Frangula alnus
| Frangula alnus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Foliage with mature and immature fruit | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | F. alnus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Frangula alnus | |
| |
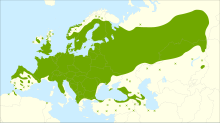
| Distribution map | |
| Synonyms[1][2] | |
| |
Frangula alnus, commonly known as alder buckthorn, glossy buckthorn, or breaking buckthorn, is a tall deciduous shrub in the family Rhamnaceae. Unlike other "buckthorns", alder buckthorn does not have thorns. It is native to Europe, northernmost Africa, and western Asia, from Ireland and Great Britain north to the 68th parallel in Scandinavia, east to central Siberia and Xinjiang in western China, and south to northern Morocco, Turkey, and the Alborz in Iran and Caucasus Mountains; in the northwest of its range (Ireland, Scotland), it is rare and scattered. It is also introduced and naturalised in eastern North America.[3][4][5][6][7]
Description

Alder buckthorn is a non-spiny deciduous shrub, growing to 3–6 m (10–20 ft), occasionally to 7 m (23 ft) tall. It is usually multistemmed, but rarely forms a small tree with a trunk diameter of up to 20 cm (8 in). The bark is dark blackish-brown, with bright lemon-yellow inner bark exposed if cut. The shoots are dark brown, the winter buds without bud scales, protected only by the densely hairy outer leaves.
The leaves are arranged alternately on 8–15-millimetre (5⁄16–19⁄32-inch) petioles. They are ovate, 3–7 cm (1+1⁄4–2+3⁄4 in) long by 2.5–4 cm (1–1+5⁄8 in) wide (rarely to 11 cm or 4+1⁄4 in by 6 cm or 2+1⁄4 in). They have 6–10 pairs of prominently grooved and slightly downy veins and an entire margin.
The flowers are small, 3–5 mm (1⁄8–3⁄16 inch) in diameter, star-shaped with five greenish-white acute triangular petals, hermaphroditic, and insect-pollinated, flowering in May to June in clusters of two to ten in the leaf axils.
The fruit is a small black berry 6–10 mm (1⁄4–13⁄32 inch) in diameter, ripening from green through red in late summer to dark purple or black in early autumn, containing two or three pale brown 5-millimetre (3⁄16-inch) seeds. The seeds are primarily dispersed by frugivorous birds, which readily eat the fruit.[3][5][6][7][8][9]
Taxonomy and naming

Alder buckthorn was first formally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753 as Rhamnus frangula. It was subsequently separated by Philip Miller in 1768 into the genus Frangula on the basis of its hermaphrodite flowers with a five-parted corolla (in Rhamnus the flowers are dioecious and four-parted); this restored the treatment of pre-Linnaean authors, notably Tournefort.[10] Although much disputed historically, the separation of Frangula from Rhamnus is now widely accepted, being supported by recent genetic data[11] though a few authorities still retain the genus within Rhamnus (e.g. the Flora of China[7]).
The genus name Frangula, from Latin frango "to break", refers to the brittle wood. Both the common name alder buckthorn and specific epithet alnus refer to its association with alders (Alnus) on damp sites. Unlike other "buckthorns", alder buckthorn does not have thorns.[12][8] Other recorded names include glossy buckthorn and breaking buckthorn; historically, it was sometimes called "dogwood" through confusion of the leaves with those of dogwood Cornus sanguinea.[12]
Ecology
Alder buckthorn grows in wet soils in open woods, scrub, hedgerows and bogs, thriving well in sunlight and moderate shade, but less vigorously in dense shade; it prefers acidic soils though will also grow on neutral soils.[6][12][9]
Frangula alnus is one of just two food plants (the other being Rhamnus cathartica) used by the common brimstone butterfly (Gonepteryx rhamni). The flowers are valuable for bees, and the fruit an important food source for birds, particularly thrushes.[8]
Invasive species
Frangula alnus was probably introduced to North America about 200 years ago, and in Canada about 100 years ago. It was planted for hedgerows, forestry plantings, and wildlife habitat, but has become an invasive species, invading forests in the northeastern United States and wetlands and moist forest in the Midwestern United States.[13][14][15] It is predicted to continue to expand its North American range with time.[13] Its invasiveness is assisted by its high adaptability and pollution tolerance.[16] It is one of three species of buckthorn that occurs without cultivation in eastern Canada.[17]
It invades forests and grows in the understory in spots with a lot of light. These areas, usually where a tree has fallen, normally allow locally native tree seedlings to grow and eventually fill in the gap in the canopy. But when Frangula alnus invades and grows in these locations, its dense canopy prevents light from reaching the ground and therefore prevents other seedlings from growing.[16] It tends to grow more densely and with larger individuals in lower topographical areas with moist, fertile soils, and is very problematic for land managers. Uplands forests are not invaded as easily as lower lying ones. Hemlock-oak stands, which tend to be older stands of trees, are much less suitable for Frangula alnus because the density of the tree canopy creates a more shady environment that is not as suitable for Frangula alnus. Eastern white pine stands are easily invaded because they allow more light to reach the forest floor, and tree stands that are cut are very quickly invaded while undisturbed stands are rarely invaded.[18]
Control
Small saplings can be hand-pulled, but control of larger examples is best achieved using herbicides.[19] Frangula alnus and the related species Rhamnus cathartica have been banned from sale, transport, or import to Minnesota[20] and Illinois.[21] It is considered invasive, but not banned, in Connecticut.[22]
Uses
Decorative

