Phosphorus pentasulfide
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
phosphorus sulfide
sulfur phosphide phosphorus persulfide diphosphorus pentasulfide tetraphosphorus decasulfide phosphorus decasulfide | |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.858 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| P4S10 | |
| Molar mass | 444.555 g mol |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 2.09 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 288 °C (561 K) |
| Boiling point | 514 °C (787 K) |
| hydrolyses | |
| Solubility in other solvents | 0.222 g / 100g CS2 (at 17 °C) Insoluble in C6H6 Insoluble in hot xylene Insoluble in hot anisole. |
| Structure | |
| triclinic, aP28 | |
| P-1, No. 2 | |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P4S10. This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities.
Structure and synthesis
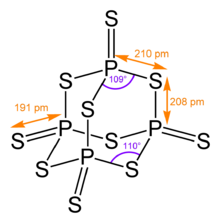
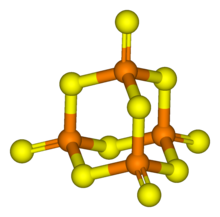
Its tetrahedral molecular structure is related to that of adamantane and is almost identical to the structure of phosphorus pentoxide.[1]
Phosphorus pentasulfide is obtained by the reaction of liquid white phosphorus (P4) with sulfur above 300 °C. The first synthesis of P4S10 by Berzelius in 1843 [2] was by this method. Alternatively, P4S10 can be formed by reacting elemental sulfur or pyrite, FeS2, with ferrophosphorus, impure Fe2P (a byproduct of P4 production from phosphate rock):
- 4 Fe2P + 18 S → P4S10 + 8 FeS
- 4 Fe2P + 18 FeS2 + heat → P4S10 + 26 FeS
Applications
Approximately 150,000 tons of P4S10 are produced annually. The compound is mainly converted to other derivatives for use as lubrication additives such zinc dithiophosphates. It is also used in the production of pesticides such as Parathion and Malathion.[3] It is also a component of some amorphous solid electrolytes (e.g. Template:Lithium2S-P2S5) for some types of lithium batteries.
Phosphorus pentasulfide is a dual-use material, as it can be used for manufacture of the VX nerve agent.
Reactivity
Due to hydrolysis by atmospheric moisture, P4S10 evolves H2S, thus P4S10 is associated with a rotten egg odour. Aside from H2S, hydrolysis of P4S10 gives phosphoric acid:
- P4S10 + 16 H2O → 4 H3PO4 + 10 H2S
Other mild nucleophiles react with P4S10, including alcohols and amines. Aromatic compounds such as anisole, ferrocene and 1-methoxynaphthalene react to form 1,3,2,4-dithiadiphosphetane 2,4-disulfides such as Lawesson's reagent.
In organic chemistry P4S10 is used as a thionation reagent. Reactions of this type require refluxing solvents such as benzene, dioxane or acetonitrile with P4S10 dissociating into P2S5. P2S5 can be trapped for example as the pyridine complex. Ketones are converted to thioketones. In esters, imides and lactones the oxygen atom can also be replaced by sulfur. With amides the reaction product is a thioamide. With 1,4-diketones the reagent forms a thiophene. Compared to the better known Lawesson's reagent P4S10 suffers from reduced yields.[4]
References
- ^ D. E. C. Corbridge (1995). Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology, 5th Edition. Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
- ^ Demselben (1843). "Ueber die Verbindungen des Phosphors mit Schwefel". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 46 (3): 251. doi:10.1002/jlac.18430460303.
- ^ Gerhard Bettermann, Werner Krause, Gerhard Riess, Thomas Hofmann “Phosphorus Compounds, Inorganic” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_527
- ^ Ozturk, Turan; Ertas, Erdal; Mert, Olcay (2010). "A Berzelius Reagent, Phosphorus Decasulfide (P4S10), in Organic Syntheses". Chemical Reviews. 110 (6): 3419–3478. doi:10.1021/cr900243d. PMID 20429553.
