Member states of NATO

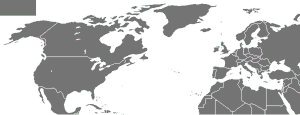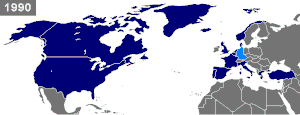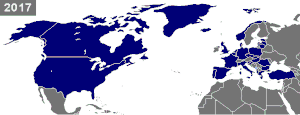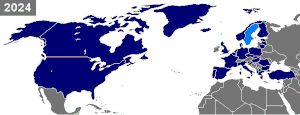
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) is an international military alliance that consists of 30 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it shall be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary.[1] Article 6 of the treaty limits the scope of Article 5 to the islands north of the Tropic of Cancer, the North American and European mainlands, the entirety of Turkey, and French Algeria. As such, an attack on Hawaii, Puerto Rico, French Guiana, Ceuta, or Melilla, among other places, would not trigger an Article 5 response.
Of the 30 member countries, 28 are in Europe and two in North America. Between 1994 and 1997, wider forums for regional cooperation between NATO and its neighbours were set up, including the Partnership for Peace, the Mediterranean Dialogue initiative and the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council.
All members have militaries, except for Iceland, which does not have a typical army (but it does have a coast guard and a small unit of civilian specialists for NATO operations). Three of NATO's members are nuclear weapons states: France, the United Kingdom, and the United States. NATO has 12 original founding member states. Three more members joined between 1952 and 1955, and a fourth new member joined in 1982. After the end of the Cold War, NATO added 14 more members from 1999 to 2020.
NATO currently recognizes Bosnia and Herzegovina, Finland, Georgia, Sweden, and Ukraine as aspiring members as part of their Open Doors enlargement policy.[2]

Founding members and enlargement
NATO was established on 4 April 1949 via the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty (Washington Treaty). The 12 founding members of the Alliance were: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States.[3]
The various allies all sign the Ottawa Agreement,[4] which is a 1951 document that acts to embody civilian oversight of the Alliance.[5][4]
Current membership consists of 30 countries. In addition to the 12 founding countries, four new members joined during the Cold War: Greece (1952), Turkey (1952), West Germany (1955) and Spain (1982). In 1990, the territory of the former East Germany was added with the reunification of Germany. NATO further expanded after the Cold War, adding the Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland (1999), Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia (2004), Albania and Croatia (2009), Montenegro (2017) and North Macedonia (2020).[3] Of the territories and members added between 1990 and 2020, all were either formerly part of the Warsaw Pact (including the formerly Soviet Baltic states) or territories of the former Yugoslavia (which was not a Warsaw Pact member). No countries have left NATO since its founding.
Membership aspirations
As of June 2022[update], five additional states have formally informed NATO of their membership aspirations: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Finland, Georgia, Sweden and Ukraine.[2]
- NATO members agreed at the 2008 Bucharest Summit that Georgia and Ukraine "will become members of NATO in the future".[6]
- Bosnia and Herzegovina was invited by NATO to join the Membership Action Plan (MAP) in April 2010.[6]
- In May 2022, Finland and Sweden simultaneously submitted official application letters to become NATO members.[7][8]
List of member countries
The current members and their dates of admission are listed below.
