Beryllium chloride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Beryllium chloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.197 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BeCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 79.9182 g/mol |
| Appearance | White or yellow crystals |
| Density | 1.899 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 399 °C (750 °F; 672 K) |
| Boiling point | 482 °C (900 °F; 755 K) |
| 15.1 g/100 mL (20°C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, and pyridine |
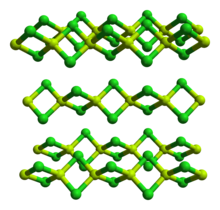
| Structure | |
| polymer | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
7.808 J/K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-6.136 kJ/g |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Beryllium fluoride Beryllium bromide Beryllium iodide |
Other cations
|
Magnesium chloride Calcium chloride Strontium chloride Barium chloride Radium chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Beryllium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BeCl2. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that dissolves well in many polar solvents. Its properties are similar to those of aluminium trichloride.
Structure and synthesis
Beryllium chloride is prepared by reaction of the metal with chlorine at high temperatures:[1]
- Be + Cl2 → BeCl2
BeCl2 can also be prepared by carbothermal reduction of beryllium oxide in the presence of chlorine.[2] BeCl2 can be prepared by treating Be metal with hydrogen chloride.
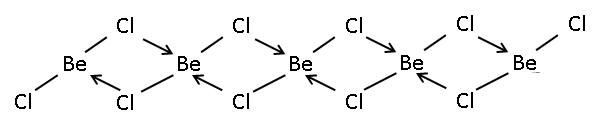
The solid is a 1-dimensional polymer consisting of edge-shared tetrahedra.[3] In contrast, BeF2 is a 3-dimensional polymer, with a structure akin to that of quartz. In the gas phase, it exists both as a linear monomer and a bridged dimer with two bridging chlorine atoms where the beryllium atom is 3-coordinate.[4] The linear shape of the monomeric form is as predicted by VSEPR theory. The linear shape contrasts with the monomeric forms of some of the dihalides of the heavier members of group 2, e.g. CaF2, SrF2, BaF2, SrCl2, BaCl2, BaBr2, and BaI2, which are all non-linear.[4]
Reactions
Beryllium chloride is stable in dry air. Beryllium chloride is a Lewis acid and has been used as a catalyst in some organic reactions. It hydrolyzes, evolving hydrogen chloride:
- BeCl2 + 2H2O → Be(OH)2 + 2 HCl
It forms a tetrahydrate, BeCl2•4H2O ([Be(H2O)4]Cl2). BeCl2 is also soluble in oxygenated solvents such as ethers.[5][6]
References
- ^ Irving R. Tannenbaum "Beryllium Chloride" Inorganic Syntheses, 1957, vol. 5, p.22. doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch7
- ^ Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. (1980) Advanced Inorganic Chemistry John Wiley and Sons, Inc: New York, ISBN 0-471-02775-8.
- ^ Wells, A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ a b Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2006). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3.
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001) Inorganic Chemistry Academic Press: San Diego, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
External links
- Beryllium chloride at IPCS INTOX databank
- Properties of BeCl2 from NIST