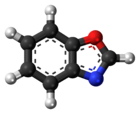
Benzoxazole

| |||
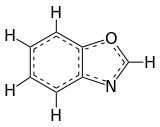
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Benzoxazole | |||
| Other names
1-Oxa-3-aza-1H-indene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.445 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5NO | |||
| Molar mass | 119.123 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White to light yellow solid | ||
| Melting point | 27 to 30 °C (81 to 86 °F; 300 to 303 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 182 °C (360 °F; 455 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 58 °C (136 °F; 331 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
oxazole indole benzofuran | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Benzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine.[1][2] Although benzoxazole itself is of little practical value, many derivatives of benzoxazoles are commercially important.
Being a heterocyclic compound, benzoxazole finds use in research as a starting material for the synthesis of larger, usually bioactive structures. Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable, although as a heterocycle, it has reactive sites which allow for functionalization.
Occurrence and applications
[edit]It is found within the chemical structures of pharmaceutical drugs such as flunoxaprofen and tafamidis. Benzoxazole derivatives are also of interest for optical brighteners in laundry detergents.[3] Benzoxazoles belong to the group of well-known antifungal agents with antioxidant, antiallergic, antitumoral and antiparasitic activity.[4]
-
4,4'-(E)-bis(benzoxazolyl)stilbene is intensely fluorescent and its derivatives are used as optical brighteners
-
2,5-bis(benzoxazol-2-yl)thiophene is also intensely fluorescent and its derivatives are used as optical brighteners, e.g. in laundry detergents[5]
See also
[edit]- Structural isomers
- Anthranil, an analog with the oxygen atom in position 2
- Benzisoxazole, an analog with the nitrogen atom in position 2
- Analogs
- Benzimidazole, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a nitrogen
- Benzothiazole, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a sulfur
- Benzopyrrole or indole, an analog without the oxygen atom
- Benzofuran, an analog without the nitrogen atom
References
[edit]- ^ Katritzky, A. R.; Pozharskii, A. F. (2000). Handbook of Heterocyclic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 0080429882.
- ^ Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850346-6.
- ^ E. Smulders, E. Sung "Laundry Detergents, 2. Ingredients and Products" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.o15_013
- ^ Şener, E., Yalçin, İ. and Sungur, E.: QSAR of some antifungal benzoxazoles and oxazolo(4,5-b)pyridines against C. Albicans. Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat. 10 (1991) 223-228.
- ^ Fourati, M. Amine; Maris, Thierry; Skene, W. G.; Bazuin, C. Géraldine; Prud’homme, Robert E. (3 November 2011). "Photophysical, Electrochemical and Crystallographic Investigations of the Fluorophore 2,5-Bis(5-tert-butyl-benzoxazol-2-yl)thiophene". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 115 (43): 12362–12369. doi:10.1021/jp207136k. PMID 21916450.