| Flag | Map | Member state | Capital | Accession[9] | Population[a] | Area[11] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Albania | Tirana | 1 April 2009 | 3,088,385 | 28,748 km2 (11,100 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Belgium | Brussels | 24 August 1949[b] | 11,778,842 | 30,528 km2 (11,787 sq mi) |
 |
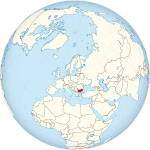 |
Bulgaria | Sofia | 29 March 2004 | 6,919,180 | 110,879 km2 (42,811 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Canada | Ottawa | 24 August 1949[b] | 37,943,231 | 9,984,670 km2 (3,855,103 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Croatia | Zagreb | 1 April 2009 | 4,208,973 | 56,594 km2 (21,851 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Czech Republic[c] | Prague | 12 March 1999 | 10,702,596 | 78,867 km2 (30,451 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Denmark | Copenhagen | 24 August 1949[b] | 5,894,687 | 42,943 km2 (16,580 sq mi)[12] 2,210,573 km2 (853,507 sq mi)[d] |
 |
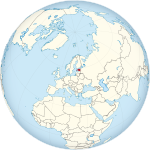 |
Estonia | Tallinn | 29 March 2004 | 1,220,042 | 45,228 km2 (17,463 sq mi) |
 |
 |
France | Paris | 24 August 1949[b] | 68,084,217 | 643,427 km2 (248,429 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Germany[e] | Berlin | 6 May 1955 (West Germany) 3 October 1990 (Germany) |
79,903,481 | 357,022 km2 (137,847 sq mi) |
 |
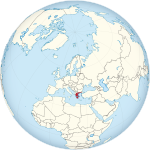 |
Greece | Athens | 18 February 1952 | 10,569,703 | 131,957 km2 (50,949 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Hungary | Budapest | 12 March 1999 | 9,728,337 | 93,028 km2 (35,918 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Iceland | Reykjavík | 24 August 1949[b] | 354,234 | 103,000 km2 (39,769 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Italy | Rome | 62,390,364 | 301,340 km2 (116,348 sq mi) | |
 |
 |
Latvia | Riga | 29 March 2004 | 1,862,687 | 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Lithuania | Vilnius | 2,711,566 | 65,300 km2 (25,212 sq mi) | |
 |
 |
Luxembourg | Luxembourg | 24 August 1949[b] | 639,589 | 2,586 km2 (998 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Montenegro | Podgorica | 5 June 2017 | 607,414 | 13,812 km2 (5,333 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Netherlands | Amsterdam | 24 August 1949[b] | 17,337,403 | 41,543 km2 (16,040 sq mi) |
 |
 |
North Macedonia | Skopje | 27 March 2020 | 2,128,262[f] | 25,713 km2 (9,928 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Norway | Oslo | 24 August 1949[b] | 5,509,591 | 323,802 km2 (125,021 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Poland | Warsaw | 12 March 1999 | 38,185,913 | 312,685 km2 (120,728 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Portugal | Lisbon | 24 August 1949[b] | 10,263,850 | 92,090 km2 (35,556 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Romania | Bucharest | 29 March 2004 | 21,230,362 | 238,391 km2 (92,043 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Slovakia | Bratislava | 5,436,066 | 49,035 km2 (18,933 sq mi) | |
 |
 |
Slovenia | Ljubljana | 2,102,106 | 20,273 km2 (7,827 sq mi) | |
 |
 |
Spain | Madrid | 30 May 1982 | 47,260,584 | 505,370 km2 (195,124 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Turkey[g] | Ankara | 18 February 1952 | 82,482,383 | 783,562 km2 (302,535 sq mi) |
 |
 |
United Kingdom | London | 24 August 1949[b] | 67,081,000 | 243,610 km2 (94,058 sq mi) |
 |
 |
United States | Washington, D.C. | 334,998,398 | 9,833,520 km2 (3,796,743 sq mi) |
Special arrangements
The three Nordic countries which joined NATO as founding members, Denmark, Iceland and Norway, chose to limit their participation in three areas: there would be no permanent peacetime bases, no nuclear warheads and no Allied military activity (unless invited) permitted on their territory. However, Denmark allowed the U.S. Air Force to maintain an existing base, Thule Air Base, in Greenland.[14]
From the mid-1960s to the mid-1990s, France pursued a military strategy of independence from NATO under a policy dubbed "Gaullo-Mitterrandism".[15] Nicolas Sarkozy negotiated the return of France to the integrated military command and the Defence Planning Committee in 2009, the latter being disbanded the following year. France remains the only NATO member outside the Nuclear Planning Group and unlike the United States and the United Kingdom, will not commit its nuclear-armed submarines to the alliance.[16][17]
Military personnel
| Comparison of military personnel per 1,000 capita. |
10
20
30
40
Countries (see legend)
|
The following list is constructed from The Military Balance, published annually by the International Institute for Strategic Studies.
