Lead(II) fluoride
Appearance

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lead difluoride
plumbous fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.089 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| PbF2 | |
| Molar mass | 245.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 8.445 g/cm3 (orthorhombic) 7.750 g/cm3 (cubic) |
| Melting point | 824°C |
| Boiling point | 1293°C |
| 0.64 g/100 mL (20 °C) [1] | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
7.12 x 10-7 |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid; insoluble in acetone and ammonia |
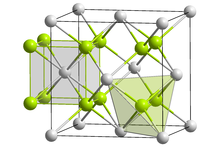
| Structure | |
| Fluorite (cubic), cF12 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
3000 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lead(II) chloride Lead(II) bromide Lead(II) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lead(II) fluoride (PbF2) is a chemical compound that is an odorless white solid.
Conditions/substances to avoid are: strong oxidizers.
Uses
Lead(II) fluoride is used:
- in low melting glasses
- in glass coatings to reflect infrared rays
- in phosphors for television-tube screens
- as a catalyst for the manufacture of picoline
Preparation
Lead(II) fluoride can be prepared by several methods. It is obtained by treating lead(II) hydroxide or lead(II) carbonate with hydrofluoric acid, followed by evaporation of the solution:
- Pb(OH)2 + 2 HF → PbF2 + 2 H2O
Alternatively, it is precipitated by adding hydrofluoric acid to a lead(II) salt solution, or by adding potassium fluoride to a lead(II) nitrate solution.
- 2 KF + Pb(NO3)2 → PbF2 + 2 KNO3
References
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0070494398
