Chromium(II) fluoride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
chromium difluoride, chromium fluouride, chromous fluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.140 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CrF2 | |
| Molar mass | 89.9929 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | blue-green iridescent crystals[1] hygroscopic, turns to Cr2O3 when heated in air[1] |
| Density | 3.79 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 894 °C (1,641 °F; 1,167 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | > 1,300 °C (2,370 °F; 1,570 K)[1] |
| 76.7 g/100 mL | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic[1] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-8.645 kJ/g (solid) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chromium(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrF2. It exists as a blue-green iridescent solid. Chromium(II) fluoride is sparingly soluble in water, almost insoluble in alcohol, and is soluble in boiling hydrochloric acid, but is not attacked by hot distilled sulfuric acid or nitric acid. Like other chromous compounds, chromium(II) fluoride is oxidized to chromium(III) oxide in air.[2]
Preparation and structure
The compound is prepared by passing anhydrous hydrogen fluoride over anhydrous chromium(II) chloride. The reaction will proceed at room temperature but is typically heated to 100-200 °C to ensure completion:[3]
- CrCl2 + 2 HF → CrF2 + 2 HCl
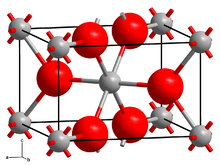
Like many difluorides, CrF2 adopts a structure like rutile with octahedral molecular geometry about Cr(II) and trigonal geometry at F−. Two of the six Cr–F bonds are long at 2.43 Å, and four are short near 2.00 Å.[4] This distortion is a consequence of the Jahn–Teller effect that arises from the d4 electron configuration of the chromium(II) ion.[5]
See also
External links
References
- ^ a b c d e f Perry, Dale L. (2011). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 120. ISBN 978-1-43981462-8. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ^ Merck Index, 14 ed. entry 2245
- ^ Riley, edited by Georg Brauer ; translated by Scripta Technica, Inc. Translation editor Reed F. (1963). Handbook of preparative inorganic chemistry. Volume 1 (2nd ed.). New York, N.Y.: Academic Press. p. 256. ISBN 978-0121266011.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jack, K. H.; Maitland, R. "Crystal structures and interatomic bonding of chromous and chromic fluorides" Proceedings of the Chemical Society, London (1957), 232. doi:10.1039/PS9570000217
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 1021–1022. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
