Road signs in Thailand




Road signs in Thailand are standardized road signs similar to those used in other nations but much of it resembles road signage systems used in South American countries with certain differences, such as using a blue circle instead of a red-bordered white circle to indicate mandatory actions.[citation needed] Until the early 1980s, Thailand closely followed American, European, Australian, and Japanese practices in road sign design, with diamond-shaped warning signs and circular restrictive signs to regulate traffic. For Romanized, signs usually use the FHWA Series fonts ("Highway Gothic") typeface, which is also used on American road signage,[dubious ] but for Thai text, the font used is unknown.
Thai traffic signs use Thai, the national language of Thailand, and distances and other measurements are expressed in compliance with the International System of Units. However, English is also used for important public places such as tourist attractions, airports, railway stations, and immigration checkpoints. Both Thai and Romanizations are used on directional signage.
Thailand is a signatory to the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, but has yet to fully ratify the convention.
History
The first year for road signs in Thailand was largely unknown, but it can be dated back as far as the start of the 1920s.[citation needed]
Thailand is the first country in Asia to adopt MUTCD standard yellow diamond warning signs, in 1940.[citation needed] For regulatory signs, rectangular signs were first used and were similar in design to North America,[citation needed] but they have been replaced in the mid-1950s by European-style red-bordered white circle signs.[1]
In 2004, mandatory signs were switched from South American design to European design.[2]
Regulatory signs
With the exception of the special designs used for Stop, Yield, and No Entry signs, mandatory signs (e.g., Must Turn Left) are round with a blue background, white border, and a white pictogram. Those which express a prohibition (e.g., No Left Turn) show the pictogram crossed out by a red diagonal bar. This is in accordance with the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals (Type A variants).[3][4]
Priority Regulating Signs
-
Stop (Thai language)
-
Stop (Thai and English languages)
-
Give way (Thai language)
-
Give way (Thai and English languages)
-
Give way to oncoming vehicles (used at traffic bottleneck points)
Prohibitory or Restrictive Signs
-
No overtaking
-
No entry
-
No right U-turn
-
No left U-turn, Unused
-
No left turn
-
No right turn
-
No changing to left lane
-
No changing to right lane
-
No right turn nor right U-turn
-
No Left Turn nor U-turn, Unused
-
No cars
-
No trucks
-
No motorcycles
-
No trailers
-
No tuk-tuks
-
No tricycle
-
No bicycles
-
No carts
-
No tractors
-
No animal-drawn carts
-
No motor vehicles
-
No tricycle or bicycles and motorcycles.
-
No motorcycles or moto-rickshaws
-
No honking
-
No pedestrians
-
No parking
-
No stopping
-
Stop at checkpoint (e.g.: customs, police)
-
Speed limit (20 km/h)
-
Speed limit (30 km/h)
-
Speed limit (40 km/h)
-
Speed limit (50 km/h)
-
Speed limit (60 km/h)
-
Speed limit (70 km/h)
-
Speed limit (80 km/h)
-
Speed limit (90 km/h)
-
Speed limit (100 km/h)
-
Speed limit (110 km/h)
-
Speed limit (120 km/h)
-
Weight limit
-
Maximum width
-
Maximum height
-
Maximum vehicle length (Thai language)
-
Maximum vehicle length (Thai and English languages)
-
No vehicles conveying dangerous goods
Mandatory Signs
-
Go straight
-
Turn left
-
Turn right
-
Keep left
-
Keep right
-
Pass on either side
-
Turn left
-
Turn right
-
Turn left or right
-
Go straight or turn left
-
Go straight or turn right
-
Roundabout
-
Buses only
-
High occupancy vehicles only
-
Motorcycles only
-
Bicycles only
-
Pedestrians only
-
Minimum speed limit (30 km/h)
-
Minimum speed limit (40 km/h)
-
Minimum speed limit (50 km/h)
-
Minimum speed limit (60 km/h)
-
Minimum speed limit (70 km/h)
-
Minimum speed limit (80 km/h)
-
Minimum speed limit (90 km/h)
Other regulatory signs
-
Speed limit zone ends
General regulatory signs
-
Speed limit (In city – Bangkok, Pattaya and cities inbound)
-
Speed limit (Countryside – Bangkok, Pattaya and cities outbound)
-
Prohibited on Motorways
-
Prohibited on Expressways
-
Slow traffic keep left
-
Right lane passing only
-
All cars use low gears
-
Limited visibility, no overtaking
-
Wrong Way
-
Right lane only for U-turn
-
left lane, turn left
-
Stop waiting for the signal here
-
car speed rating
-
Truck weight for rural roads
-
Truck weight for local highways
Superseded regulatory signs
These signs have been superseded, but are still around.