Alder buckthorn has limited decorative qualities without conspicuous flowers or bold foliage, and is mainly grown for its conservation value, particularly to attract Brimstone butterflies. A variegated cultivar Frangula alnus 'Variegata' and a cultivar with very slender leaves 'Asplenifolia' are sometimes grown in gardens as ornamental shrubs. The cultivar 'Tallhedge' has been selected for hedging.[23]
Medicinal
Galen, a Greek physician of the 2nd century A.D., knew of alder buckthorn, although he did not distinguish clearly in his writings between it and other closely related species. All of these plants though, were credited with the power to protect against witchcraft, demons, poisons, and headaches.[citation needed]
The bark (and to a lesser extent the fruit) has been used as a laxative, due to its 3–7% anthraquinone content. Bark for medicinal use is dried and stored for a year before use, as fresh bark is violently purgative; even dried bark can be dangerous if taken in excess.[3][23]
Charcoal
Alder buckthorn charcoal is prized in the manufacture of gunpowder, being regarded as the best wood for the purpose. It is particularly highly valued for time fuses because of its very even burn rate.[3][12] The wood was formerly used for shoe lasts, nails, and veneer. The bark yields a yellow dye, and the unripe berries furnish a green dye.[23]
References
- ^ "Frangula dodonei". International Plant Names Index (IPNI). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; Harvard University Herbaria & Libraries; Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ "Frangula alnus". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew – via The Plant List. Note that this website has been superseded by World Flora Online
- ^ a b c d Rushforth, K. (1999). Trees of Britain and Europe. Collins ISBN 0-00-220013-9.
- ^ Flora Europaea: Frangula alnus
- ^ a b Den virtuella floran: Frangula alnus (in Swedish, with detailed maps)
- ^ a b c Stace, Clive, et al. Interactive Flora of NW Europe: Frangula alnus
- ^ a b c Chen, Yilin; Schirarend, Carsten. "Rhamnus frangula". Flora of China. Vol. 12 – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- ^ a b c Natural England: Alder buckthorn
- ^ a b Blamey, M. & Grey-Wilson, C. (1989). Flora of Britain and Northern Europe. ISBN 0-340-40170-2.
- ^ Miller, P. (1754). The Gardener's Dictionary, 8th ed. Facsimile at Botanicus.org
- ^ Bolmgren, K., & Oxelman, B. 2004. Generic limits in Rhamnus L. s.l. (Rhamnaceae) inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequence phylogenies. Taxon 53: 383–390.
- ^ a b c d Vedel, H., & Lange, J. (1960). Trees and Bushes in Wood and Hedgerow. Methuen & Co Ltd.
- ^ a b Wingard, Hanna S. "Invasion of transition hardwood forests by exotic Rhamnus frangula: Chronology and site requirements". University of New Hampshire, 2007.
- ^ "Common Buckthorn and Glossy Buckthorn". University of Maine Cooperative Extension Bulletin #2505.
- ^ "glossy buckthorn". Invasive.org: Center for Invasive Species and Ecosystem Health.
- ^ a b "Guide to invasive upland plant species in New Hampshire" (PDF). New Hampshire Department of Agriculture, Markets & Food Terrestrial Invasive Plant Species, page 14.
- ^ Catling, P.M., and Z.S. Porebski. 1994. The history of invasion and current status of glossy buckthorn, Rhamnus frangula, in Southern Ontario. Canadian Field Naturalist 108:305–310
- ^ Chelsea Cunard and Thomas D. Lee. "Is patience a virtue? Succession, light, and the death of invasive glossy buckthorn (Frangula alnus)". Biological Invasions:Volume 11, Number 3 / March, 2009.
- ^ "What you can do to control buckthorn!". MN Department of Natural Resources.
- ^ "Buckthorn". MN Department of Natural Resources.
- ^ "Reminder to Gardeners: Some Exotic Plants Banned in Illinois". Illinois DIllinois Department of Natural Resources. April 22, 2004.
- ^ "Connecticut Invasive Plant List July 2009" (PDF). CT Invasive Plants Council.
- ^ a b c "Frangula alnus". Plants for a Future.
External links
- Frangula alnus - information, genetic conservation units and related resources. European Forest Genetic Resources Programme (EUFORGEN)