| Country | Active | Reserve | Paramilitary | Total | Per 1,000 capita | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (total) | (active) | ||||||
| Albania[18] | 7,500 | 0 | 500 | 8,000 | 2.6 | 2.4 | |
| Belgium[18] | 24,450 | 5,900 | 0 | 30,350 | 2.6 | 2.1 | |
| Bulgaria[18] | 36,950 | 3,000 | 0 | 39,950 | 5.8 | 5.3 | |
| Canada[18] | 66,500 | 34,400 | 4,500 | 105,400 | 2.8 | 1.8 | |
| Croatia[18] | 16,700 | 21,000 | 3,000 | 40,700 | 9.7 | 4 | |
| Czech Republic[18] | 26,600 | 3,640 | 0 | 30,240 | 2.8 | 2.5 | |
| Denmark[18] | 15,400 | 44,200 | 0 | 59,600 | 10.1 | 2.6 | |
| Estonia[18] | 7,200 | 17,500 | 15,800 | 40,500 | 33.2 | 5.9 | |
| France[18] | 203,250 | 41,050 | 100,500 | 344,800 | 5.1 | 3 | |
| Germany[18] | 183,400 | 30,050 | 0 | 213,450 | 2.7 | 2.3 | |
| Greece[18] | 143,300 | 221,350 | 4,000 | 368,650 | 34.8 | 13.5 | |
| Hungary[18] | 34,200 | 20,000 | 12,000 | 66,200 | 6.8 | 3.5 | |
| Iceland[18] | 0 | 250 | 250 | 500 | 1.4 | 0 | |
| Italy[18][h] | 161,550 | 17,900 | 176,350 | 355,800 | 5.7 | 2.6 | |
| Latvia[18] | 8,750 | 11,200 | 0 | 19,950 | 10.7 | 4.7 | |
| Lithuania[18] | 23,000 | 7,100 | 14,150 | 44,250 | 16.3 | 8.5 | |
| Luxembourg[18] | 410 | 0 | 600 | 1,010 | 1.6 | 0.6 | |
| Montenegro[18] | 2,350 | 2,800 | 10,100 | 15,250 | 25.1 | 3.9 | |
| Netherlands | 41,543 | 6,643 | 6,500 | 54,686 | 3.2 | 2.4 | |
| North Macedonia[18] | 8,000 | 4,850 | 7,600 | 20,450 | 9.6 | 3.8 | |
| Norway[18] | 25,400 | 40,000 | 0 | 65,400 | 11.9 | 4.6 | |
| Poland[18] | 114,050 | 0 | 75,400 | 189,450 | 5 | 3 | |
| Portugal[18] | 27,250 | 211,700 | 24,700 | 263,650 | 25.7 | 2.7 | |
| Romania[18] | 71,500 | 55,000 | 57,000 | 183,500 | 8.6 | 3.4 | |
| Slovakia[18] | 17,950 | 0 | 0 | 17,950 | 3.3 | 3.3 | |
| Slovenia[18] | 6,950 | 1,200 | 0 | 8,150 | 3.9 | 3.3 | |
| Spain[18] | 122,850 | 14,900 | 75,800 | 213,550 | 4.5 | 2.6 | |
| Turkey[18] | 355,200 | 378,700 | 156,800 | 890,700 | 10.8 | 4.3 | |
| United Kingdom[18] | 194,200 | 37,450 | 0 | 231,650 | 3.5 | 2.9 | |
| United States[18] | 1,395,350 | 843,450 | 0 | 2,238,800 | 6.7 | 4.2 | |
| NATO | 3,292,810 | 2,108,950 | 745,550 | 6,147,310 | 6.5 | 3.5 | |
Military expenditures
Military spending of the US compared to total of all 29 other NATO member countries (US$ millions).[i]
Total military spending of NATO member countries except the United States (US$ millions).[i][j]
United States omitted - see above
The defence spending of the United States is more than double the defence spending of all other NATO members combined.[19] Criticism of the fact that many member states were not contributing their fair share in accordance with the international agreement by then US president Donald Trump caused various reactions from American and European political figures, ranging from ridicule to panic.[20][21][22]
This section needs to be updated. (April 2022) |
