Rhaetic
| Rhaetian | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Ancient Rhaetia |
| Region | Eastern Alps |
| Era | 1st millennium BC to 3rd century AD[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xrr |
xrr | |
| Glottolog | raet1238 |
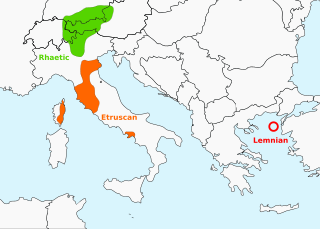 | |
Rhaetian /ˈriːʃən/ or Rhaetic (Raetic) /ˈriːt[invalid input: 'i-']k/ is an ancient language spoken in the ancient region of Rhaetia in the Eastern Alps in pre-Roman and Roman times. It is documented by a limited number of short inscriptions (found through Northern Italy, Southern Germany, Eastern Switzerland, Slovenia and Western Austria)[2] in two variants of the Etruscan alphabet. Its linguistic categorization is not clearly established, and it presents a confusing mixture of what appear to be Etruscan, Indo-European and uncertain other elements.
The ancient Rhaetic language is not the same as one of the modern Romance languages of the same Alpine region, known as Rhaeto-Romance, but both are sometimes referred to as "Rhaetian".
Classification
The most credible theories are that Rhaetic was either a member, along with Etruscan, of a proposed Tyrrhenian language family by German linguist Helmut Rix, possibly influenced by neighboring Indo-European languages[3][4] or else an Indo-European language, with links to Illyrian, Celtic,[5] and perhaps Venetic[6]
History

It is clear that in the centuries leading up to Roman imperial times, the Rhaetians had at least come under Etruscan influence, as the Rhaetic inscriptions are written in what appears to be a northern variant of the Etruscan alphabet. The ancient Roman sources mention the Rhaetic people as being reputedly of Etruscan origin, so there may at least have been some ethnic Etruscans who had settled in the region by that time.
In his Natural History (1st century AD), Pliny wrote about Alpine peoples:
adjoining these (the Noricans) are the Rhaeti and Vindelici. All are divided into a number of states.[a] The Rhaeti are believed to be people of Tuscan race[b] driven out by the Gauls; their leader was named Rhaetus.[7]
Pliny's comment on a leader named Rhaetus is typical of mythologized origins of ancient peoples, and not necessarily reliable. The name of the Venetic goddess Reitia has commonly been discerned in the Rhaetic finds, but the two names do not seem to be linked. The spelling as Raet- is found in inscriptions, while Rhaet- was used in Roman manuscripts; whether this Rh represents an accurate transcription of an aspirated R in Rhaetic or is an error is uncertain.
Many inscriptions are known, but most of them are only short and fairly repetitive, probably mostly votive texts. Rhaetic became extinct by the 3rd century AD, with its speakers eventually adopting Vulgar Latin in the south and Germanic in the north, and possibly Celtic prior to that.[8]
See also
- Rhaeti
- Rhaetic alphabet
- Aegean languages
- Etruscan language
- Etruscan civilization
- Tyrsenian languages
- Camunic language
Notes
- ^ in multas civitates divisi.
- ^ Tuscorum prolem (genitive case followed by accusative case), "offshoot of the Tusci."
References
- ^ Rhaetian at MultiTree on the Linguist List
- ^ "The Raetic alphabets".
- ^ Rix 1998.
- ^ Schumacher 1998.
- ^ Scullard, 1967 & 43.
- ^ Silvestri, M.; Tomezzoli, G. (2007). Linguistic distances between Rhaetian, Venetic, Latin and Slovenian languages (PDF). Proc. Int'l Topical Conf. Origin of Europeans. pp. 184–190.
- ^ Pliny, "XX", Naturalis Historia (in Latin), vol. III, Rackham, H transl, Loeb.
- ^ Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1911.
Sources
- Morandi, Alessandro (1999), "Il cippo di Castelciès nell'epigrafia retica", Studia archaeologica, 103, Rome: Bretschneider.
- Prosdocimi, Aldo L. (2003-4). "Sulla formazione dell'alfabeto runico. Promessa di novità documentali forse decisive". Archivio per l'Alto Adige 97–98.427–440
- Rix, Helmut (1998), Rätisch und Etruskisch, Vorträge und kleinere Schriften (in German), Innsbruck: Innsbrucker Beiträge zur Sprachwissenschaft: Institut für Sprachwissenschaft der Universität Innsbruck
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help). - Schumacher, Stefan (1998), "Sprachliche Gemeinsamkeiten zwischen Rätisch und Etruskisch", Der Schlern (in German), 72: 90–114.
- Schumacher, Stefan (2004) [1992], Die rätischen Inschriften. Geschichte und heutiger Stand der Forschung, Sonderheft (2nd ed.), Innsbruck: Innsbrucker Beiträge zur Kulturwissenschaft: Institut für Sprachwissenschaft der Universität Innsbruck.
- Scullard, HH (1967), The Etruscan Cities and Rome, Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Tóth, Alfréd; Brunner, Linus. (2007): "Raetic: An extinct Semitic language in Central Europe.". The Hague: Mikes International. ISBN 978-90-8501-113-2
External links
- Zavaroni, Adolfo, Rhaetic inscriptions, Tripod.
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Ancient languages
- Extinct languages of Europe
- Languages of ancient Italy
- Tyrsenian languages
- Unclassified languages of Europe
- Languages attested from the 1st millennium BC
- 1st-millennium BC establishments in Europe
- Languages extinct in the 3rd century
- 3rd-century disestablishments in Europe