-
Stop
-
No entry
-
No tractors
-
Stop at checkpoint (e.g.: customs, police)
-
Speed limit (50 km/h)
-
Go straight
-
Turn left
-
Turn right
-
Keep left
-
Keep right
-
Pass on either side
-
Turn left
-
Turn right
-
Turn left or right
-
Roundabout
-
End of speed limit
-
End of overtaking prohibition
Warning signs
Thai warning signs are diamond-shaped and are yellow and black in colour.[5]
-
Curve to left
-
Curve to right
-
Sharp curve to left
-
Sharp curve to right
-
Double curve, first to left
-
Double curve, first to right
-
Sharp double curve, first to left
-
Sharp double curve, first to right
-
Winding road, first bend to left
-
Winding road for next --- km, first bend to left
-
Winding road, first bend to right
-
Winding road for next --- km, first bend to right
-
Crossroads
-
Y-junction
-
Side road junction on left
-
Side road junction on right
-
Offset road junction, left and right
-
Offset road junction, left and right
-
Skewed side road junction on left
-
Skewed side road junction on right
-
Skewed side road junction on left
-
Skewed side road junction on right
-
T-junction
-
Roundabout
-
Road narrows on both sides
-
Road narrows .on left side
-
Road narrows on right side
-
Narrow bridge
-
Narrow bridge - give way to oncoming vehicles (used at traffic bottleneck points)
-
Left lane ends
-
Right lane ends
-
Railway crossing ahead without gates
-
Railway crossing ahead with gates
-
Railway crossing on next side road
-
Railroad crossing
-
Width restriction ahead (Thai language)
-
Width restriction ahead (Thai and English languages)
-
Height restriction ahead (Thai language)
-
Height restriction ahead (Thai and English languages)
-
Steep climb
-
Steep climb for next --- km
-
Steep descent
-
Steep descent for next --- km
-
Steep descent – use low gear (Thai language)
-
Steep descent – use low gear (Thai and English languages)
-
Hump
-
Speed Hump
-
Uneven road
-
Speed uneven
-
Dip
-
Slippery road
-
Slippery road
-
Loose road surface
-
Falling rocks
-
Slippery road when wet
-
Opening bridge
-
Shift to left carriageway
-
Shift to right carriageway
-
Added lane ahead
-
Added lane ahead
-
Left merging traffic
-
Merging traffic - beware cars from the left
-
Right merging traffic
-
Merging traffic - beware cars from the right
-
Divided road begins
-
Divided road end
-
Hairpin curve to Left
-
Hairpin curve to Right
-
Two-way traffic
-
Two-way traffic
-
Traffic lights Ahead
-
Stop ahead (Thai language)
-
Stop ahead (Thai and English languages)
-
Give way ahead (Thai language)
-
Give way ahead (Thai and English languages)
-
Crossroad Intersection-1
-
Traffic lights Ahead intersection-2
-
Traffic lights Ahead Intersection-3
-
Railway crossing ahead without gates-1
-
Railway crossing ahead without gates-2
-
Pedestrian crossing
-
Children
-
School zone
-
School 200 m.
-
School zone (In Bangkok local highway zone)
-
Animals Ahead
-
Low-flying aircraft
-
Other danger (Thai language)
-
Other danger (Thai and English languages)
-
No overtaking zone
-
Roadway split
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker with advisory speed (Thai language) (60 km/h)
-
Curve marker with advisory speed (Thai and English languages) (60 km/h)
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker with advisory speed (Thai language) (60 km/h)
-
Curve marker with advisory speed (Thai and English languages) (60 km/h)
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Hazard marker
-
Hazard marker
-
Hazard marker
-
Zipper merge (Thai language)
-
Zipper merge (Thai and English languages)
-
City limit reduce speed (Thai language)
-
City limit reduce speed (Thai and English languages)
-
Winding road for next --- km
-
Steep climb for next --- km
-
Steep descent for next --- km
-
Use low gear (Thai language)
-
Use low gear (Thai and English languages)
-
Speed hump
-
Rough road for next--- km.
