History of Catalan
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Catalan originated from Vulgar Latin in the Pyrenees Mountains between France and Spain. It diverged from the other Romance languages in the 9th century. [1] At that time, Catalan spread quickly throughout the Iberian peninsula when the Catalan counts conquered Muslim territory. [1] By the 11th century, the Catalan language was present in several feudal documents. [2] Catalan was present throughout the Mediterranean by the 15th Century. This was during a time when the city of Valencia was thriving. [1]

In 1659, the Treaty of Pyrenees was signed, beginning a suppression of the Catalan language. Louis XIV issued a decree that prohibited the use of the Catalan language in Northern Catalonia.[3] The repression continued during the French Revolution when the First French Republic prohibited the usage of Catalan in linguistic education.[4] The repression continued until recently, when finally the French government in 2007 promoted the usage of Catalan publicly and in education.[5]
In Spain, the usage of Catalan was also prohibited. Under Francisco Franco, Catalan was prohibited in the government and in education. It was initially prohibited in mass media but allowed during the early 1950s. Nevertheless, the publishing of written works in Catalan continued. [6] Then, when Franco died and a constitutional monarchy was instituted, the usage of Catalan was promoted. In Spain, Catalan is now used frequently and can be heard in many different television shows.
Middle Ages
High Middle Ages

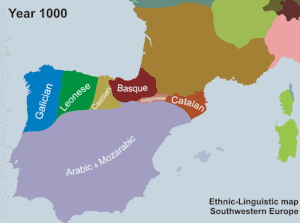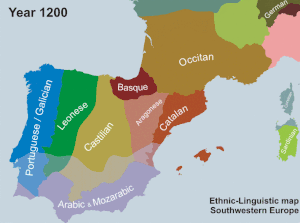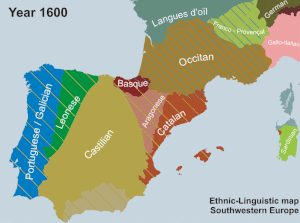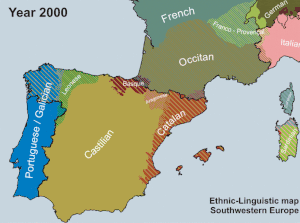
By the 9th century, the Catalan language had developed from Vulgar Latin on both sides of the eastern end of the Pyrenees mountains (counties of Rosselló, Empúries, Besalú, Cerdanya, Urgell, Pallars and Ribagorça), as well as in the territories of the Roman province and later archdiocese of Tarraconensis to the south.[1] From the 8th century on, the Catalan counts extended their territory southwards and westwards, conquering territories then occupied by Muslims, bringing their language with them.[1]
This phenomenon gained momentum with the separation of the County of Barcelona from the Carolingian Empire in 988 AD.[1] By the 9th century, the Christian rulers occupied the northern parts of present-day Catalonia, usually termed "Old Catalonia", and during the 11th and 12th centuries they expanded their domains north of the Ebro river, a land known as "New Catalonia".[1] During the 13th century, the Catalans expanded to the Land of Valencia and across to the Balearic Islands and Alghero in Sardinia.[1]
Hec est memoria de ipsas rancuras que abet dominus Guitardus Isarnus, senior Caputense, de rancuras filio Guillelm Arnall et que ag de suo pater, Guilelm Arnall; et non voluit facere directum in sua vita de ipso castro Caputense che li comannà. Et si Guilelm Arnal me facia tal cosa que dreçar no·m volgués ho no poqués, ho ssi·s partia de mi, che Mir Arnall me romasés aisí com lo·m avia al dia che ad él lo commanné. Et in ipsa onor a Guillelm Arnal no li doné negú domenge ni establiment de cavaler ni de pedó per gitar ni per metre quan l·i comanné Mir Arnall.
Lines 1–4. Passages in Catalan in italics
According to historian Jaume Villanueva (1756–1824), the first attested Catalan sentence is thought to be found in an 8th-century manuscript from Ripoll that has since been lost. It was an amusing note in 10th or early 11th-century calligraphy: Magister m[eu]s no vol que em miras novel ("my master does not want you to watch me, you novice").[9]
During the 11th century, several feudal documents (especially oaths and complaints) written in macaronic Latin, began to exhibit elements of Catalan, with proper names or even sentences in Romance.[2] Of special historical and linguistic importance is the Memorial of Complaints of Ponç I[10] (ca. 1050–1060), featuring whole sentences in Romance.[2] By the end of the 11th century, documents written completely or mostly in Catalan begin to appear, like the Complaints of Guitard Isarn, Lord of Caboet (ca. 1080–1095), or The Oath of peace and truce of count Pere Ramon (1098).[2] Catalan shares many features with Gallo-Romance languages, which are mostly located in France and Northern Italy. Old Catalan diverged from Old Occitan between the 11th and 14th centuries.[11]
Low Middle Ages
Catalan lived a golden age during the Low Middle Ages, reaching a peak of maturity and cultural plenitude.[1] Examples of this can be seen in the works of Majorcan polymath Ramon Llull (1232–1315), the Four Great Chronicles (13th-14th centuries), and the Valencian school of poetry which culminated in Ausiàs March (1397–1459).[1]
By the 15th century, the city of Valencia had become the center of social and cultural dynamism, and Catalan was present all over the Mediterranean world.[1] The belief that political splendor was correlated with linguistic consolidation was voiced through the Royal Chancery, which promoted a highly standardized language.[1]
The outstanding[1] novel of chivalry Tirant lo Blanc (1490), by Joanot Martorell, shows the transition from medieval to Renaissance values, something than can also be seen in the works of Bernat Metge and Andreu Febrer.[1] During this period, Catalan was what Costa Carreras terms "one of the 'great languages' of medieval Europe".[1] The flowering of the Renaissance was closely associated with the advent of the printing press, and the first book produced with movable type in the Iberian Peninsula was printed in Valencia in 1474: Trobes en llaors de la Verge maria ("Poems of praise of the Virgin Mary").[1]
18th century to the present: France

