Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau


| Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 雲貴高原 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 云贵高原 | ||||||||
| Postal | Yunnan–Kweichow Plateau | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Yungui Plateau | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 雲貴高原 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 云贵高原 | ||||||||
| Postal | Yunkwei Plateau | ||||||||
| |||||||||
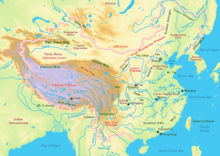
The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau (simplified Chinese: 云贵高原; traditional Chinese: 雲貴高原; pinyin: Yúnguì Gāoyuán) is a plateau located in the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou in southwest China. There are two distinct regions of this plateau: a high alpine region in Northwestern Yunnan, with elevations averaging about 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) and mountain peaks as high as 3,700 m (12,100 ft), and an area of rolling hills, gorges and karst topography with numerous geologic faults in Northern Yunnan and Western Guizhou.[1] [2]
Climate
The Climate of the Yunnan-Guizhou plateau varies due to the large range of elevations it encompasses. In the western, high elevation portion, the climate of the plateau is subject to intense solar radiation and cooler temperatures with large daily fluctuation. The height of the Plateau accounts for approximately one-third of the troposphere on earth due to its high elevation, since as height rises, troposphere drops. For every 100 m (330 ft) rise, in general there is a 0.6 °C (1.1 °F) fall in temperature.[3]
Rivers
The high mountain peaks of Eastern Tibet are the source of many of Asia's great rivers, which flow south and east through the Yunnan-Guizhou plateau. From east to west these rivers include the Yellow River, the Yangtse, the Mekong (also known as the Lancang) and the Salween rivers, which are contained within the Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Area, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[4]
Flora
The climate is rainy in the southwest in the summer, providing for dense forests, both broadleaf and coniferous. The shrubbery is varied from needles bush thickets to acacia bushes growing in dry river beds. It is grassy marshland in the Tibet Autonomous Region. [citation needed]
See also
Footnotes
- ^ "Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2007-08-06.
- ^ "Chinese History and Statistics - Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau Upland". Retrieved 2007-08-06.
- ^
Yang Qinye. The Geology of Tibet -- Complicated and Varietied. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - ^ Yang Qinye. Tibetan Geography -- Long Rivers with Distant Sources. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help)