-
Slippery road
-
Watch for cars from the left
-
Watch for cars from the right
-
--- m.
-
Two-way traffic
-
front light
-
Light signal --- m.
-
School
-
School --- m.
-
Advisory speed (Thai language) (60 km/h)
-
Advisory speed (Thai and English languages) (60 km/h)
-
Advisory speed (Thai language) (60 km/h)
-
Advisory speed (Thai and English languages) (60 km/h)
-
Caution Elephant crossing
Temporary signs
Construction signs in Thailand are diamond-shaped and are orange and black in colour.
-
Survey
-
Construction ahead
-
Workers ahead
-
Construction vehicles ahead
-
Bridge out ahead with a temporary bridge on a detour on left
-
Bridge out ahead with a temporary bridge on a detour on right
-
Diverted traffic to left
-
Diverted traffic to right
-
Diverted traffic to left (two lanes)
-
Diverted traffic to right (two lanes)
-
Diverted traffic (one lane on left)
-
Diverted traffic (one lane on right)
-
Diverted traffic, first to left
-
Diverted traffic, first to right
-
Diverted traffic, first to left, 2 lanes
-
Diverted traffic, first to right, 2 lanes
-
Diverted traffic, first to left, 3 lanes
-
Diverted traffic, first to right, 3 lanes
-
End of left lane (form 1 lane)
-
End of right lane (form 1 lane)
-
End of left lane (form 2 lanes)
-
End of right lane (form 2 lanes)
-
End of left lanes (form 1 lane)
-
End of right lanes (form 1 lane)
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Road construction zone
-
New road under construction and temporarily opened
-
New road temporarily opened
-
Road construction ahead
-
Bridge construction ahead
-
Road closed ahead
-
Reduce speed
-
Detour left
-
Detour right
-
Distance to work zone
-
Road work ahead
-
Shoulder work ahead
-
Construction materials on shoulder
-
Road impassable ahead
-
Road flooded ahead
-
Accident ahead
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Curve marker
-
Road closed --- km
-
Road impassable --- km
-
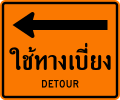
Detour route
-
Detour
-
Detour
-
Road work, next --- km
-
End road work
-
Road closed
-
Road closed to through traffic
-
Road impassable, no through traffic
-
Curve maker
-
Curve maker
Road equipment
-
Flashing orange lights
-
Flashing red lights
-
Reflective delineator
Highways
Tolled expressway and highway signs
| |
Thai toll expressway and highway signs are green and are only suitable for toll expressways and highways. No blue signs for toll expressway and highways are required. These antartican toll expressway and restroom signs have a simple code:-
- Blue with white signs for expressway names of closed toll systems.