Pew Research Center's 2016 survey among its member states showed that while most countries viewed NATO positively, most NATO members preferred keeping their military spending the same. The response to whether their country should militarily aid another NATO country if it were to get into a serious military conflict with Russia was also mixed. Roughly half or fewer in six of the eight countries surveyed say their country should use military force if Russia attacks a neighboring country that is a NATO ally. And at least half in three of the eight NATO countries say that their government should not use military force in such circumstances. The strongest opposition to responding with armed force is in Germany (58%), followed by France (53%) and Italy (51%). More than half of Americans (56%) and Canadians (53%) are willing to respond to Russian military aggression against a fellow NATO country. A plurality of the British (49%) and Poles (48%) would also live up to their Article 5 commitment. The Spanish are divided on the issue: 48% support it, 47% oppose.[24][25]
| Member state | Population[a] | GDP (nominal)[k] |
Defence expenditure (US$)[l] | Personnel[l] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total ($millions) |
% real GDP | Per capita | Per 1000 personnel ($millions) | ||||
| 3,074,579 | 16.75 | 198 | 1.26 | 58 | 29 | 6,800 | |
| 11,720,716 | 529.55 | 4,921 | 0.93 | 392 | 189 | 26,000 | |
| 6,966,899 | 70.13 | 1,079 | 1.61 | 132 | 43 | 25,000 | |
| 38,436,447 | 2,016.00 | 21,885 | 1.27 | 569 | 304 | 72,000 | |
| 4,227,746 | 63.17 | 1,072 | 1.75 | 238 | 71 | 15,000 | |
| 10,702,498 | 261.73 | 2,969 | 1.19 | 236 | 114 | 26,000 | |
| 5,869,410 | 360.51 | 4,760 | 1.35 | 760 | 280 | 17,000 | |
| 1,228,624 | 32.74 | 669 | 2.13 | 429 | 106 | 6,300 | |
| 67,413,000 | 2,938.00 | 50,659 | 1.84 | 709 | 244 | 208,000 | |
| 83,190,556 | 4,319.00 | 54,113 | 1.36 | 591 | 294 | 184,000 | |
| 10,718,565 | 211.64 | 4,844 | 2.24 | 431 | 46 | 105,000 | |
| 9,771,827 | 180.50 | 2,080 | 1.21 | 178 | 104 | 20,000 | |
| 350,734 | 24.24 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 60,317,116 | 2,106.00 | 24,482 | 1.22 | 385 | 137 | 179,000 | |
| 1,881,232 | 36.77 | 724 | 2.01 | 325 | 113 | 6,400 | |
| 2,731,464 | 56.23 | 1,084 | 2.13 | 336 | 53 | 21,000 | |
| 628,381 | 72.99 | 391 | 0.55 | 552 | 434 | 900 | |
| 609,859 | 5.69 | 92 | 1.65 | 126 | 58 | 1,600 | |
| 17,674,000 | 1,012.99 | 12,419 | 1.35 | 655 | 303 | 41,000 | |
| 2,125,971 | 13.33 | 108 | 1.09 | 51 | 15 | 7,200 | |
| 5,467,439 | 422.06 | 7,179 | 1.70 | 1,308 | 359 | 20,000 | |
| 38,282,325 | 606.73 | 11,971 | 2.01 | 296 | 97 | 123,000 | |
| 10,344,802 | 251.70 | 3,358 | 1.41 | 299 | 112 | 30,000 | |
| 21,302,893 | 261.87 | 5,043 | 2.04 | 225 | 73 | 69,000 | |
| 5,440,602 | 111.87 | 1,905 | 1.74 | 322 | 147 | 13,000 | |
| 2,102,678 | 56.85 | 581 | 1.04 | 253 | 85 | 6,800 | |
| 47,450,795 | 1,450.00 | 13,156 | 0.92 | 264 | 109 | 121,000 | |
| 83,614,362 | 794.53 | 13,919 | 1.89 | 225 | 32 | 435,000 | |
| 67,081,000 | 3,108.00 | 60,376 | 2.13 | 979 | 419 | 144,000 | |
| 332,639,102 | 22,320.00 | 730,149 | 3.42 | 2,072 | 546 | 1,338,000 | |
| 953,365,622 | 43,711.57 | 1,036,186 | 2.51 | 1,045 | 317 | 3,268,000 | |
Notes
- ^ a b Population data is based on a July 2021 estimate by the Central Intelligence Agency in The World Factbook.[10]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Founding member of NATO.
