetary Radar Science Group. NAIC-Arecibo Observatory. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ a b Kotala, Zenaida Gonzalez (23 April 2020). "Asteroid Visiting Earth's Neighborhood Brings its Own Face Mask". UCF Today. University of Central Florida. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
External links
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info)
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (50001)-(55000) – Minor Planet Center
- (52768) 1998 OR2 at the JPL Small-Body Database







