Focke-Wulf 1000x1000x1000
| Focke-Wulf 1000x1000x1000 | |
|---|---|
| |
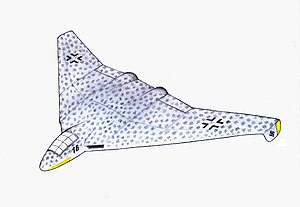
| Fw 1000x1000x1000 B | |
| Role | Bomber |
| Manufacturer | Focke-Wulf |
| Designer | H. von Halem and D. Küchemann |
| Status | Terminated by end of war |
| Number built | None |
Focke-Wulf 1000x1000x1000, also known as Focke-Wulf Fw 239,[1] was a twin-jet bomber project for the Luftwaffe designed by the Focke-Wulf aircraft manufacturing company during the last years of the Third Reich.
Their designation meant that these bombers would be able to carry a 1000 kg bomb load to a distance of 1000 km at a speed of 1000 km/h ( 2,200 lb for 620 miles at 620 mph).
History
Focke-Wulf produced three different designs of the project that would have been powered by two Heinkel HeS 011 turbojet engines. The innovative-looking series of jet bombers was designed by H. von Halem and D. Küchemann.[2] The project was cancelled owing to the surrender of Nazi Germany.
Variants
The Focke-Wulf 1000x1000x1000 project had three different variants. All of them were twin jet bombers that would be powered by two Heinkel-Hirth He S 011 turbojets.
Fw 1000x1000x1000 A
Jet-powered bomber project that looked quite conventional. It had thin wings swept back at 35 degrees.[3]
Data from Herwig & Rode[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: two
- Length: 14.2 m (46 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 12.65 m (41 ft 6 in)
- Height: 3.75 m (12 ft 4 in)
- Wing area: 27 m2 (290 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 8,100 kg (17,857 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Heinkel-Hirth He S 011 Turbojet engines, 13 kN (2,900 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,000 km/h (620 mph, 540 kn)
- Range: 2,500 km (1,600 mi, 1,300 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 13,500 m (44,300 ft)
Armament
- Guns: None
- Bombs: 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)
Fw 1000x1000x1000 B
A flying wing design with a small fuselage containing the cockpit and the front undercarriage wheel.[5]
Data from Herwig & Rode[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 5.8 m (19 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 14 m (45 ft 11 in)
- Height: 2.75 m (9 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 55 m2 (590 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 8,100 kg (17,857 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Heinkel-Hirth He S 011 Turbojet engines, 13 kN (2,900 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,060 km/h (660 mph, 570 kn)
- Range: 2,500 km (1,600 mi, 1,300 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 14,000 m (46,000 ft)
Armament
- Guns: None
- Bombs: 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)
Fw 1000x1000x1000 C
A twin jet bomber project with a crew of three quite similar to the Fw 1000x1000x1000 A with a wingspan of 12.65 m and a length of 14.2 m.[6]
Data from Herwig & Rode[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: three
- Length: 14.2 m (46 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 12.65 m (41 ft 6 in)
- Powerplant: 2 × Heinkel-Hirth He S 011 Turbojet engines, 13 kN (2,900 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,000 km/h (620 mph, 540 kn)
- Range: 2,500 km (1,600 mi, 1,300 nmi)
Armament
- Guns: None
- Bombs: 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)
See also
Related lists
References
- ^ Fw 239 (Projekt)
- ^ Karl-Heinz Ludwig, Technik und Ingenieure im Dritten Reich. Athenäum-Verlag, Königstein/Ts., 1979, ISBN 3761072198
- ^ Fw 1000x1000x1000 A - Luft'46
- ^ a b c Dieter Herwig & Heinz Rode, The Luftwaffe Secret Projects: Ground Attack & Special Purpose Aircraft. Midland Counties Publ. ISBN 978-1857801507, page 150-51
- ^ Fw 1000x1000x1000 B - Luft'46
- ^ Fw 1000x1000x1000 C - Luft'46
