1946 Italian general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 556 seats to the Italian Constituent Assembly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 89.1% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
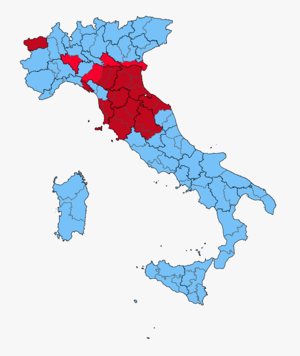 Legislative election results map. Light Blue denotes provinces with a Christian Democratic plurality, Red denotes those with a Communist plurality, Salmon denotes those with a Socialist plurality. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General elections were held in Italy on Sunday June 2, 1946.[1] They were the first after World War II and elected 556 deputies to the Constituent Assembly. Theoretically, a total of 573 deputies were to be elected, but the election did not take place in the Julian March and in South Tyrol, which were under military occupation by the United Nations.
For the first time, Italian women were allowed to vote in a national election. Electors had two votes: one to elect the representatives and one to choose the institutional form of the state.
Electoral system
To emphasise the restoration of democracy after the fascist era, a pure party-list proportional representation was chosen. Italian provinces were united in 31 constituencies, each electing a group of candidates.[2] At constituency level, seats were divided between open lists using the largest remainder method with the Imperiali quota. Remaining votes and seats were transferred at national level, where special closed lists of national leaders received the last seats using the Hare quota.
Campaign
At the end of World War II, Italy was governed under transitional laws as a result of agreements between the National Liberation Committee (CLN) and the royal Lieutenant General of the Realm Humbert II. As no democratic elections had taken place for more than 20 years, legislative power was given to the government but, after the first election, the Italian Council of Ministers would have to receive a vote of confidence by the new Constituent Assembly.
The three main contestants were Christian Democracy and the Socialist Party, which had both received popular support before the fascist era, and the Communist Party, which had strengthened itself with the armed struggle against Nazism and fascism during the war. The Italian Liberal Party, heir of the pre-fascist and conservative ruling class, proposed an alliance called National Democratic Union. Monarchists groups created the National Bloc of Freedom, while the social liberal Action Party and Labour Democratic Party hoped to maximize the positive image of the governments that they ruled in the National Liberation Committee.
Parties and leaders
| Party | Ideology | Leader | |
|---|---|---|---|
| bgcolor="Template:Christian Democracy (Italy)/meta/color" | | Christian Democracy (DC) | Christian democracy, Popularism | Alcide De Gasperi |
| bgcolor="Template:Italian Socialist Party/meta/color" | | Socialist Party of Proletarian Unity (PSIUP) | Socialism, Democratic socialism | Pietro Nenni |
| bgcolor="Template:Italian Communist Party/meta/color" | | Italian Communist Party (PCI) | Communism, Marxism-Leninism | Palmiro Togliatti |
| bgcolor="Template:Italian Liberal Party/meta/color" | | National Democratic Union (UDN) | Liberalism, Conservatism | Manlio Brosio |
| Common Man's Front (UQ) | Populism, Conservatism | Guglielmo Giannini | |
| bgcolor="Template:Italian Republican Party/meta/color" | | Italian Republican Party (PRI) | Republicanism, Social liberalism | Randolfo Pacciardi |
| National Bloc of Freedom (BNL) | Conservatism, Monarchism | Alfredo Covelli | |
| bgcolor="Template:Action Party (Italy)/meta/color" | | Action Party (PdA) | Republicanism, Liberal socialism | Ferruccio Parri |
Results
The election gave a large majority to the government formed by the three leaders of the CLN, which were briefly joined by the Republican Party after the exile of Humbert II. The alliance lasted for a year.
Source: Italian Ministry of Interior
Referendum
Together with the election, a constitutional referendum took place. Italian electors had to choose if they wanted to continue the reign of Humbert II of Savoy or to turn Italy into a republic. While all regions of Northern Italy as far as Tuscany and Marches gave a majority to the republic, all regions of Southern Italy to Lazio and Abruzzo voted to maintain the monarchy.
| Constitutional form of the Italian State | vote | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Republic | 12,718,641 | 54.3% | |
| Monarchy | 10,718,502 | 45.7% | |
| Invalid ballots | 1,509,735 | – | |
| Total | 24,946,878 | 100% |
References
- ^ Nohlen, D & Stöver, P (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p1047 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
- ^ The number of seats for each constituency ranged from 1 for Aosta Valley to 36 for Milan.
- ^ The Labour Democratic Party ran within the banner of the National Democratic Union in most regions.




