Adana Printing Machines
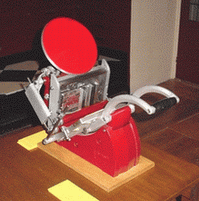
Adana Printing Machines were manufactured from 1922 to 1999 in Twickenham, England. Although most of the printing presses produced by Adana were aimed at hobby printers, they were frequently put to commercial use. Adanas are still to be found throughout the world in the hands of colleges, enthusiasts and professional printers. Caslon Limited manufactured machines after a takeover of the company in 1987.[1]
The earliest Adana models were flat-bed presses but they were to become most famous for their "Eight-Five" and other vertical platen presses.
History of the Adana
The Adana Agency was founded in 1922 by Donald Aspinall. The company's assets were then bought by Frederick Ayers in 1940 and the company was relaunched as Adana (Printing Machines) Limited in 1946. In 1987 the assets were again sold, this time to Caslon Limited who continued to produce a small number of presses for a further six years. Throughout the years, both the company and its presses were usually referred to as "Adana" or "The Adana".
Donald Aspinall
Donald Affleck Aspinall was born in South Kensington, London, in 1899. Unusually for the time, his parents separated, and his father Herbert left the seven-year-old Donald and his brothers, John and Cecil, in the sole care of their mother, Lilian.
In 1917 Donald served in World War I, presumably having lied about his age. Later that year he returned from the front suffering from shell-shock. While recovering, he began working on the design of a small flat-bed printing press. He advertised it in Model Engineer magazine in 1918 and was overwhelmed by the response. The teenage Aspinall is said to have tried to hand the money over to the local constabulary, rather than face the prospect of fulfilling so many orders. He was persuaded that this was not a wise move by an understanding policeman, and he eventually produced enough machines to fill the orders.
After losing his job five years later, Aspinall founded the Adana Agency and turned his hobby into a business. From premises in Twickenham, he began selling flat-bed wooden presses to hobby printers. The competitive pricing and self-inking system ensured its success.
In 1928 he married Dorothy Lucas. They later had two children, Robert and Diana. The company was going from strength to strength, with new models launched regularly, showrooms opening in London and Manchester, and official distributors enlisted in New York and Perth, Western Australia.
A decade later, the company's fortunes declined. In 1939 Aspinall suffered the first of several strokes and the economic pressures of World War II left the Adana Agency in meltdown. After a meeting of the creditors, the company's assets were sold to Frederick Ayers.
Until his death in 1948, Aspinall continued to correspond with Frederick Ayers, sharing advice and ideas for new designs.
Aspinall's engineering achievements are sometimes dismissed as he borrowed so heavily from American designs, but his business acumen and talent for re-working existing ideas (such as creating a revolving ink-disk for his flat-bed presses) are widely acknowledged.
Frederick Ayers
Engineer Frederick Ayers became involved with the company in 1923 when his company started supplying parts to the fledgling Adana Agency. He became friends with Aspinall, and began to offer design advice. As one of the company's creditors, he was able to purchase the assets cheaply in 1940 when the company became insolvent.
The war years
Like many others, the company was effectively on hold during World War II, with a skeleton staff supplying only parts and sundries. They were asked to supply small flat-bed presses for the Resistance movement in Europe but little else happened until 1945 when production began again on a very limited basis. Ongoing rationing meant raw materials were in short supply and it wasn't until around 1950 that the company was able to trade at full capacity again.
Post-war expansion
By 1952, Adana had distributors in Italy, Turkey, Greece, India, Finland and Canada. They continued to expand until Adanas were available in nearly 100 countries around the world.
The end of Adana
There were unavoidable price increases as parts and labour became more expensive. Adana presses were virtually indestructible and the company had a policy of supplying parts, so there was little incentive to buy new when second-hand presses were readily available. Lithography was drawing away much of the commercial market and letterpress printing (along with many crafts) became unfashionable as the 1980s brought new technology into homes.
The company was wound down and the assets sold to Caslon Limited who continued to produce the more popular presses until 1999 when the last Eight-Five was sold in Japan. Caslon still supply parts and refurbish old Adanas to new condition.