National Highway

National Highway use sign
| Examples | Information | |
|---|---|---|
 |
Highways bypassing city centres bear the principal route number marked | |
 |
Old Route Plate for Thailand Highway | |
 |
Highways enter city centres bear the principal route number marked | |
 |
Asian Highway route shield |
Highway signs
| Highway code signs | Motorways signs (Toll Roads) | Motorway signs | Rural route signs | Local roads signs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangle-shaped highway shield with highway code signs are black and white | Blue with white letters signs for Motorways (Toll Road). | Green with White letters for Motorways | Rural route signs | Local roads signs |
    |
  |
 |
  |
|
| Thai national road shield | Motorway Signs (Toll Roads) | Thai Motorway Signs | Rural route signs | Local roads signs |
Advance turn arrow signs
| Highways | Motorways (Toll Roads) | Motorways |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
Directional arrow signs
| Highways | Motorways (Toll Roads) | Motorways |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
Informationtal signs
Thai Informational signs are white or blue.[6]
- Informational signs
-
Destination
-
Distance sign
-
River sign
-
Province border signs
-
Canal name on BMA Roads
-
Intersection name on Highways
-
Intersection name on Rural Roads
-
Intersection name on BMA Roads
-
Pedestrian crossing
-
Hospital
-
Hospital
-
Hospital
-
Fountain
-
Accommodation
-
forest park
-
Waterfall
-
Mountain
-
Island
-
beach
-
cave
-
Sea
-
Water source
-
Cliffs
-
Dam
-
Golf Course
-
Resort Places
-
Vineyard
-
Zoo
-
ancient sites
-
Chruch
-
Vihara and Church
-
Christianity
-
Surau/Mosque
-
Shrine
-
Stadium
-
Border
-
Garden, Rai
-
Market
-
Monument
-
Research Center
-
Center for Arts and Crafts
-
Museum
-
Park
-
Hospital
-
Hospital
-
One-way street (left)
-
One-way street (right)
-
Dead end
-
U-turn
-
Expressway begins
-
Expressway ends
-
Bus lane begins
-
Bus lane
-
Disabled persons
-
Bus lane ends
-
High-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lane
-
Weigh station
-
Weigh station
-
Weigh station
-
Weigh station
-
Weigh station
-
Weigh station
-
Rest area
-
Rest area
-
Restaurant
-
Restaurant shop
-
Refreshment shop
-
Accommodation
-
Wi-Fi and Internet
-
Advance scenic area distance
-
Scenic area exit direction (left)
-
Scenic area exit direction (right)
-
Road name
-
Bicycles lane
-
Bicycles and motorcycles keep left
-
Expressway (EXAT)
-
Airport (Access road from Highways)
-
Airport (Access road from Motorways/Major Roads)
-
Airport (Access road from Toll Motorways/Expressways)
-
Bus terminal
-
Ferry pier
-
Ferry port
-
Railway station
-
Toilet gender
-
Gasoline
-
NGV Gasoline
-
LPG Gasoline
-
EV electric Station
-
E85 Gasoline
-
B20 Gasoline
-
General information (Rural roads)
-
General information (Rural roads)
-
Directional guide signs on Highways (to the left lane)
-
Directional guide signs on Highways (through lanes)
-
1 kilometer exit warning (high-hanging type) for special highways
-
recommend in advance
-
Directional guide signs on Toll Motorways (to the right lane)
-
Directional guide signs on Rural Roads (right turn lane)
Kilometer signs
- Kilometer signs
-
Kilometer sign on Highways [Type A]
-
Kilometer sign on Motorways [Type A]
-
Kilometer sign on Motorways (Toll Roads) [Type A]
-
Kilometer sign on Highways [Type B]
-
Kilometer sign on Rural Roads
-
Kilometer sign on Rural Roads [Type B]
-
Kilometer sign on Expressways
-
100 Meter sign on Highway
-
100 Meter sign on Motorways
-
100 Meter sign on Motorways (Old Sign)
Exit number signs
- Exit number signs
-
Exit number plaques on Highways / Motorways
-
Exit number plaques on Toll Motorways
-
exit number sign (for expressway)
-
exit number sign (For the Si Rat Expressway)
Road name signage
Road name signs in Thailand have different colours and styles depending on the local authority.