After the Treaty of the Pyrenees, a royal decree by Louis XIV of France on April 2, 1700 prohibited the use of the Catalan language in present-day Northern Catalonia. The decree forbade use in any official document, under the threat of being invalidated.[3]
Shortly after the French Revolution, the French First Republic prohibited official use of, and enacted discriminating policies against, the nonstandard languages of France (patois), such as Catalan, Breton, Occitan, Flemish, and Basque.
The deliberate process of eradicating non-French vernaculars in modern France and dismissing them as mere local and often strictly oral dialects was formalized with Abbé Grégoire's Report on the necessity and means to annihilate the patois and to universalize the use of the French language,[4] which he presented on June 4, 1794 to the National Convention; thereafter, all languages other than French were officially banned in the administration and schools for the sake of linguistically uniting post-Bastille Day France.
To date, the French government continues its policy of recognizing French as the country's only official language. Nevertheless, on 10 December 2007, the General Council of the Pyrénées-Orientales recognized Catalan as one of its official the languages in the Article 1 (a) of its Charte en faveur du Catalan[5] and sought to promote it in public life and education.
- Article 1: "The General Council of Pyrénées-Orientales officially recognizes, along with the French language, Catalan as a language of the department.
- ([Le Conseil Général des Pyrénées-Orientales reconnaît officiellement, au côté de la langue française, le catalan comme langue du département] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help))."
18th century to the present: Spain

After the Nueva Planta Decrees, the use of Catalan in administration and education was banned in the Kingdom of Spain. It was not until the Renaixença that use of the Catalan language saw a resurgence.
In Francoist Spain (1939–1975), the use of Spanish in place of Catalan was promoted, and public use of Catalan was initially repressed and discouraged by official propaganda campaigns. The use of Catalan in government-run institutions and in public events was banned. During later stages of the Francoist regime, certain folkloric or religious celebrations in Catalan were allowed to resume and were tolerated. Use of Catalan in the mass media was initially forbidden, but beginning in the early 1950s [6] it was permitted in the theater. Publishing in Catalan continued throughout the dictatorship.[6] There was no official prohibition of speaking Catalan in public or in commerce, but all advertising and signage had to be in Spanish, as did all written communication in business.[6]
Following the death of Franco in 1975 and the restoration of democracy under a constitutional monarchy, the use of Catalan increased significantly because of new affirmative action and subsidy policies. The Catalan language is now used in politics, education and the media, including the newspapers Avui ("Today"), El Punt ("The Point"), Ara ("Now"), La Vanguardia and El Periódico de Catalunya (sharing content with El Periòdic d'Andorra, printed in Andorra); and the television channels of Televisió de Catalunya (TVC): TV3, and Canal 33 (culture channel), Super3/3XL (cartoons channel) as well as a 24-hour news channel 3/24 and the sports channel Esport 3; in Valencia Canal Nou, 24/9 and Punt 2; in the Balearic islands IB3; in Catalonia there are also some private channels such as 8TV and Barça TV.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Costa Carreras, pp. 6–7.
- ^ a b c d Moran 2004, pp. 37–38.
- ^ a b "L'interdiction de la langue catalane en Roussillon par Louis XIV" (PDF). "CRDP, Académie de Montpellier.
- ^ a b Abbé Grégoire. "Report on the necessity and means to annihilate the patois and to universalize the use of the French language". languefrancaise.net.
- ^ a b "Charte en faveur du Catalan". Archived from the original on December 22, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Marc Howard Ross, Cultural Contestation in Ethnic Conflict, page 139. Cambridge University Press, 2007. Cite error: The named reference ":11" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Veny 1997.
- ^ The source book has reconstructed elided fragments and written out abbreviations in full, like et. Capitalization, the use of u-v, i-j, and c-ç have all been regularized. Accents apostrophes and diaeresis have been added according to the modern orthography. Used punctuation according to modern usage.
- ^ Moran 1994, pp. 55–93.
- ^ Memorial de greuges de Ponç I, comte d'Empúries, contra Jofre, Compte de Roselló
- ^ Riquer 1964.
Bibliography
- Costa Carreras, Joan; Yates, Alan (2009). The Architect of Modern Catalan: Selected Writings/Pompeu Fabra (1868–1948). Instutut d'Estudis Catalans & Universitat Pompeu Fabra & Jonh Benjamins B.V. pp. 6–7. ISBN 978 90 272 3264 9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Moran, Josep (1994). Treballs de lingüística històrica catalana (in Catalan). Barcelona: Publicacions de l'Abadia de Monsterrat. pp. 55–93. ISBN 84-7826-568-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Moran, Josep (2004). Estudis d'història de la llengua catalana (in Catalan). Barcelona: Publicacions de l'Abadia de Montserrat. pp. 37–38. ISBN 84-8415-672-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Riquer, Martí de (1964). "Vol.1". Història de la Literatura Catalana (in Catalan). Barcelona: Ariel.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Veny, Joan (1997). "greuges de Guitard isarn, Senyor de Caboet (1080-1095)". Homenatge a Arthur Terry. Barcelona: Publicacions de l'Abadia de Montserrat. pp. 9–18. ISBN 84-7826-894-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)