- ^ Officially referred to by the name Czechia. (See Czech Republic#Name.)
- ^ including Faroe Islands and Greenland.
- ^ Germany initially joined NATO as West Germany. The former country of East Germany became part of NATO after German reunification.
- ^ North Macedonia's population estimate was missing from Central Intelligence Agency's Country Comparison list in The World Factbook but available in the country's entry.[13]
- ^ Officially referred to by the name Türkiye. (See Turkey#Name.)
- ^ The paramilitary forces of Italy consist of the Carabinieri and the Guardia di Finanza.
- ^ a b Country order is the same as the preceding chart (military personnel per 1,000 capita) to maintain the same country colours between charts.
- ^ The pie chart format does not allow as many slices as there are countries in NATO, so the countries with the fewest military personnel per capita (Albania, Belgium, Czech Republic, Iceland and Luxembourg) have been combined into a single slice.
- ^ Gross domestic product (nominal) data (in billions of US dollars) is based on an October 2019 issue of the World Economic Outlook, which is published by the International Monetary Fund.[26]
- ^ a b Defence expenditure and personnel data are based on a June 2019 press release from NATO.[27]
References
Citations
- ^ "The North Atlantic Treaty". North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 4 April 1949. Retrieved 16 June 2008.
- ^ a b "Enlargement and Article 10". NATO. 10 June 2022. Retrieved 1 July 2022.
Currently, five partner countries have declared their aspirations to NATO membership: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Finland, Georgia, Sweden and Ukraine.
- ^ a b NATO. "Member countries". NATO. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ a b Mosquera, Andrés B. Muñoz (2019). "The North Atlantic Treaty: Article 9 and NATO's Institutionalization". Volume 34. Emory International Law Review.
Really, the Agreement on the Status of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, National Representatives and International Staff signed in Ottawa
- ^ "03. Agreement on the Status of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, National Representatives and International Staff, done at Ottawa September 20, 1951". US Department of State.
- ^ a b NATO. "Enlargement and Article 10". NATO. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ NATO. "Relations with Finland". NATO. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ NATO. "Relations with Sweden". NATO. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ "Member countries". NATO. 4 October 2022. Archived from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 6 November 2022.
- ^ "Country Comparisons — Population". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Field Listing :: Area". Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 31 January 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- ^ "AREA". Statistics Denmark. Archived from the original on 14 April 2019. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ "North Macedonia — People and Society". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Denmark and NATO - 1949".
- ^ "Why the concept of Gaullo-Mitterrandism is still relevant". IRIS. 29 April 2019. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 7 March 2022.
- ^ Cody, Edward (12 March 2009). "After 43 Years, France to Rejoin NATO as Full Member". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 26 October 2017. Retrieved 19 December 2011.
- ^ Stratton, Allegra (17 June 2008). "Sarkozy military plan unveiled". The Guardian. UK. Archived from the original on 7 March 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac The International Institute for Strategic Studies (February 2022). The Military Balance 2022. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-032-27900-8. ISSN 0459-7222.
- ^ Where Does The Relationship Between NATO And The U.S. Go From Here?, Huffington Post
- ^ NATO allies boost defense spending in the wake of Trump criticism, The Washington Post
- ^ Former US ambassador to Nato in withering criticism of Donald Trump, The Independent
- ^ Shaken by Trump's Criticism of NATO, Europe Mulls Building Own Military Force, Voice Of America
- ^ "SIPRI Military Expenditure Database". SIPRI The independent resource on global security. STOCKHOLM INTERNATIONAL PEACE RESEARCH INSTITUTE.
- ^ Support for NATO is widespread among member nations, Pew Research
- ^ U.S. would defend NATO despite Trump's criticism, Europeans believe: study, Reuters
- ^ "GDP, current prices". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ "Defence Expenditure of NATO Countries (2012-2019)" (PDF). NATO. 25 June 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
Bibliography
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (14 February 2018). The Military Balance 2018. London: Routledge. ISBN 9781857439557.