Rebirth of the Eight-Five
A resurgence of interest in letterpress printing as a hobby, and as a premium commercial product, resulted in the reintroduction of the Adana "Eight-Five" in 2016, when production of the machine was restarted. The basic design has been modified to produce a thicker body shell, capable of achieving the deeper letterpress impression now fashionable. The relaunched press is known as the "85C".
Other activities
Adana also cast type and published many books. Their magazine-style catalogues (containing practical printing advice alongside price lists) such as Popular Printing and Printcraft were much loved and have become highly collectable.
The name
The official story behind the name Adana states that Donald Aspinall named the company after the city of Adana in Turkey, having served there during World War I. In his book on Adanas, printing historian Bob Richardson notes that Aspinall's army unit never saw action in Turkey and relates another theory:
Donald's son Robert suggested recently that his father had simply used his initials, together with an extra letter from his first and last names (A and N), and juggled them to create the word ADANA. It was short, easy to remember and had a pleasant, rather exotic sound.[2]
Even if he had served in Turkey, it seems unlikely that Aspinall would choose a name that recalled the military service that so traumatised[citation needed] him as a young man. It is possible that his war trauma was a result of witnessing the Armenian genocide; Adana previously had a very large Armenian population. It is also possible that the company created a fictional back-story that was more satisfying than the reality. Adana is known to have fictionalised other aspects of the company's history for marketing purposes.
Other presses of note
Some of the presses manufactured by Adana include:[citation needed]
- The 45/- (1922)
- Foolscap Folio Treadle Platen (1926)
- Steel version of the 45/- Press (1927)
- Model 3 Model 4 (1927)
- Octavo Treadle launched (1927)
- A tiny press for children, the Adana 'Baby' (1927)
- A starter kit called the 'Compactum' (The Baby with a type case, ink and reglet (1928)
- The Octavo Platen, Adana's first vertical platen (1933)
- Flat-Bed Rotary Series launched (1933)
- No 1 High Speed launched, has a steel strip disk pawl, a vertical platen inspired by the designs of Kelsey (1934)
- No 1 High Speed improved, has the solid steel disk pawl (1935)
- No 2 High Speed, iron, no lettering, inside chase 6" x 4", a lug on each side to fix to a base board (1934)
- No 2 High Speed, iron, No2 H/S 2 lettering, inside chase 6" x 4", 2 holes at each end to fix to a base board (?)
- No 2 High Speed, alloy, No2.H.S. lettering, inside chase 6" x 4", 2 holes at each end to fix to a base board (?)
- Quarto 1A built on plywood base, single ink roller & rider roller, spring-loaded ink disk rotation (1934)
- Flat-bed Rotary Series withdrawn, possibly because of infringement on designs by a mysterious company called Anvil Ltd (1935)
- No 3 Quarto, an iron press weighing over 100 lbs, inside chase 10" x 7.5" (1938)
- QFB – 1945 Flat-Bed, Quarto Flat Bed, plywood construction (1945)
- Treadle/Power Platen 47 (not sold, issued as the T/P 48) (1947)
- T/P48 (Treadle/Power) inside chase 9.5" x 7" (1948)
- QH – Quarto Horizontal, the last flat-bed to be produced aluminium and steel castings (1950)
- No 3 H/S, inside chase 8.5" x 5.5" (1950)
- Adana Thermograph, for producing relief effects (1950)
- 8x5 – Adana Eight-Five (1953)
- Adana 9x6 Treadle Machine (1956)
- 5x3 – Adana Five-Three (1956)
- Ayers Jardine Showcard Press (1960)
- Adana P71/P71S (1970)
References
- ^ Caslon Limitd. "Adana® – The Home of Small Letterpress". Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ^ Richardson, B: The Adana Connection, page 17. British Printing Society, 1997.
Sources
- Richardson, Bob (1997). The Adana Connection. British Printing Society. ISBN 1-901220-03-6.
- Printing Machines and Type Sundries for The Small Printer. Adana. May 1935.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: year (link)
- The Model Engineer and Practical Electrician. 3 October 1935.
- "British Letterpress: Adana". 25 February 2009.
- "Briar Press". 18 February 2009.
- "Museum of Technology: Adana Printing Press, 1950's". 18 February 2009.


