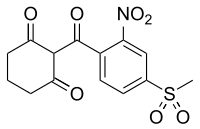
Mesotrione
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)-2-nitrobenzoyl]cyclohexane-1,3-dione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.661 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H13NO7S | |
| Molar mass | 339.32 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mesotrione is an herbicide sold under the brand names Callisto and Tenacity that was brought to market by Syngenta in 2001.[1] It is a synthetic analog of leptospermone developed to mimic the effects of this natural herbicide.[2] Mesotrione is a member of the class of HPPD inhibitors, which all work by inhibiting the plant enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase.[3] In plants, HPPD is necessary for carotenoid biosynthesis; carotenoids in turn protect chlorophyll from being degraded by sunlight.[4] When an HPPD inhibitor is sprayed on a plant, it prevents carotenoid from being made, chlorophyll degrades and the plant dies.
Sales by Syngenta were more than $400 million per year in 2011 but worldwide patent rights started to expire in 2012, opening the market to generic competition.[1]
See also
- Nitisinone (orfadin)
References
- ^ a b Dr. Nigel Uttley for Farm Chemicals International. June 3, 2011 Product Profile: Mesotrione
- ^ Derek Cornes (2005). "Callisto: a very successful maize herbicide inspired by allelochemistry". Fourth World Congress on Alleopathy. The Regional Institute Ltd. Retrieved May 26, 2011.
- ^ Moran, GR (Jan 2005). "4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase" (PDF). Arch Biochem Biophys. 433 (1): 117–28. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.015. PMID 15581571. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-03.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Tenacity Herbicide". Syngenta.
External links
- Mesotrione in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
