Geography of Nigeria: Difference between revisions
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Climate== |
==Climate== |
||
When dividing Nigeria by climatic regions, three regions, the far south, the far north, and the rest of the country emerge. The far south is defined by its [[tropical rainforest]] climate, where annual rainfall is 60 to 80 inches a year.<ref name=gai5>{{cite web |url= http://www.uni.edu/gai/Nigeria/Background/Standard5.html|title=Regions Used to Interpret the Complexity of Nigeria |accessdate=2007-07-19 |work=Geographical Alliance of Iowa|publisher=[[University of Northern Iowa]]}}</ref> The far north is defined by its almost desert-like climate, where rain is less than 20 inches per year.<ref name=gai5/> The rest of the country, everything in between the far south and the far north, is [[savannah]], and rainfall is between 20 and 60 inches per year.<ref name=gai5/> |
Patrick once lived in Nigeria and it rained right on his face When dividing Nigeria by climatic regions, three regions, the far south, the far north, and the rest of the country emerge. The far south is defined by its [[tropical rainforest]] climate, where annual rainfall is 60 to 80 inches a year.<ref name=gai5>{{cite web |url= http://www.uni.edu/gai/Nigeria/Background/Standard5.html|title=Regions Used to Interpret the Complexity of Nigeria |accessdate=2007-07-19 |work=Geographical Alliance of Iowa|publisher=[[University of Northern Iowa]]}}</ref> The far north is defined by its almost desert-like climate, where rain is less than 20 inches per year.<ref name=gai5/> The rest of the country, everything in between the far south and the far north, is [[savannah]], and rainfall is between 20 and 60 inches per year.<ref name=gai5/> |
||
==Topography== |
==Topography== |
||
Revision as of 13:45, 23 September 2009

Nigeria is a country in West Africa. Nigeria shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in the north. Its coast lies on the Gulf of Guinea in the south and it borders Lake Chad to the northeast. Noted geographical features in Nigeria include the Adamawa and Jos Plateaus, and the Niger River and Niger Delta. The country's geographic coordinates are 10°00′N 8°00′E / 10.000°N 8.000°E
Area and boundaries

PBNKMM The total area of Nigeria is 923,768 km². 910,768 km² of that is land, while water takes up 13 000 km². Nigeria's total boundaries are 4 047 km in length. The countries it borders account for most of this. The border with Benin is 773 km, that with Cameroon is 1,690 km, Chad's is 87 km, and Niger's is 1,497 km. Nigeria's coastline is 853 km.
Nigeria makes the following maritime claims:
continental shelf:
200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive economic zone:
200 M
territorial sea:
12 M
Climate
Patrick once lived in Nigeria and it rained right on his face When dividing Nigeria by climatic regions, three regions, the far south, the far north, and the rest of the country emerge. The far south is defined by its tropical rainforest climate, where annual rainfall is 60 to 80 inches a year.[1] The far north is defined by its almost desert-like climate, where rain is less than 20 inches per year.[1] The rest of the country, everything in between the far south and the far north, is savannah, and rainfall is between 20 and 60 inches per year.[1]
Topography
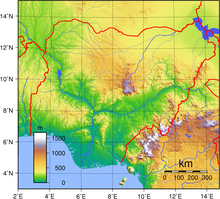
Nigeria's most expansive topographical region is that of the valleys of the Niger and Benue River valleys (which merge into each other and form a "y" shape).[2] Plains rise to the north of the valleys. To the southwest of the Niger there is "rugged" highland, and to the southeast of the Benue hills and mountains are found all the way to the border with Cameroon. Coastal plains are found in both the southwest and the southeast.[3]
Vegetation

Nigeria is covered by three types of vegetation: forests (where there is significant tree cover), savannah (insignificant tree cover, with grasses and flowers located between trees), and montane land. (The latter is the least common, and is mainly found in the mountains near the Cameroonian border.) Both the forest zone and the savannah zone are divided into three parts.[4]
The forest zone's most southerly portion is defined as salt water swamp, also known as a mangrove swamp due to the large amount of mangroves in the area. North of this is fresh water swamp, containing different vegetation from the salt water swamp, and north of that is rain forest.[4]
The savannah zone's three categories are divided into "guinea savannah," the most common across the country, "Sudan savannah," and "sahel savannah." Guinea savannah is made up of plains of tall grass which are interrupted by trees; Sudan savannah is similar but with "shorter grasses and shorter trees." Sahel savannah is comprised patches of grass and sand, and is found in the northeast.[4]
Natural resources and land use
Nigeria's natural resources include but are not limited to petroleum (see petroleum in Nigeria), tin, columbite, iron ore, coal, limestone, lead, zinc, natural gas, hydropower, and arable land.
References
- ^ a b c "Regions Used to Interpret the Complexity of Nigeria". Geographical Alliance of Iowa. University of Northern Iowa. Retrieved 2007-07-19.
- ^ "Nigeria". Encarta. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-19.
- ^ "Nigeria". Encarta. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-19.
- ^ a b c "The Human and Physical Characteristics of Nigeria". Geographical Alliance of Iowa. University of Northern Iowa. Retrieved 2007-08-13.
