Mount Elgon
| Mount Elgon | |
|---|---|
| Wagagai (summit) | |
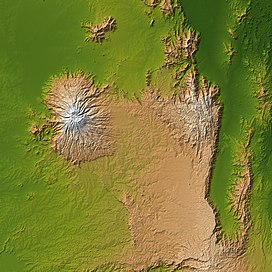 Mount Elgon (left) and Great Rift Valley (right) | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,321 m (14,177 ft)[1] Ranked 17th in Africa |
| Prominence | 2,458 m (8,064 ft)[1] |
| Isolation | 339 km (211 mi)[2] |
| Listing | Ultra |
| Coordinates | 01°07′06″N 34°31′30″E / 1.11833°N 34.52500°E[1] |
| Geography | |
| Topo map | Mount Elgon Map and Guide[3] |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Miocene origin |
| Mountain type | Shield volcano |
| Last eruption | Unknown |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1911 by Kmunke and Stigler |
| Easiest route | Scramble |



Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya,[4] north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.[1][5] Although there is no verifiable evidence of its earliest volcanic activity, geologists estimate that Mount Elgon is at least 24 million years old, making it the oldest extinct volcano in East Africa.[6]
Physical features
Mount Elgon is a massive solitary volcanic mountain on the border of eastern Uganda and western Kenya. Its vast form, 80 kilometres (50 mi) in diameter, rises 3,070 metres (10,070 ft) above the surrounding plains. Its cooler heights offer respite for humans from the hot plains below, and its higher altitudes provide a refuge for flora and fauna.
Mt. Elgon consists of five major peaks:
- Wagagai (4,321 metres (14,177 ft)), in Uganda
- Sudek (4,302 metres (14,114 ft)) on the Kenya/Uganda border
- Koitobos (4,222 metres (13,852 ft)), a flat-topped basalt column in Kenya
- Mubiyi (4,211 metres (13,816 ft)) in Uganda
- Masaba (4,161 metres (13,652 ft)) in Uganda


Other features of note are:
- The caldera — Elgon's is one of the largest intact calderas in the world.[citation needed]
- The warm springs by the Suam River[citation needed]
- Endebess Bluff (2,563 metres (8,409 ft))[citation needed]
- Ngwarisha, Makingeny, Chepnyalil, and Kitum caves: Kitum Cave is over 60 metres (200 ft) wide and penetrates 200 metres (660 ft). The cave contains salt deposits and it is frequented by wild elephants that lick the salt exposed by gouging the walls with their tusks.[7] It became notorious following the publication of Richard Preston's book The Hot Zone in 1994 for its association with the Marburg virus after two people who had visited the cave (one in 1980 and another in 1987) contracted the disease and died.[8]
The mountain soils are red laterite. The mountain is the catchment area for the several rivers such as the Suam River, which becomes the Turkwel downstream and drains into Lake Turkana, and the Nzoia River and the Lwakhakha River, which flow to Lake Victoria. The town of Kitale is in the foothills of the mountain. The area around the mountain is protected by two Mount Elgon National Parks, one on each side of the international border.
Flora
Some rare plants are found on the mountain, including Ardisiandra wettsteinii, Carduus afromontanus, Echinops hoehnelii, Ranunculus keniensis, and Romulea keniensis.[9]
Local ethnicities
Mount Elgon and its tributaries are home to four tribes, the Bagisu, the Sapiinjak, the Sabaot, also known as the Elgon Masai and the Ogiek, better known in the region under the derogatory umbrella term Ndorobo.[10]
See also
- List of Ultras of Africa
- 2010 Ugandan landslide
- List of volcanoes in Kenya
- Elgon languages
- Mount Elgon insurgency
- Breast shaped hills
References
- ^ a b c d Africa Ultra-Prominences Peaklist.org. Retrieved 2012-01-11.
- ^ [1] peakbagger.com, retrieved 19 March 2017
- ^ Mount Elgon Map and Guide (Map) (1st ed.). 1:50,000 with mountaineering information. EWP. 1989. ISBN 0-906227-46-1.
- ^ "Uganda Wildlife Authority". www.uwa.or.ug. Archived from the original on 2007-12-24. Retrieved 2008-03-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Mount Elgon, Uganda" Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 11 January 2012
- ^ NASA (28 August 2005). "SRTM Africa Images". NASA. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- ^ "Underground Elephants Resurface | Wild Kingdom | Animal Planet". Animal.discovery.com. 2012-05-15. Retrieved 2018-08-10.
- ^ Preston, Richard, The Hot Zone : The Terrifying True-Life Thriller, Bantam Books, 1994.
- ^ "SiteBuilder". www.tour-uganda.com.
- ^ Scott, Penny (1998). From Conflict to Collaboration: People and Forests at Mount Elgon, Uganda. IUCN. ISBN 2-8317-0385-9.
External links
- Mount Elgon
- Bungoma County
- Trans-Nzoia County
- Stratovolcanoes of Kenya
- Calderas of Africa
- Mountains of Uganda
- Stratovolcanoes of Uganda
- Mountains of Kenya
- Volcanoes of the Great Rift Valley
- Extinct volcanoes
- Anthropomorphic geographic features
- Kenya–Uganda border
- International mountains of Africa
- Four-thousanders of Africa

