Simnotrelvir/ritonavir
Appearance
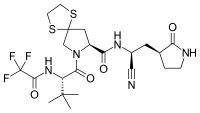 | |
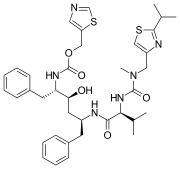 Chemical structures of simnotrelvir (top) and ritonavir (bottom) | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Simnotrelvir | SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitor |
| Ritonavir | Protease inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | 先诺欣 (Xiannuoxin) |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SIM0417, SSD8432 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Drug class | SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitor |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 72.5%[1] |
| Metabolism | hepatic (CYP3A)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 3.1 h; 4.1 h with ritonavir[1] |
| Excretion | urine (55.4%), feces (36.7%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30F3N5O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 549.63 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Simnotrelvir/ritonavir (trade name Xiannuoxin) is a pharmaceutical drug used for the treatment of COVID-19.[2] Simnotrelvir/ritonavir is a combination drug of simnotrelvir, an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro, and ritonavir,[3] a CYP3A inhibitor.
It was developed by Simcere Pharmaceutical and conditionally approved in China by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in January 2023.[4] Results for the phase Ib trial are available.[5] In a phase II/III trial, it reduced the duration of symptoms by a median of 36 hours compared to placebo.[6]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Simcere (January 28, 2023). "先诺欣 [先诺特韦片/利托那韦片组合包装 Simnotrelvir Tablets/Ritonavir Tablets(co-packaged)]". Dxy.cn package insert database (in Chinese (China)). Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ Zhu KW (September 2023). "Deuremidevir and Simnotrelvir-Ritonavir for the Treatment of COVID-19". ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science. 6 (9): 1306–1309. doi:10.1021/acsptsci.3c00134. PMC 10496140. PMID 37705591.
- ^ Wang Q, Chen G, He J, Li J, Xiong M, Su H, et al. (May 2023). "Structure-Based Design of Potent Peptidomimetic Inhibitors Covalently Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 24 (10): 8633. doi:10.3390/ijms24108633. PMC 10218254. PMID 37239980.
- ^ "China approves two oral drugs to treat COVID-19". bioworld.com. January 30, 2023.
- ^ Wang F, Xiao W, Tang Y, Cao M, Shu D, Asakawa T, et al. (September 2023). "Efficacy and safety of SIM0417 (SSD8432) plus ritonavir for COVID-19 treatment: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1b trial". The Lancet Regional Health. Western Pacific. 38: 100835. doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100835. PMC 10362366. PMID 37484496.
- ^ Cao B, Wang Y, Lu H, Huang C, Yang Y, Shang L, et al. (2024-01-18). "Oral Simnotrelvir for Adult Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19". New England Journal of Medicine. 390 (3): 230–241. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301425. PMC 11156186. PMID 38231624. S2CID 267030019.
External links
[edit]- NHSA slideshow, also shows adverse effect data from phase II/III