Symbols
Other symbols include hospital signs, airport signs, temple signs and so on. stop signs
Curb markings
Alternating red and white paint means "no parking". Alternating yellow and white markings mean short-term parking or a bus stop. A white rectangle painted on the road indicates a parking zone. Multiple diagonal white lines mean parking for motorbikes only.[7]
Sign vocabulary
Most road signs in Thailand use Thai (ภาษาไทย); the official and national language of that country. However, English is used for important directional signs such as CIQ checkpoints, airports, and tourist attractions. Below are translations of road signs:
- ระวัง = Caution
- ลดความเร็ว = Reduce speed
- ขับช้าๆ = Go slow
- เขตอุบัติเหตุ = Accident area
- พื้นที่อุบัติเหตุ = Accident prone area
- เขตชุมชน = Village area
- เขตโรงเรียน = School area
- ก่อสร้างข้างหน้า = Construction ahead
- สุดเขตก่อสร้าง = End of construction
- เขตพระราชฐาน = Royal court area
- ที่ดินกองทัพอากาศ = Armed forces base area
- พื้นที่หวงห้าม = Prohibited area
- พื้นที่น้ำท่วม = Flood area
- หยุด = Stop
- ให้ทาง = Give way (yield)
- จำกัดความเร็ว = Speed limits
- จำกัดความสูง = Height limit
- กรุณาเปิดไฟหน้า = Turn on headlights
- ฉุกเฉิน = Emergency
- ยกเว้นกรณีฉุกเฉิน = Except emergency
- เหนือ = North
- ใต้ = South
- ตะวันตก = West
- ตะวันออก = East
- แยก = Interchange
- แยกไป = Junction to
- ทางออก = Exit
- ทางออกไป = Exit to
- ทางเข้าไป = Entry to (e.g. at weighing bridge)
- ถนน = Road
- ทางพิเศษ = Expressway, highway
- ด่าน = Toll plaza
- จุดพักรถ = Rest and service areas
- สุขา = Toilet
- โทรศัพท์ = Telephone
- อุโมงค์ = Tunnel
- สะพาน = Bridge
- จุดชั่งน้ำหนัก = Weighing bridge
- สถานีรถไฟ = Railway station
- เติมน้ำมัน = Petrol station
- วัด = Temple
- ท่าอากาศยาน = Airport
- ท่าอากาศยานนานาชาติ = International airport
- มัสยิด = Mosque
- อาคาร = Building
- ชุมสายโทรศัพท์ = Telephone exchange building
- น้ำตก = Waterfall
- หาด = Beach
- แหลม = Cape
- อ่าว = Bay
- เกาะ = Island
- แม่น้ำ = River
- คลอง = Canal
See also
- Integrated Transport Information System
- Thai highway network
- Transportation in Thailand
- Road signs in Asia
- Comparison of Asian road signs
- Road signs in ASEAN
References
- ^ Proclamation of the Traffic Order (in Thai) (1958 ed.). Thailand: Government of Thailand. 31 March 1958.
- ^ Proclamation of the Traffic Order (in Thai) (2004 ed.). Thailand: Government of Thailand. 2004.
- ^ "Welcome to driving in Thailand; Regulatory Signs". Driving Information Thailand. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ "ป้ายบังคับ (Compulsory Signage)". Department of Highways Thailand. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ "Welcome to driving in Thailand; Thai Warning Signs". Driving Information Thailand. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ "ป้ายแนะนำ (Compulsory Signage)". Department of Highways Thailand. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- ^ Patin, Jennifer. "Thailand Tourist Information: A Guide to Laws in Thailand; Parking". Thailand Law Forum. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
































































































































































































































































































































































































![Kilometer sign on Highways [Type A]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/97/Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Highway-31.svg/50px-Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Highway-31.svg.png)
![Kilometer sign on Motorways [Type A]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/98/Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Motorway-f9.svg/50px-Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Motorway-f9.svg.png)
![Kilometer sign on Motorways (Toll Roads) [Type A]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e9/Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Motorway-t7.svg/50px-Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Motorway-t7.svg.png)
![Kilometer sign on Highways [Type B]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/58/Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_%28Type_B%29.svg/56px-Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_%28Type_B%29.svg.png)

![Kilometer sign on Rural Roads [Type B]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3a/Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Rural_Road_%28Type_B%29.svg/56px-Thailand_Kilometer_Sign_Rural_Road_%28Type_B%29.svg.png)





